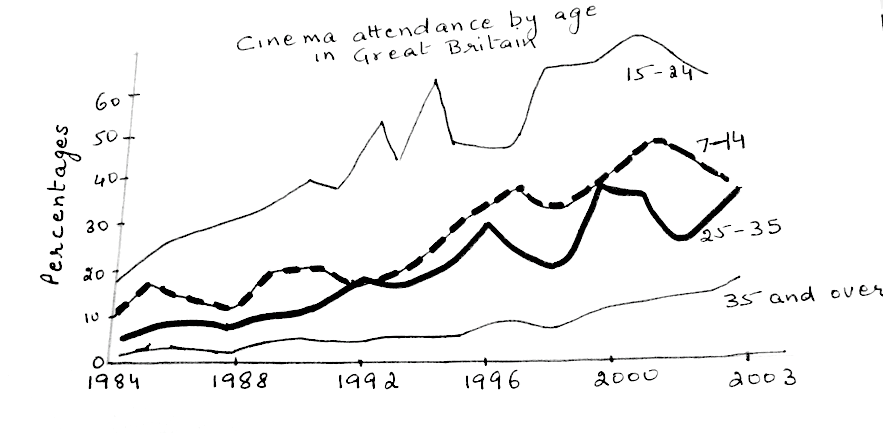
Cinema attendance by age in Great Britain
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Line Graph

IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The graph below shows cinema attendance by age in Great Britain. Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information shown.
Common Questions for the Line Graph
1. Graph Type: Line Graph
2. Title: Cinema Attendance by Age in Great Britain (1984–2003)
3. What are the units of measurement?: Percentage of cinema attendance
4. Who: People of different age groups in Great Britain
5. When: 1984 to 2003
6. Where: Great Britain
7. Topic: Trends in cinema attendance across various age groups
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Comparison 1 : 15–24 Age Group (Highest Growth)
- Details:
1. Increased from about 18% in 1984 to over 50% in 2003.
2. Fluctuated between 1992 and 1998 but consistently had the highest attendance.
Comparison 2 : Older Age Groups (35+)
- Details:
1. Attendance rose steadily from 2% in 1984 to over 10% in 2003.
Comparison 3 : 7–14 and 25–35 Age Groups
- Details:
1. Followed similar patterns from 1984 to 2002, with fluctuations.
2. Diverged after 2002—attendance among 7–14-year-olds decreased, while 25–44-year-olds saw an increase.
Sample Answer
The line graph illustrates the percentage of people in different age groups who attended cinemas in Great Britain from 1984 to 2003.
Overall, cinema attendance increased across all age groups during this period, with the 15–24 age group consistently leading in attendance.
The most significant growth was observed in the 15–24 age group, which rose from 18% in 1984 to over 50% by 2003. Despite some fluctuations between 1992 and 1998, this age group consistently recorded the highest attendance rates throughout the period.
Older individuals (35+) also showed a noticeable increase in cinema attendance, rising from approximately 2% in 1984 to over 10% in 2003. Meanwhile, the 7–14 and 25–35 age groups followed similar trends, with attendance rates fluctuating from 1984 to 2002. After 2002, the patterns diverged as attendance among 7–14-year-olds decreased, whereas it increased for the 25–44 age group.
