Percentage of Graduates with Various Degrees in 1980 and 2008
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Pie Chart
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
Two charts below show the percentage of qualified graduates in a particular country. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Common Questions for Data Summary
1. Graph Type: Pie Chart
2. Title: Percentage of Graduates with Various Degrees in 1980 and 2008
3. What are the units of measurement? Percentage
4. Who: Graduates in a particular country (1980 and 2008)
5. When: 1980 and 2008
6. Where: A specific country (unspecified)
7. Topic: Proportion of graduates holding different degrees (First, Masters, and PhD) in 1980 and 2008
Comparison Showing and Trends
Comparison 1: First Degrees in Arts and Sciences
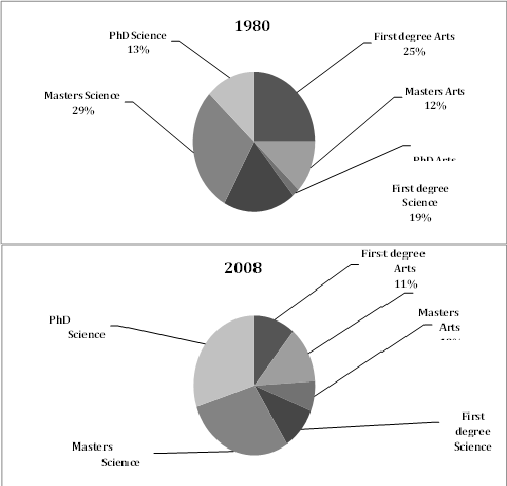
- In 1980, a quarter of graduates held a first degree in Arts, while about a fifth held a first degree in Science. By 2008, the proportion of graduates with first degrees in both Arts and Science decreased significantly.
Comparison 2: Masters Degrees
- In 1980, around 12% of graduates had a Masters in Arts, and 30% had a Masters in Science. By 2008, these figures dropped, with only 11% and 10% of graduates holding Masters in Arts and Science, respectively.
Comparison 3: PhD Degrees
- In 1980, PhD graduates in Arts and Science made up a very small percentage (2% and 13%, respectively). However, by 2008, PhD graduates in Arts rose to 7%, while PhD graduates in Science grew significantly to 30%.
Sample Answer
The pie charts given illustrate the distribution of graduates holding various degrees in a particular country in 1980 and 2008.
In conclusion, the data reveals a shift towards graduate studies over time, with more graduates pursuing Masters and PhD courses compared to first-degree courses.
In 1980, 25% of graduates held a first degree in Arts, and 19% held a first degree in Science. Meanwhile, the percentage of graduates with Masters degrees in Arts and Science was 12% and 30%, respectively. A small percentage (2%) held a PhD in Arts, and 13% had a PhD in Science.
By 2008, the proportion of graduates with first degrees in Arts and Science had decreased significantly. The percentage of graduates with Masters in Arts and Science dropped to 11% and 10%, respectively. However, the proportion of PhD holders in both Arts and Science rose, with PhD in Arts growing to 7%, and PhD in Science increasing sharply to 30%.
