The production of carbon dioxide in five different countries in 2006
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Table

IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The table below shows the production of carbon dioxide in five different countries in 2006. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
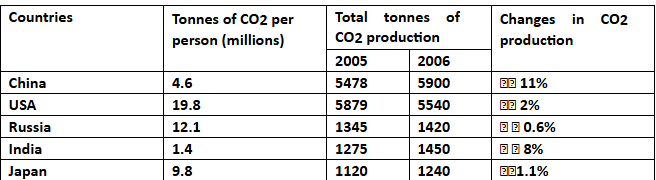
Comparison Data Table
1. Diagram Type: Data Table
2. Title: Comparison of CO2 Emissions Across Countries
3. What are the units of measurement? Million tonnes for per capita emissions and percentage change for year-over-year data
4. Who: China, USA, Russia, India, Japan
5. When: Year 2006 (with a comparison to 2005)
6. Where: Emissions data from five countries
7. Topic: Production of CO2 emissions per person and total change over a year
Detailed Process and Observations
Data Summary:
- The table compares the CO2 emissions per person in 2006 across China, the USA, Russia, India, and Japan, showing both total tonnes and percentage change from 2005 to 2006.
CO2 Emissions per Person in 2006 :
- USA: Produced the highest per capita emissions with 19.8 million tonnes per person.
- Russia and Japan: Produced 12.1 and 9.8 million tonnes per person, respectively.
- China and India: Had comparatively low per capita emissions, with 4.6 million and 1.4 million tonnes per person, respectively.
Total CO2 Emissions and Year-over-Year Change:
- 2005 Data: The USA led with 5879 million tonnes, followed by China (5478 million tonnes). Russia, India, and Japan were below 1500 million tonnes, with Japan producing the lowest CO2 emissions.
- 2006 Data: China showed a significant increase of 11%, overtaking the USA as the highest emitter. Russia, India, and Japan also recorded slight increases in CO2 production.
- USA’s Decline: The USA was the only country to show a decrease in emissions from 2005 to 2006.
Sample Answer
The table provides a comparison of CO2 emissions per person for China, the USA, Russia, India, and Japan in 2006, alongside a summary of the total CO2 emissions and percentage change from 2005 to 2006.
Overall, the data indicate that while per capita emissions were highest in developed countries, China’s rapid increase in total emissions shifted it to the top emitter position by 2006.
In 2006, the USA recorded the highest per capita emissions at 19.8 million tonnes, followed by Russia with 12.1 million tonnes and Japan with 9.8 million tonnes per person. China and India produced considerably less CO2 per capita, at 4.6 and 1.4 million tonnes, respectively.
Regarding total CO2 output, the USA led in 2005 with 5879 million tonnes, with China close behind at 5478 million tonnes.
In 2006, however, China’s emissions increased by 11%, surpassing the USA to become the largest overall emitter. Russia, India, and Japan all registered smaller increases in total emissions. Notably, the USA was the only country to record a decline in emissions from 2005 to 2006.
Top 25+ Vocabularies
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Verb Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per capita | Per person, average per individual | Per person, each | China’s per capita emissions were 4.6 million tonnes. | Adverb |
| Emissions | Release of substances, especially gas or pollutants | Discharge, release | The USA recorded the highest per capita CO2 emissions. | Noun |
| Decline | Reduction, decrease | Decrease, drop | The USA showed a decline in CO2 emissions from 2005 to 2006. | Noun/Verb |
| Supersede | Replace, surpass | Overtake, surpass | China superseded the USA in CO2 emissions in 2006. | Verb |
| Significant | Noticeable, important | Remarkable, notable | China showed a significant increase in emissions by 11%. | Adjective |
| Comparison | The act of comparing two or more things | Contrast, evaluation | The table provides a comparison of CO2 emissions among countries. | Noun |
| Total | The complete amount or sum of something | Entirety, whole | China’s total emissions surpassed those of the USA in 2006. | Noun |
| Increase | The process of becoming larger or greater | Rise, growth | China’s emissions saw an 11% increase in 2006. | Noun/Verb |
| Surpass | To exceed or go beyond in quantity or quality | Outdo, exceed | China surpassed the USA in emissions by 2006. | Verb |
| Rank | A position in a scale or hierarchy | Position, level | The USA ranked highest in per capita emissions in 2006. | Noun/Verb |
| Developed | Referring to a country with a high level of industrialization | Industrialized, advanced | Developed countries showed higher per capita emissions. | Adjective |
| Registered | Recorded or officially noted | Documented, reported | Russia registered a smaller increase in emissions in 2006. | Verb |
| Output | The total amount produced or emitted | Yield, production | China had a significant increase in total CO2 output in 2006. | Noun |
| Close behind | Just after or slightly behind in rank or position | Almost equal, following | China was close behind the USA in total emissions in 2005. | Phrase |
| Emission rate | The speed or frequency at which emissions occur | Discharge rate, release | The emission rate of CO2 per person in the USA was the highest. | Noun |
| Shift | A change or movement from one state or position to another | Change, transition | China’s rapid shift in total emissions was notable. | Noun/Verb |
| High | A large amount or degree of something | Elevated, considerable | The USA had high per capita emissions in 2006. | Adjective |
| Rapid | Occurring in a short time period | Quick, fast | China’s rapid increase in emissions changed the global landscape. | Adjective |
| Position | The rank or location of something in a list | Placement, standing | The USA held the highest position in per capita emissions. | Noun |
| Subsequent | Following in time or order | Following, ensuing | Subsequent increases in emissions were recorded in other countries. | Adjective |
| Data | Facts or statistics collected for analysis | Information, statistics | The data showed a decrease in emissions for the USA. | Noun |
| Emission source | The origin or cause of emissions | Release point, origin | The table shows various emission sources for each country. | Noun |
| Trend | A general direction in which something is developing or changing | Direction, tendency | The trend indicates an overall increase in emissions from China. | Noun |
| Overall | Considering everything as a whole | In total, all in all | Overall, the USA and China dominated the global CO2 emissions. | Adverb/Adjective |
| Notably | In a way that is particularly important or interesting | Remarkably, especially | Notably, the USA was the only country to register a decline in 2006. | Adverb |
| Surge | A sudden or dramatic increase | Spike, rise | China’s emissions surged past the USA’s total in 2006. | Noun/Verb |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...