Top 28 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary | Type | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
| Fluctuate | verb | To rise and fall irregularly | Vary, Oscillate | Attendance fluctuated between 1992 and 1998. |
| Substantial | Adjective | Noticeable or significant | Considerable, Major | There was a substantial increase in attendance by older age groups. |
| Diverge | Verb | To develop differently or separate | Split, Differ | Attendance patterns diverged after 2002 for certain age groups. |
| Consistently |
Adverb
|
Happening in a steady and reliable way | Constantly, Regularly | The 15–24 age group consistently had the highest attendance. |
| Characterize | Verb | To describe the distinct features of | Define, Mark | Fluctuations characterized the attendance trends. |
| Attendance | Noun | The act of being present at a place | Presence, Turnout | “Cinema attendance increased across all age groups.” |
| Noticeable | Adjective | Easily seen or worthy of attention | Evident, Significant | “Older individuals showed a noticeable increase in attendance.” |
| Percentage | Noun | A fraction of 100 used to express a proportion | Proportion, Ratio | “The graph shows the percentage of people attending cinemas.” |
| Consistent | Adjective | Steady and unchanging over time | Reliable, Constant | “The 15–24 age group showed consistent growth in attendance.” |
| Decline | Verb/Noun | To decrease in number or quality | Decrease, Reduction | “Attendance among 7–14-year-olds declined after 2002.” |
| Peak | Verb/Noun | To reach the highest point | Summit, Climax | “Cinema attendance peaked in the 15–24 age group.” |
