The differences in wheat exports over three different areas
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Line Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The differences in wheat exports over three different areas
Common Questions for the Line Graph
1. Diagram Type: Line graph
2. Title: Wheat Exports from Three Regions (1985-1990)
3. What are the units of measurement? Millions of tons
4. Who: University lecturers, agriculture experts, economists
5. When: 1985-1990
6. Where: Canada, European Community, Australia
7. Topic: Wheat exports comparison
Detailed Process and Observations
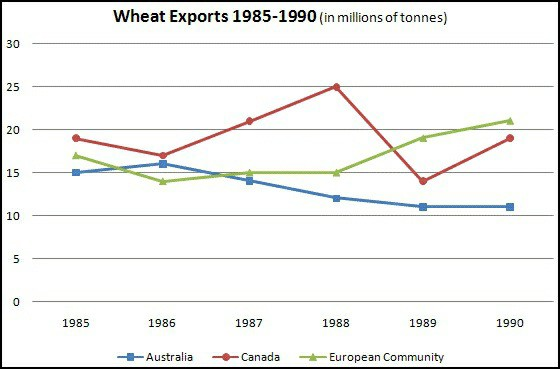
Summary of Data : The line graph compares wheat export figures for Canada, Australia, and the European Community between 1985 and 1990, showing distinct trends for each region.
- Australia:
- Australia’s wheat exports started at 15 million tons in 1985, rose slightly to 16 million tons in 1986, and then steadily declined throughout the following years. By 1990, exports had fallen to just over 10 million tons.
- Canada:
- Canada began with 19 million tons of wheat exports in 1985, but the figure dropped to 17 million tons in 1986. Afterwards, exports grew significantly, reaching 25 million tons in 1988. However, there was a sharp decline in 1989 to below 15 million tons, followed by a recovery to nearly 20 million tons in 1990.
- European Community:
- The European Community saw steady growth in wheat exports from 1985 to 1990. Starting at 16 million tons, exports fell slightly in 1986 to 14 million tons. They then increased gradually to 15 million tons in 1987 and 1988, with a more significant rise in 1989 and 1990, reaching 19 million and 21 million tons, respectively.
Sample Answer
The line graph compares wheat export figures from Canada, Australia, and the European Community over the period from 1985 to 1990.
Overall, while Australia saw a decline in wheat exports, both Canada and the European Community showed overall growth, with fluctuations in Canada’s exports.
