The amount of energy lost from generation of electricity to the time it reaches the consumer from brown and black coal
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
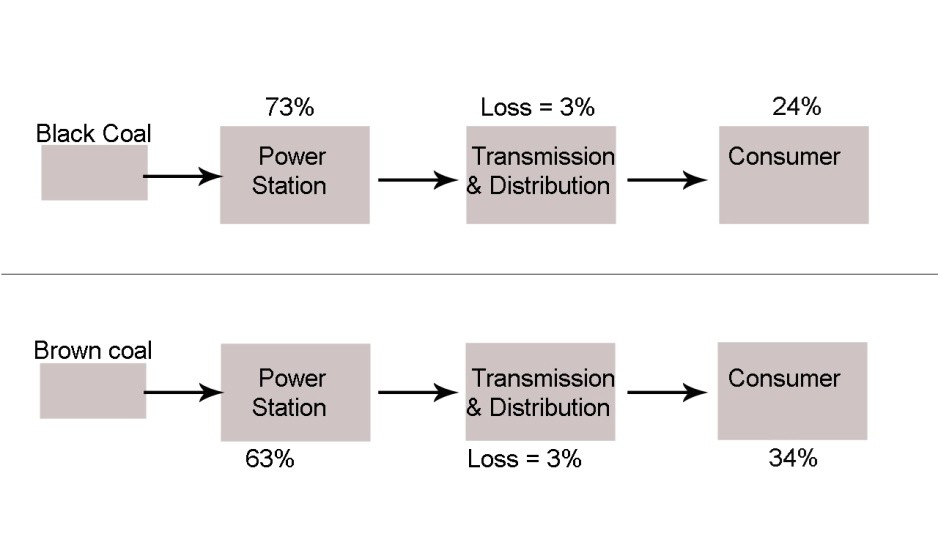
The graph below shows the amount of energy lost from generation of electricity to the time it reaches the consumer from brown and black coal. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main points and make comparisons where relevant.
Common Questions for Data Summary
1. Diagram Type: Graph.
2. Title: Energy Loss from Coal Generation to Consumer (Black and Brown Coal).
3. What is being described?: The amount of energy lost in power stations, transmission, and distribution for electricity generation from black and brown coal, before it reaches the consumer.
4. Where is this process happening?: Energy generation from black and brown coal, with energy loss occurring at power stations, and during transmission and distribution.
5. What is the data about?: Energy efficiency comparison between black and brown coal in terms of energy loss during the process of electricity generation and delivery to the consumer.
6. Topic: Comparison of energy loss and efficiency between brown and black coal.
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Details:
- Energy Loss in Power Station: 73% of energy is lost in the power station from black coal, whereas 63% of energy is lost from brown coal—indicating a 10% lower loss for brown coal.
- Energy Loss in Transmission and Distribution: The energy loss during transmission and distribution is identical for both types of coal, with 3% loss in both cases.
- Energy Reaching the Consumer: 24% of energy from black coal reaches the consumer, while 34% of energy from brown coal reaches the consumer—demonstrating that brown coal is more energy-efficient.
Sample Answer
The graph compares the energy loss and efficiency in generating and transmitting electricity from black and brown coal.
Overall, although a substantial amount of energy is lost in both cases before reaching the consumer, brown coal is more efficient than black coal in terms of energy conservation and delivery to the consumer.
From the graph, 73% of the energy from black coal is lost in the power station, while brown coal experiences a lower energy loss of 63%. The difference of 10% highlights that brown coal is relatively more efficient in power generation. Both black and brown coal experience an equal 3% loss during transmission and distribution, indicating no disparity at this stage.
However, a significant difference emerges when considering the energy that actually reaches the consumer. Only 24% of the energy generated from black coal reaches the consumer, while a higher percentage of 34% reaches the consumer from brown coal.
Top 26 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Type |
| Transmission | The process of sending energy or electricity over distances | Distribution, delivery | “Both coal types lost 3% of energy during transmission.” | Noun |
| Distribution | The act of delivering energy or resources to various locations | Allocation, supply | “Energy loss during distribution was the same for both coal types.” | Noun |
| Power station | A facility where electricity is generated | Power plant, energy station | “The power station from black coal experienced 73% energy loss.” | Noun |
| Efficient | Achieving maximum productivity with minimum wasted effort or energy | Productive, effective | “Brown coal is more efficient than black coal in delivering energy.” | Adjective |
| Loss | The amount of energy that is wasted or not used | Waste, depletion | “The loss of energy from brown coal is lower than from black coal.” | Noun |