| Contrast | Noun/Verb | A clear difference between two or more things | Difference, Distinction | “There is a contrast between younger and older age groups.” |
| Gradual | Adjective | Happening slowly over a period | Progressive, Steady | “Older individuals showed a gradual increase in attendance.” |
| Age group | Noun | A category of people based on age | Cohort, Demographic | “Each age group showed distinct trends in attendance.” |
| Fluctuation | Noun | Irregular rise and fall in numbers | Variation, Oscillation | “Fluctuations were observed between 1992 and 1998.” |
| Predominant | Adjective | More important or noticeable than others | Leading, Dominant | “The 15–24 age group remained the predominant age group.” |
| Exhibit | Verb | To display or show something | Demonstrate, Show | “Older individuals exhibited a sharp increase in attendance.” |
| Interval | Noun | A period between events | Gap, Span | “Attendance fluctuated during certain intervals.” |
| Proportional | Adjective | Corresponding in size or amount | Relative, Commensurate | “The rise in attendance was proportional to the age group.” |
| Surge | Noun/Verb | A sudden increase | Spike, Escalation | “Attendance surged in the 15–24 age group after 1998.” |
| Undergo | Verb | To experience or be subject to | Experience, Endure | “Older age groups underwent significant growth in attendance.” |
| Account for | Verb Phrase | To represent or constitute a portion of something | Represent, Make up | “The 15–24 age group accounted for the majority of cinema-goers.” |
| Prominent | Adjective | Easily noticeable or important | Noticeable, Significant | “Prominent growth was recorded among younger audiences.” |