Australia’s wheat exports began at 15 million tons in 1985, with a slight increase to 16 million tons in 1986, but then declined steadily over the next four years, reaching just over 10 million tons by 1990.
In contrast, Canada’s wheat exports fluctuated during the period. Starting at 19 million tons in 1985, exports fell to 17 million tons in 1986 before growing significantly, reaching 25 million tons in 1988. However, there was a sharp decline to under 15 million tons in 1989, followed by a recovery to nearly 20 million tons in 1990.
The European Community experienced a steady rise in wheat exports, starting at 16 million tons in 1985, dropping to 14 million tons in 1986, and then increasing each year, peaking at 21 million tons in 1990.
Top 28 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluctuations | The process of changing or varying repeatedly | Variations, changes, shifts | Canada’s wheat exports experienced significant fluctuations in the late 1980s. | Noun |
| Decline | A decrease in size, strength, or quality | Drop, decrease, reduction | Australia’s wheat exports declined steadily from 1986 to 1990. | Noun / Verb |
| Peak | The highest point or maximum level | Summit, high, top | The European Community’s wheat exports peaked at 21 million tons in 1990. | Noun / Verb |
| Recovery | A return to a normal or improved state | Improvement, comeback, bounce back | Canada’s exports showed a recovery in 1990 after a sharp decline in 1989. | Noun |
| Gradual | Taking place or changing slowly over time | Steady, slow, consistent | The European Community saw gradual increases in wheat exports each year. | Adjective |
|
Export |
Goods sent to another country for sale |
Shipment, trade |
“Canada and Australia both exported wheat during this period.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Figures |
Numerical data or statistics |
Data, statistics |
“The graph shows export figures for each country.” |
Noun |
|
Period |
A specific duration of time |
Duration, interval |