Top 27 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Type |
|
Proportion |
A part or share of a whole |
Percentage, share |
The proportion of PhD graduates in Science increased significantly. |
Noun |
|
Undergraduate |
A student pursuing a first degree |
Bachelor’s, first-degree |
The number of undergraduates in Arts decreased by 2008. |
Noun |
|
Graduate |
A person who has completed a degree course |
Postgraduate, degree holder |
More graduates chose to pursue Masters or PhD courses. |
Noun |
|
Significantly |
To a large extent or degree |
Considerably, markedly |
The proportion of PhD graduates in Science rose significantly. |
Adjective |
|
Proportion |
The comparative amount of something |
Fraction, ratio |
The proportion of Masters graduates decreased over time. |
Noun |
|
Distribution |
The way something is shared or spread out |
Allocation, division |
“The distribution of graduates changed significantly over time.” |
Noun |
|
Degree |
A qualification awarded by a university |
Qualification, diploma |
“The number of students earning higher degrees increased.” |
Noun |
|
Attainment |
The process of achieving something |
Achievement, accomplishment |
“Higher educational attainment became more common in 2008.” |
Noun |
|
Enrollment |
The process of signing up for an educational course |
Registration, admission |
“The enrollment in PhD programs saw a rise.” |
Noun |
|
Academic |
Related to education or scholarship |
Educational, scholarly |
“The academic landscape changed significantly over 28 years.” |
Adjective |
|
Trend |
A general direction in which something is changing |
Pattern, tendency |
“A noticeable trend towards postgraduate studies was observed.” |
Noun |
|
Postgraduate |
