How to Avoid Repetition of Words and Grammatical Structures
Lexical Resource & Grammatical Range and AccuracyIELTS Academic Writing Task 1

The IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 requires test takers to describe and interpret visual information, such as graphs, charts, and diagrams. It assesses their ability to present and organise information effectively using appropriate vocabulary, grammar, and cohesive devices.
Two key aspects that are evaluated in this task are Lexical Resource and Grammatical Range and Accuracy.
This article will discuss strategies to avoid repetition of words and grammatical structures, enhancing your performance in these areas.
1. Lexical Resource:
Lexical Resource refers to the range and accuracy of vocabulary used in your writing. Using a diverse and precise vocabulary helps to convey your ideas more effectively and showcases your language skills. Here are some techniques to avoid repetition of words:
a. Synonyms and Antonyms:
When you encounter a word you wish to repeat, consider using synonyms or antonyms to express the same or opposite meaning.
For example:
Original Sentence: The number of tourists increased sharply from 2000 to 2010.
Revised Sentence: There was a significant rise in the number of tourists from 2000 to 2010.
In this example, “increased sharply” is replaced with “a significant rise,” maintaining the same meaning but introducing variety in vocabulary.
b. Word Forms:
Another way to avoid repetition is by using different forms of the same word.
For instance:
Original Sentence: The government implemented strict measures to combat pollution.
Revised Sentence: Strict measures were implemented by the government to tackle the issue of pollution.
Here, the word “combat” is changed to its noun form, “tackle,” while maintaining the original meaning.
c. General and Specific Terms:
To add variety to your writing, use general and specific terms interchangeably. This can be done by specifying or generalising the information.
Example:
Original Sentence: The consumption of fast food rose dramatically. Revised Sentence: There was a substantial increase in fast food consumption.
Here, “rose dramatically” is replaced with “a substantial increase,” offering a different perspective without changing the meaning.
2. Grammatical Range and Accuracy:
Grammatical Range and Accuracy assesses your ability to use a variety of sentence structures accurately. Repetition of grammatical structures can negatively impact your score. Here are some techniques to diversify your sentence structures:
a. Compound Sentences:
Compound sentences combine two independent clauses using coordinating conjunctions such as “and,” “but,” or “so.” They help you convey complex relationships between ideas.
For example:
Original Sentence: The number of visitors increased. The revenue also increased.
Revised Sentence: The number of visitors increased, and as a result, the revenue also saw an increase.
In this revised sentence, the two separate sentences are combined using the coordinating conjunction “and.”
b. Complex Sentences:
Complex sentences contain an independent clause and a dependent clause connected by subordinating conjunctions like “although,” “because,” or “while.” They provide a variety of sentence structures and demonstrate your ability to express ideas logically.
For instance:
Original Sentence: The temperature dropped. The ice started to melt. Revised Sentence: Although the temperature dropped, the ice started to melt.
Here, the conjunction “although” introduces a dependent clause, making the sentence more complex.
c. Passive Voice and Active Voice:
Varying between passive and active voice can add diversity to your writing. Passive voice emphasises the object or the action rather than the subject. On the other hand, active voice places the subject as the doer of the action.
Example:
Original Sentence: The building was constructed in 1990.
Revised Sentence: The builders completed the construction of the building in 1990.
Changing from passive to active voice alters the sentence structure, adding variety to the writing.
In conclusion, in order to excel in the Lexical Resource and Grammatical Range and Accuracy criteria of the IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, it is crucial to avoid repetition of words and grammatical structures.
Using synonyms, antonyms, different word forms, general and specific terms, and diverse sentence structures, you can effectively showcase your language skills and enhance your performance in this task. Practice these strategies, and remember to proofread your writing to ensure accuracy and coherence.
Good luck with your IELTS preparation!



Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
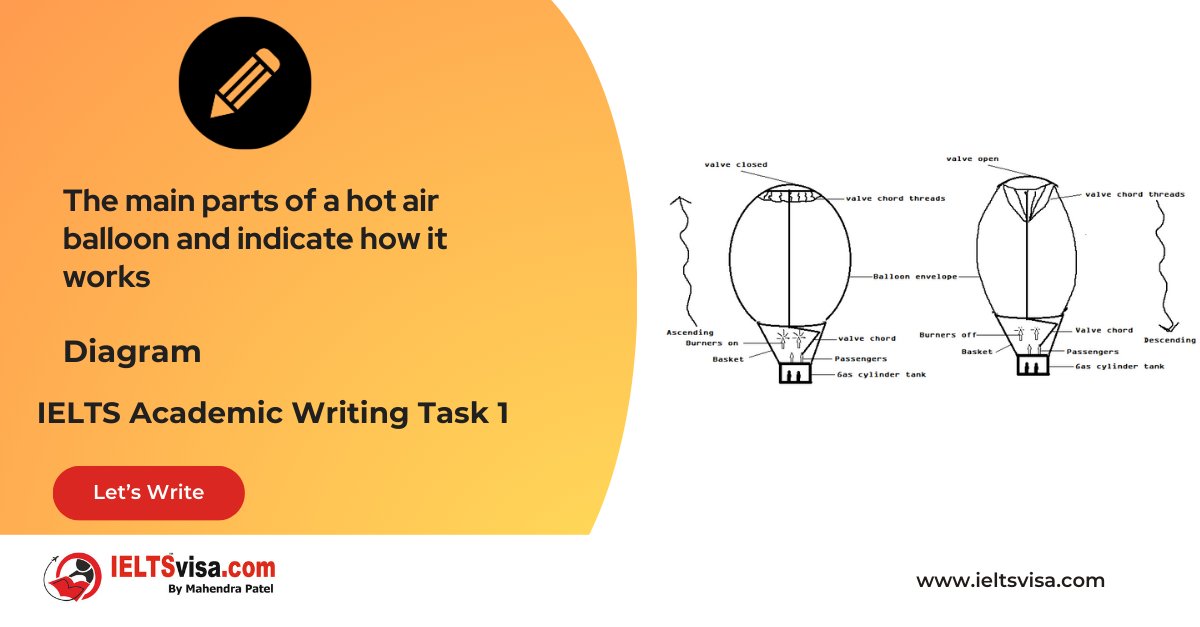
Task 1 – Diagram – A conference hall built in 1981 and planned for 2020
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
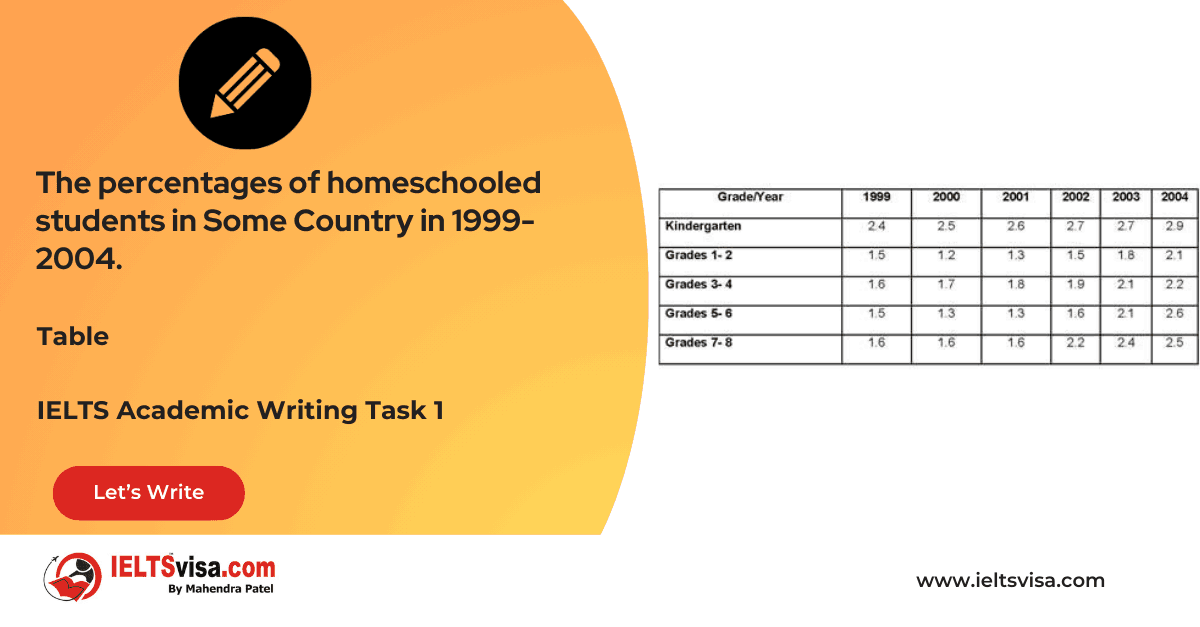
Task 1 – Table – The percentages of homeschooled students in Some Country in 1999-2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