“The period from 1985 to 1990 saw significant export changes.” |
Noun |
|
Increase |
A rise or growth in size, number, or amount |
Rise, growth, gain |
“Australia’s wheat exports increased slightly in 1986.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Steady |
Firm, constant, or unchanging over time |
Consistent, stable |
“Australia’s wheat exports declined steadily from 1986 to 1990.” |
Adjective |
|
Significant |
Of considerable importance or size |
Notable, substantial |
“Canada showed significant growth in wheat exports in 1988.” |
Adjective |
|
Sharp |
A quick and significant change in direction or amount |
Sudden, drastic |
“Canada experienced a sharp decline in exports in 1989.” |
Adjective |
|
Decline |
A decrease or reduction in something |
Drop, fall, downturn |
“The European Community’s wheat exports declined in 1986.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Recovery |
The act of returning to a normal or better state |
Comeback, rebound |
“Canada’s wheat exports recovered in 1990 after a significant drop.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Fluctuate |
To rise and fall irregularly |
Vary, change, alternate |
“Canada’s wheat exports fluctuated during the period.” |
Verb |
|
Rise |
An increase in number or amount |
Increase, growth |
“Exports from the European Community saw a steady rise.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Consistent |
Steady or unchanging over time |
Stable, regular |
“The European Community showed consistent growth in exports.” |
Adjective |
|
Sharp |
Steep or sudden in change |
Rapid, drastic |
“Canada saw a sharp decrease in exports in 1989.” |
Adjective |
|
Peaked |
To reach the highest point |
Reached, hit the top |
“The European Community’s wheat exports peaked at 21 million tons.” |
Verb |
|
Decrease |
A reduction in amount, size, or quality |
Decline, drop, reduction |
“Australia’s wheat exports saw a decrease over the years.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Trend |
The general direction or tendency of something |