A person studying after completing a degree |
Graduate student, researcher |
“More students opted for postgraduate degrees.” |
Noun |
|
Decline |
A decrease in quantity or quality |
Reduction, drop |
“There was a decline in the number of first-degree holders.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Sharp |
Sudden and intense |
Steep, significant |
“There was a sharp rise in PhD holders in Science.” |
Adjective |
|
Increase |
A rise in number or amount |
Growth, surge |
“The increase in PhD holders was remarkable.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Fluctuation |
Continuous variation or change |
Variation, inconsistency |
“There was a fluctuation in the percentage of Master’s students.” |
Noun |
|
Academic field |
A specific area of study |
Discipline, subject |
“Graduates pursued different academic fields over the years.” |
Noun |
|
Shift |
A change in position or direction |
Transition, movement |
“A shift towards higher education was evident in the data.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Dominance |
The state of being the most influential |
Prevalence, control |
“Science degrees gained dominance over the years.” |
Noun |
|
Preference |
A greater liking for one alternative |
Inclination, choice |
“There was a preference for PhD degrees in 2008.” |
Noun |
|
Evident |
Clearly seen or understood |
Obvious, noticeable |
“The shift in degree preferences was evident in the charts.” |
Adjective |
|
Outnumber |
To be more in number than another group |
Surpass, exceed |
“Master’s degree holders outnumbered undergraduate students.” |
Verb |
|
Peak |
The highest level reached |
Summit, pinnacle |
“The number of PhD graduates peaked in 2008.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Noteworthy |