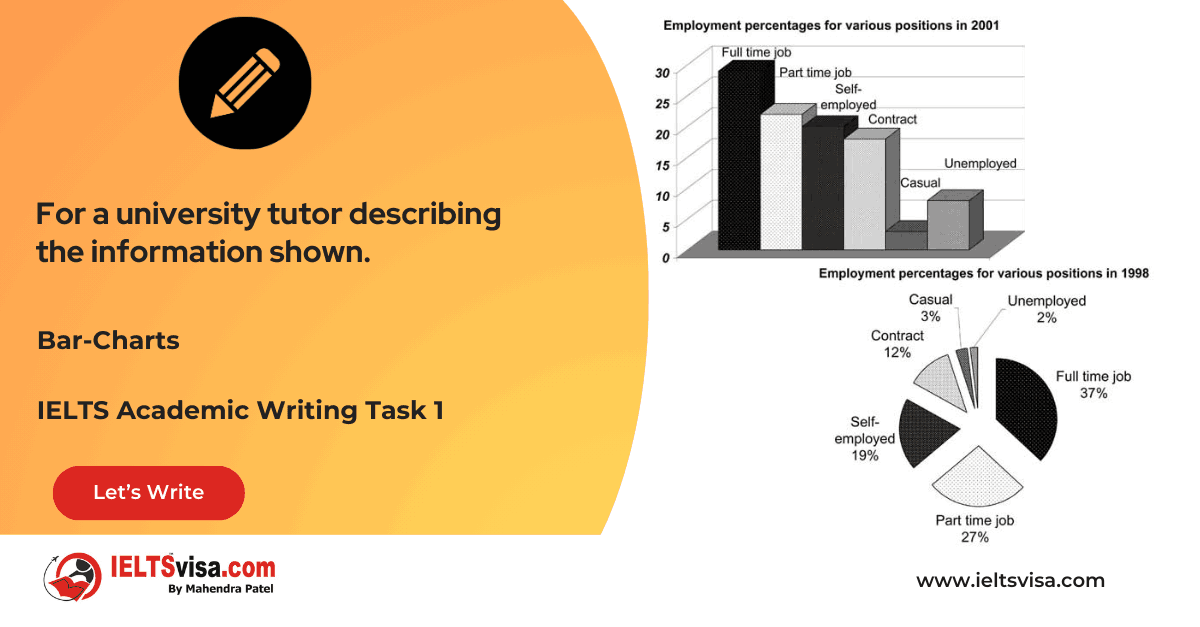
Task 1 – Table – For a university tutor describing the information shown.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
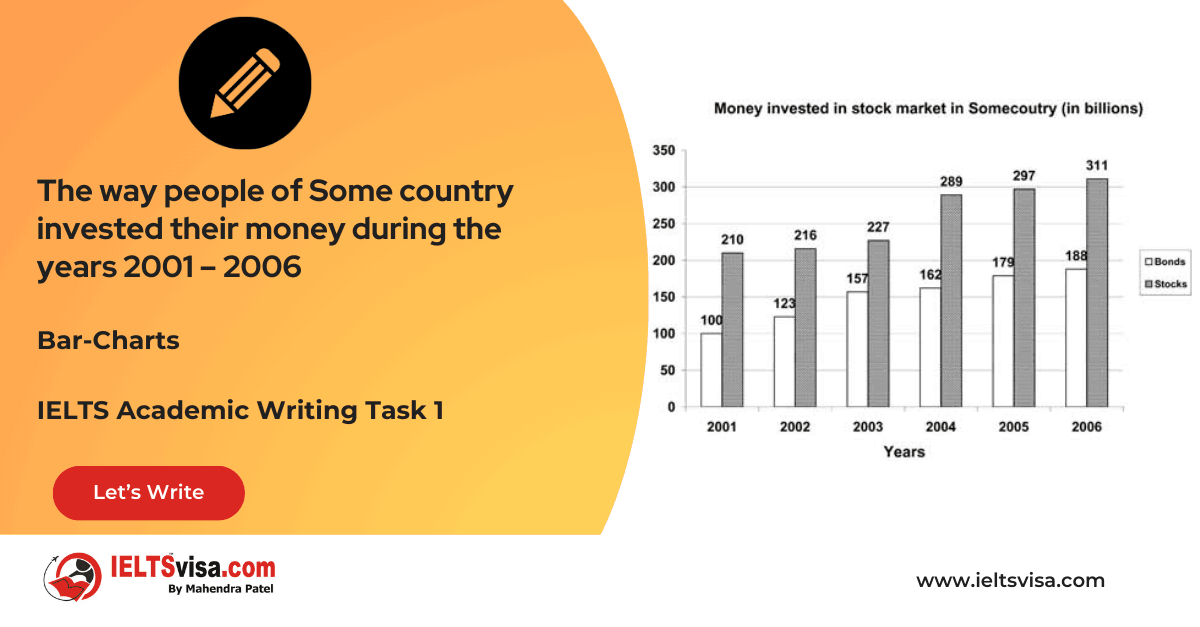
Task 1 – Bar-Charts – The way people of Some country invested their money during the years 2001 – 2006
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Rainwater Harvesting and Conversion to Drinking Water in an Australian Town.