Pattern, direction |
“The trend in wheat exports showed a rise in the European Community.” |
Noun |
|
Stabilize |
To make or become steady or unchanging |
Secure, balance |
“After the sharp decline, Canada’s exports stabilized in 1990.” |
Verb |
|
Amount |
A quantity or volume of something |
Quantity, volume |
“The amount of wheat exported by the European Community increased.” |
Noun |
|
Significantly |
In a way that is important or notable |
Considerably, notably |
“Exports in Canada grew significantly in 1988.” |
Adverb |
|
Fluctuating |
Changing or varying irregularly |
Unstable, varying |
“Canada experienced fluctuating wheat exports during the period.” |
Adjective |
|
Overall |
Considering everything or as a whole |
In total, generally |
“Overall, Canada and the European Community showed growth in exports.” |
Adverb |
|
Figures |
The numerical values shown in data or charts |
Statistics, data |
“The figures for wheat exports show clear fluctuations.” |
Noun |
|
Periodically |
Occurring at regular intervals |
Intermittently, cyclic |
“Exports increased periodically during the late 1980s.” |
Adverb |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
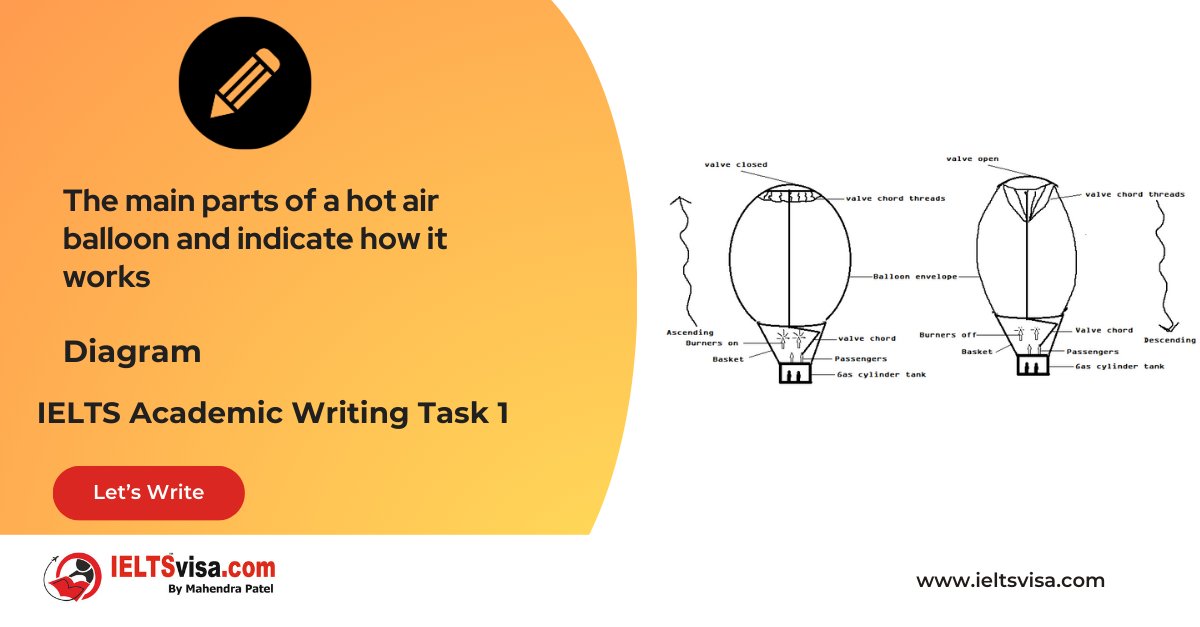
Task 1 – Diagram – A conference hall built in 1981 and planned for 2020
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
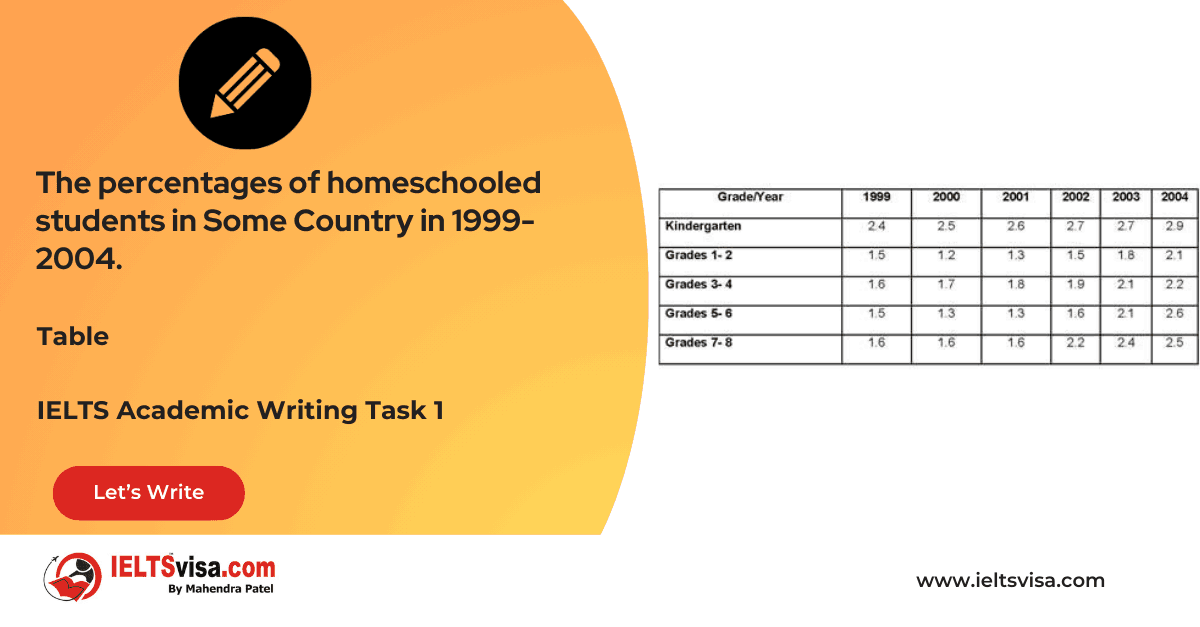
Task 1 – Table – The percentages of homeschooled students in Some Country in 1999-2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
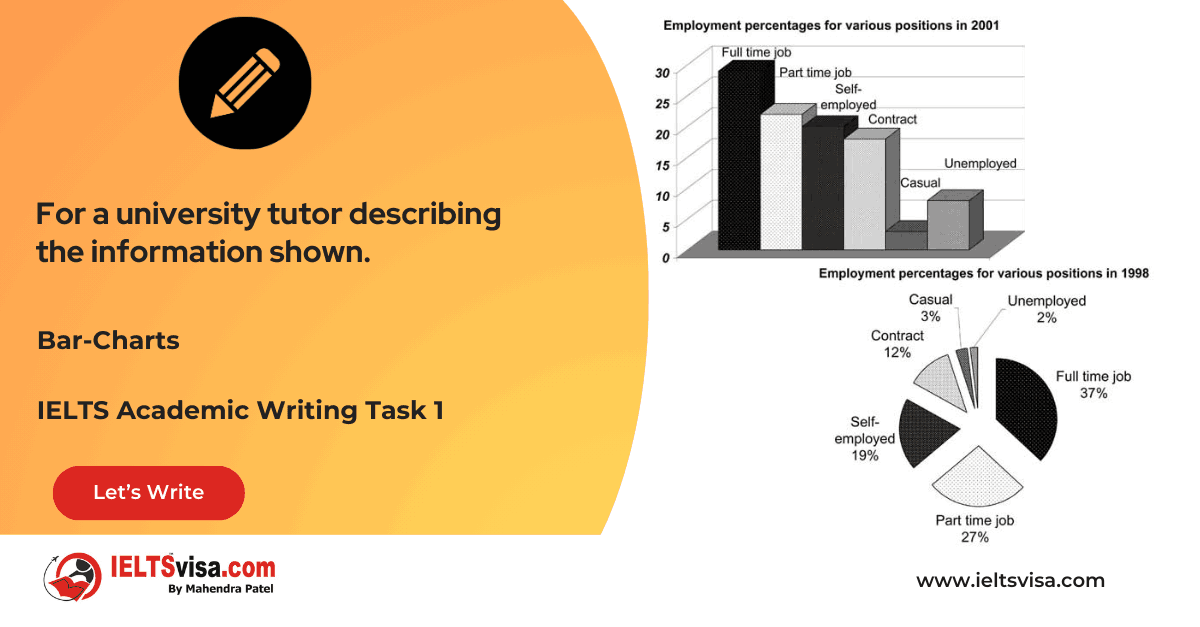
Task 1 – Table – For a university tutor describing the information shown.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
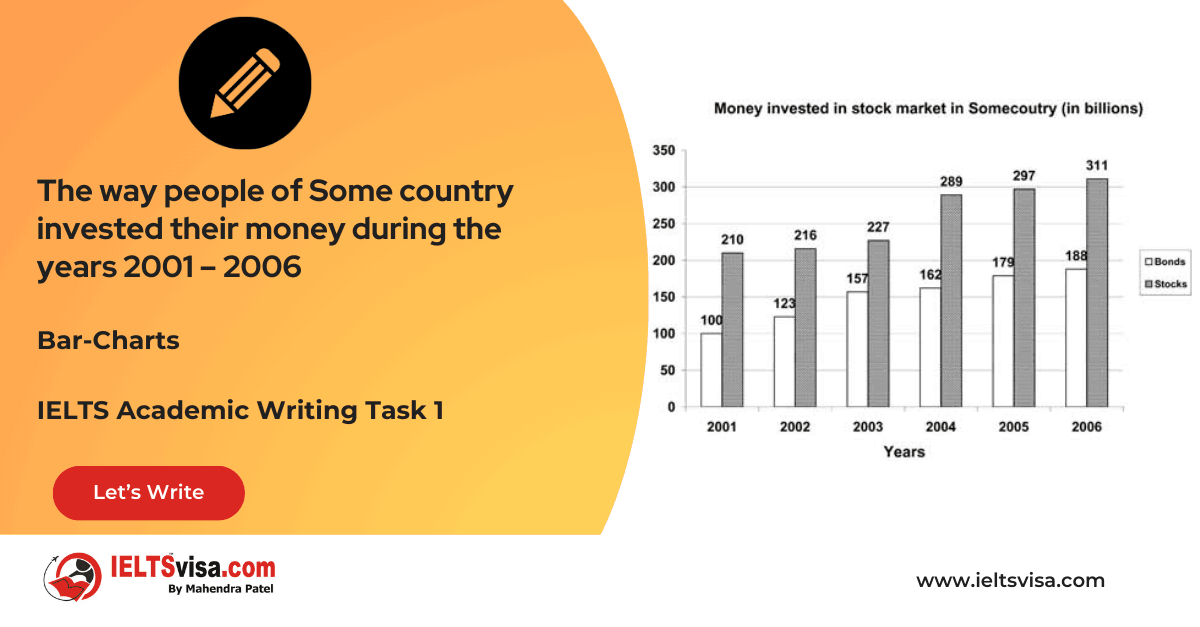
Task 1 – Bar-Charts – The way people of Some country invested their money during the years 2001 – 2006
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Rainwater Harvesting and Conversion to Drinking Water in an Australian Town.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...