| Trend | Noun | A general direction of change | Pattern, Movement | “The line graph highlights key trends in cinema attendance.” |
| Highlight | Verb | To emphasize or draw attention to | Emphasize, Underscore | “The graph highlights the attendance patterns across age groups.” |
| Divergence | Noun | A difference or separation in paths | Separation, Deviation | “The divergence in trends was observed after 2002.” |
| Observation | Noun | The act of noticing or analyzing something | Perception, Insight | “Significant observations were made regarding age group patterns.” |
| Dominant | Adjective | Having the most influence or importance | Leading, Primary | “The 15–24 age group remained the dominant demographic.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Task 1 – Map -Changes in Pentland Coastal Area from 1950 to 2007
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
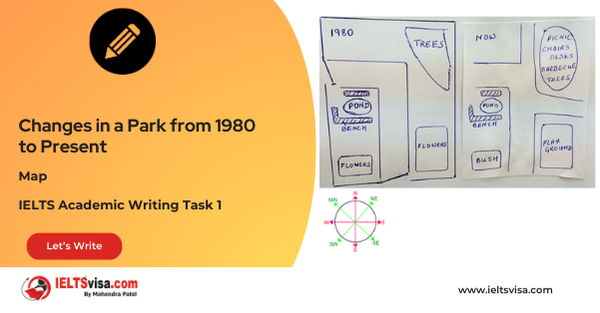
Task 1 – Map -Changes in a Park from 1980 to Present
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
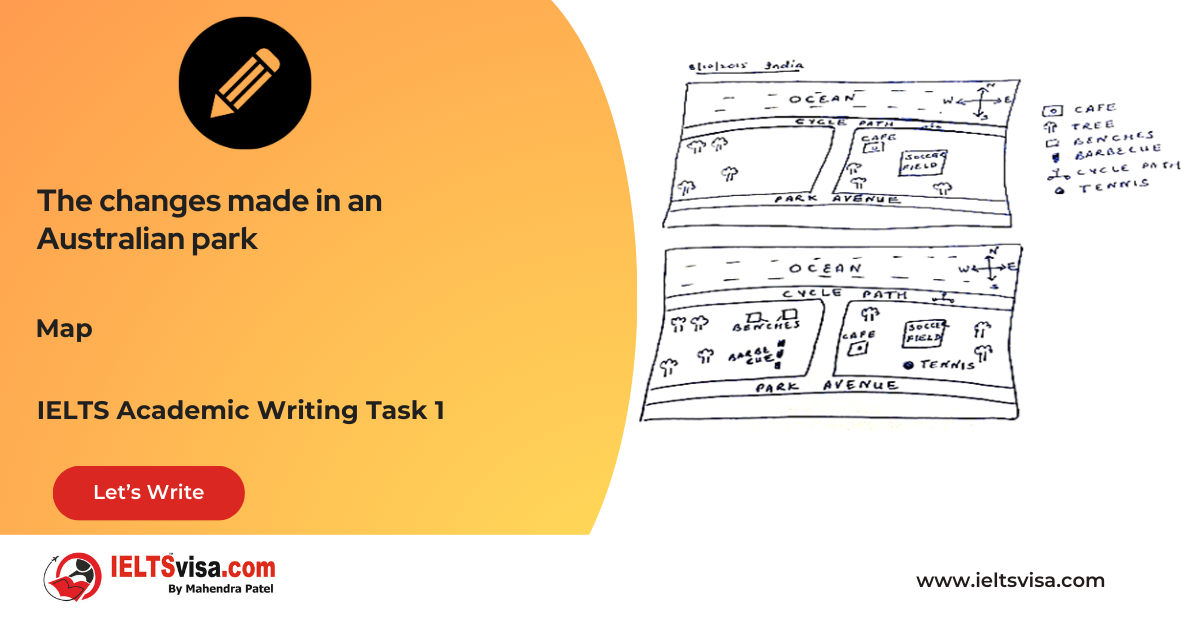
Task 1 – Maps – The changes made in an Australian park
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
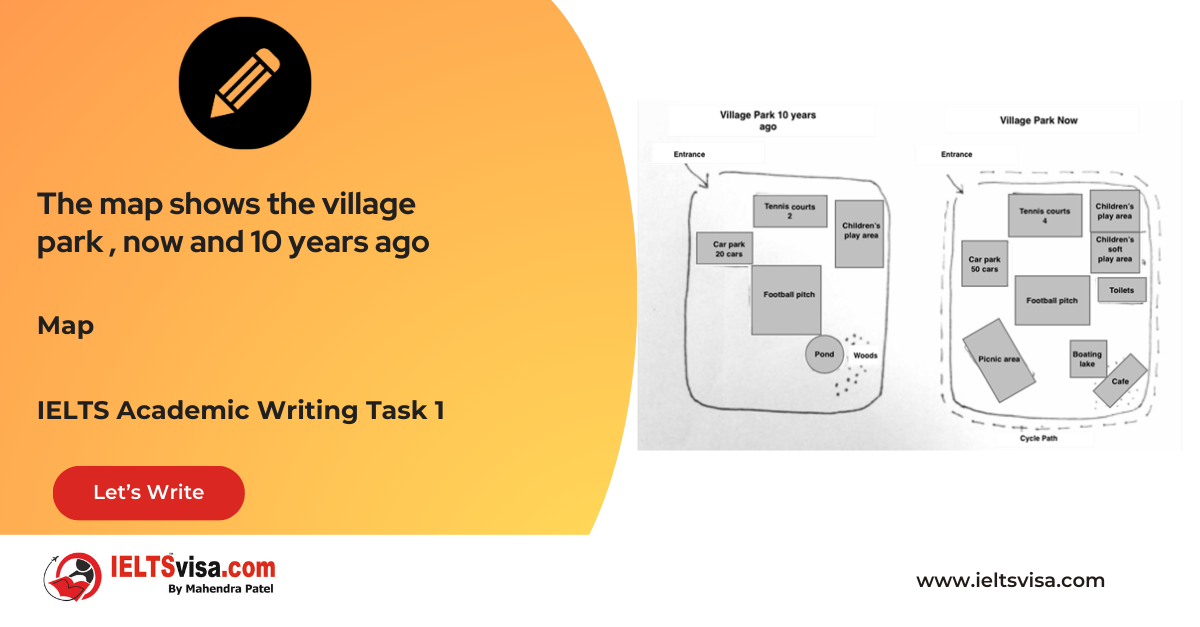
Task 1 – Maps- The map shows the village park, now and 10 years ago
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Map -Changes in Sydney International Airport from 1930 to Present
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
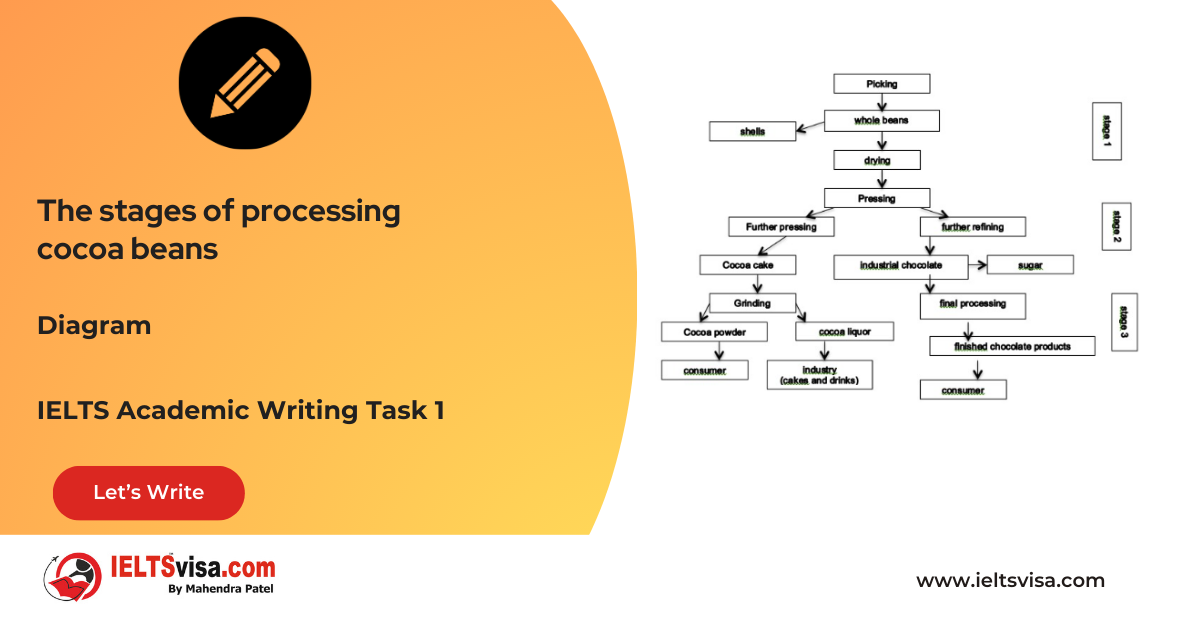
Task 1 – Diagram – The stages of processing cocoa beans
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...