| Generation | The process of producing electricity | Production, creation | “Electricity generation from coal results in energy loss.” | Noun |
| Conversion | The process of changing energy from one form to another | Transformation, alteration | “Energy conversion at the power station results in some loss.” | Noun |
| Output | The amount of energy or electricity produced | Production, yield | “The power station’s energy output is affected by losses.” | Noun |
| Consumption | The use of energy by consumers | Utilization, usage | “Only 34% of brown coal energy is available for consumption.” | Noun |
| Efficiency | The ability to minimize waste while achieving results | Productivity, effectiveness | “Brown coal has higher efficiency than black coal.” | Noun |
| Fuel source | The material used to generate power | Energy source, raw material | “Coal is a major fuel source for electricity production.” | Noun |
| Coal-fired | Powered by burning coal | Coal-based, thermal | “A coal-fired power station converts coal into electricity.” | Adjective |
| Thermal energy | Energy produced from heat | Heat energy, calorific power | “Coal burning produces thermal energy for electricity.” | Noun |
| Heat loss | The loss of thermal energy during a process | Energy dissipation, waste heat | “Heat loss occurs at various stages of electricity production.” | Noun |
| Depletion | The reduction in the amount of a resource | Exhaustion, reduction | “Energy depletion occurs due to inefficiencies in power plants.” | Noun |
| Carbon footprint | The total greenhouse gases emitted by an activity | Environmental impact, emissions level | “Coal-fired plants have a high carbon footprint.” | Noun |
| Emission | The release of gases or particles into the atmosphere | Discharge, pollution | “Coal combustion results in carbon dioxide emissions.” | Noun |
| Grid | A network for transmitting electricity | Power network, distribution system | “Electricity is delivered to consumers via the power grid.” | Noun |
| Load capacity | The maximum amount of electricity a system can handle | Power limit, capacity | “The load capacity of a grid affects energy distribution.” | Noun |
| Wastage | The unnecessary loss of energy or resources | Inefficiency, dissipation | “Wastage occurs at multiple stages in energy production.” | Noun |
| Harnessing | The act of capturing and utilizing energy | Utilizing, extracting | “Harnessing coal energy involves burning it for power.” | Verb |
| Transmission loss | The reduction in energy during transportation | Power dissipation, leakage | “Transmission loss occurs as electricity moves through wires.” | Noun |
| Retained | Kept or preserved instead of being lost | Preserved, conserved | “Brown coal retains more energy than black coal.” | Verb |
| Sustainability | The ability to maintain a process without depletion | Eco-friendliness, durability | “Coal energy lacks sustainability due to high emissions.” | Noun |
| Infrastructure | The basic facilities needed for power distribution | Framework, foundation | “Energy infrastructure includes power plants and transmission lines.” | Noun |
| Optimization | The act of making something as effective as possible | Enhancement, improvement | “Optimizing energy use reduces losses.” | Noun |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
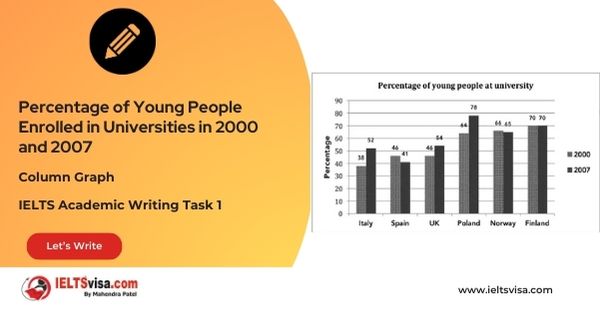
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
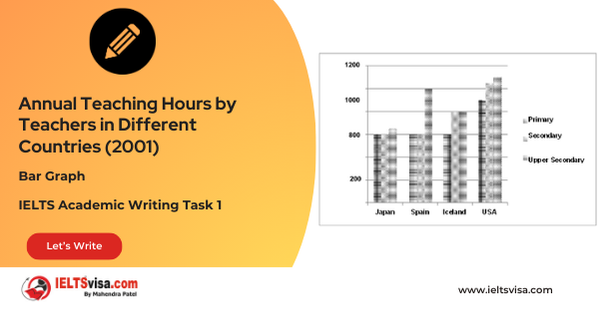
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
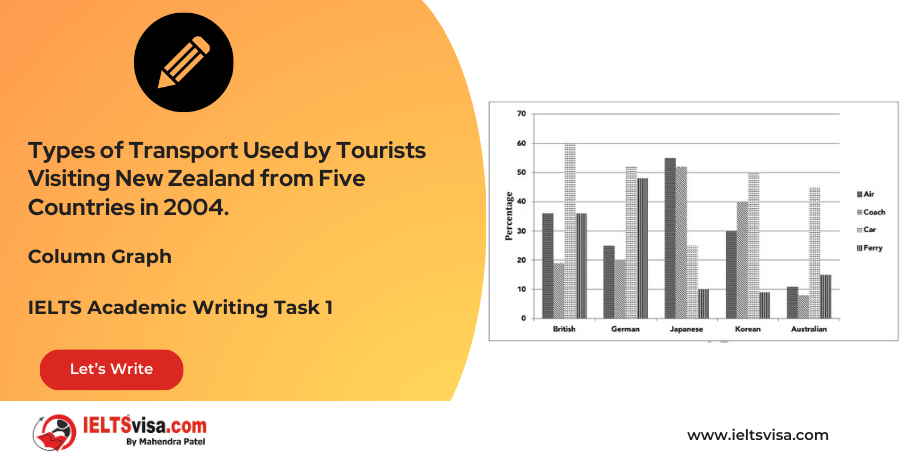
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
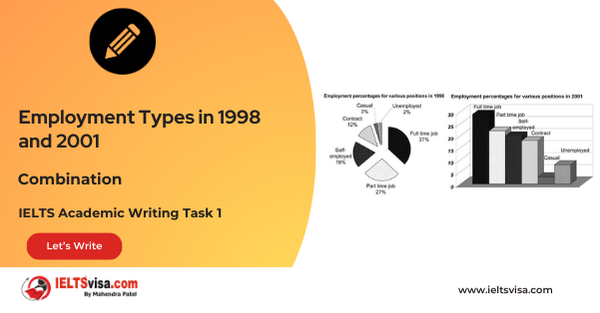
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...