Deserving attention or notice |
Remarkable, significant |
“A noteworthy change occurred in higher education trends.” |
Adjective |
|
Comparison |
Examining similarities and differences |
Contrast, evaluation |
“A comparison between the two years shows drastic changes.” |
Noun |
|
Dominant |
Having more power or influence |
Leading, prevalent |
“Science became the dominant field of study over time.” |
Adjective |
|
Expansion |
An increase in size, number, or importance |
Growth, extension |
“There was an expansion in postgraduate education.” |
Noun |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Comparison of Males Preferring Watching vs. Participating in Sports
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
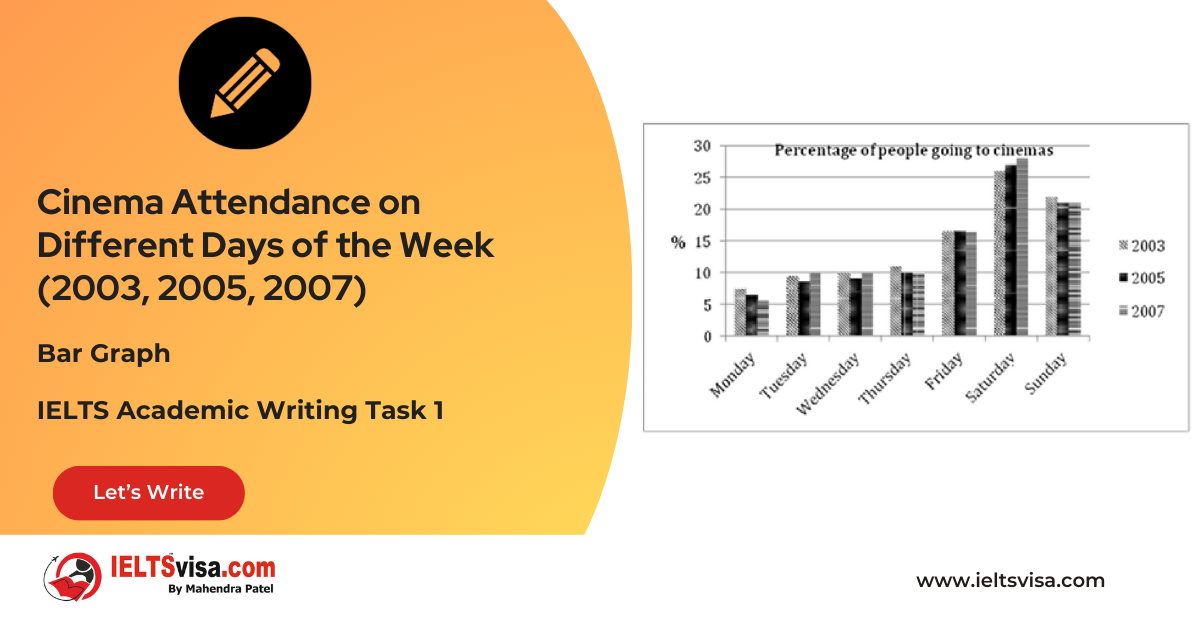
Task 1 – Line-Bar – The total volume of telephone calls (in million minutes) in Denmark, divided into three categories, from 1995- 2004
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
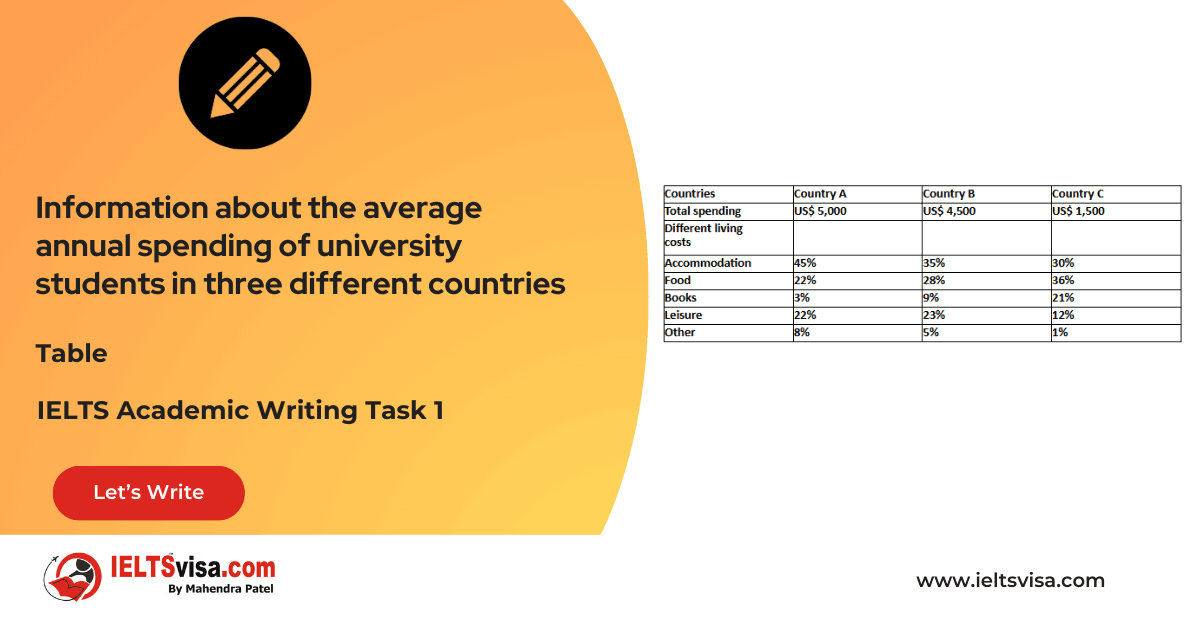
Task 1 – Table – Information about the average annual spending of university students in three different countries
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Table -The production of carbon dioxide in five different countries in 2006
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
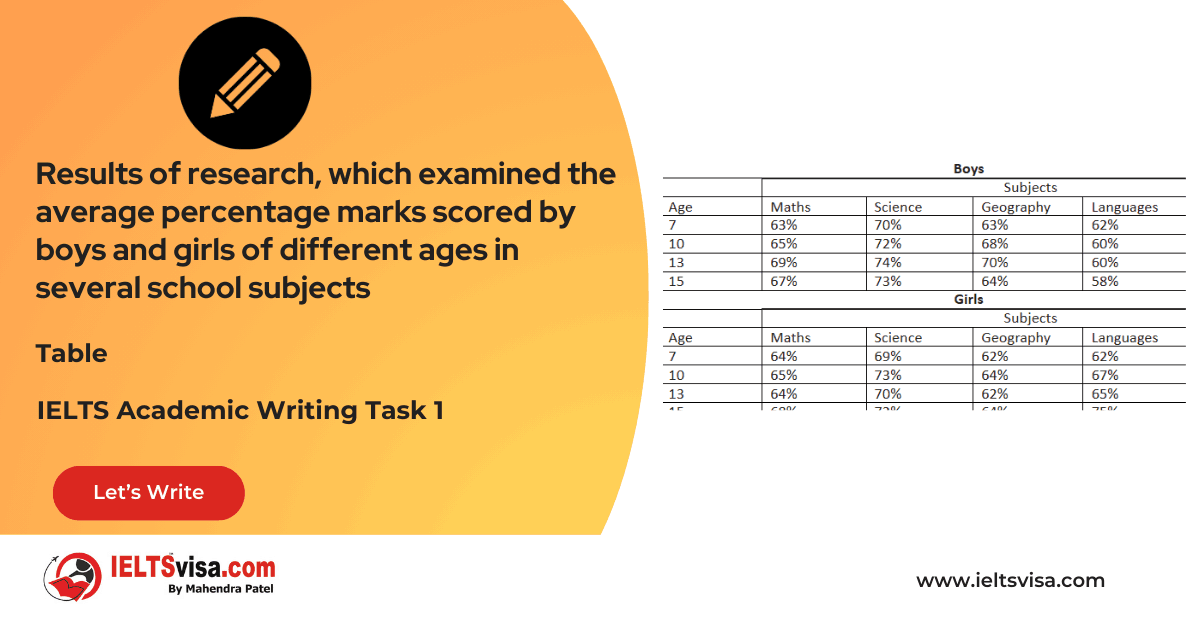
Task 1 – Table – Results of research, which examined the average percentage marks scored by boys and girls of different ages in several school subjects
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
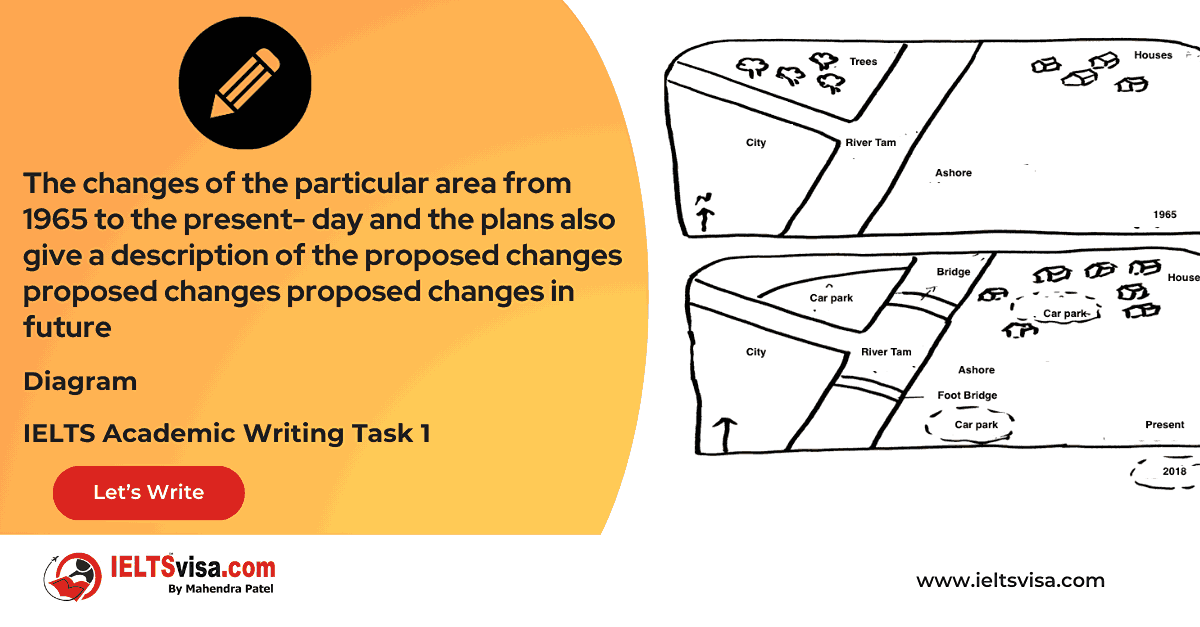
Task 1 – Diagram – The structure of a home smokery and how it works
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...