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
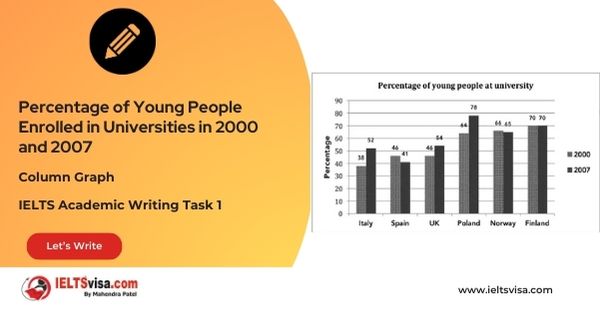
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
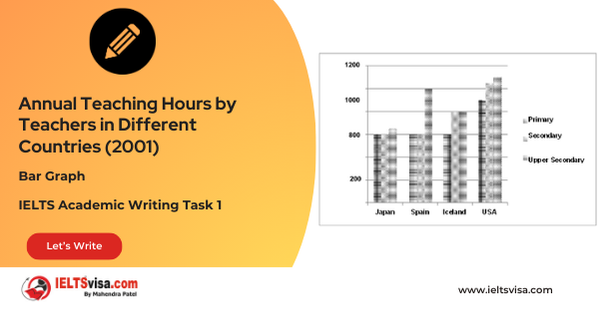
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
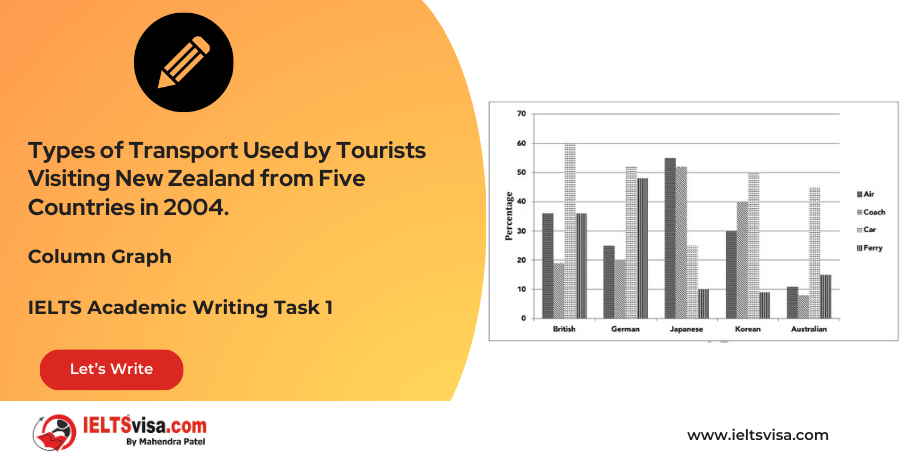
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...