The stages and equipment used in the cement-making process, and how cement is used to produce concrete for building purposes
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Diagram
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
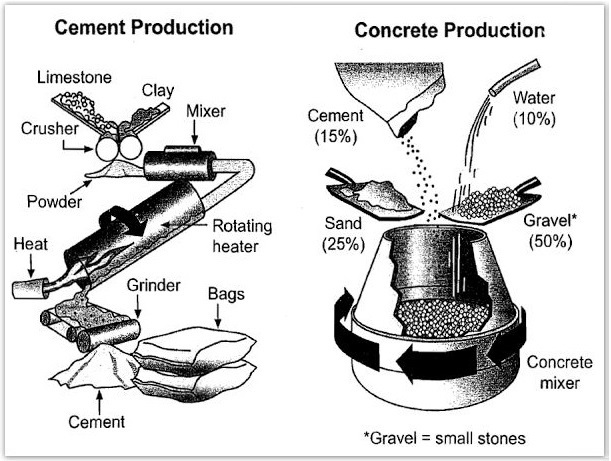
The diagram below shows the stages and equipment used in the cement-making process, and how cement is used to produce concrete for building purposes. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. You should write at least 150 words.
Common Questions for the Process Diagram
1. Diagram Type: Process Diagram
2. Title: Cement Production and Its Use in Concrete Making
3. What are the units of measurement? Percentages (%), Materials
4. Who: Manufacturers of cement and concrete for building purposes
5. When: General process description, no specific year mentioned
6. Where: Global cement production for construction purposes
7. Topic: Cement production process and its role in making concrete
Detailed Process and Observations
Summary of Data :
- The diagram illustrates the steps involved in the production of cement and the subsequent use of cement to produce concrete for building purposes. The process includes both the manufacturing of cement and the mixing of concrete for construction.
1. Cement Production Process :
- The cement-making process begins with the crushing of limestone and clay, which are then mixed to form a powder. This powder is sent through a rotating heater, where heat is applied to produce raw cement material. The raw cement is then ground to produce the final cement product, which is packed and ready for sale.
2. Concrete Production Process :
- Concrete is made by mixing 15% cement, 10% water, 25% sand, and 50% small stones in a concrete mixer. The mixer rotates at high speed to ensure thorough blending of the materials, resulting in concrete that is used in construction.
Sample Answer
The diagrams illustrate the stages of cement production and the use of cement to produce concrete for building purposes.
Overall, the cement production process is complex, involving crushing, heating, and grinding, while concrete production is a straightforward mixing process that combines cement with other materials for use in construction.
Cement production involves several steps, starting with the crushing of limestone and clay, which are mixed to create a powder. This powder is then heated in a rotating heater, transforming it into raw cement material. The raw material is ground to create finished cement, which is packed and sold.
Once cement is produced, it is used to make concrete for construction. The process begins by mixing 15% cement, 10% water, 25% sand, and 50% small stones in a concrete mixer. The mixer rotates quickly, ensuring that the ingredients are thoroughly blended to form the concrete mixture used in the building.
Top 26 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Type |
| Crushing | Breaking down or smashing material into smaller pieces | Pulverizing, Grinding | Limestone and clay are crushed to create a fine powder. | Noun/Verb |
| Heater | A device that generates heat for processing materials | Furnace, kiln, stove | The powder is passed through a rotating heater for heat treatment. | Noun |
| Raw material | A basic substance that is processed to make a final product | Unprocessed, crude material | The raw cement material is ground to produce the final cement. | Noun (Phrase) |
| Concrete mixer | A machine used to mix ingredients to make concrete | Mixing drum, cement mixer | The concrete mixer combines cement, water, sand, and stones. | Noun (Phrase) |
| Blending | The act of combining different substances evenly | Mixing, combining, merging | The ingredients in the concrete mixer are blended to form a uniform mixture. | Noun/Verb |
| Illustrates | To explain or show something clearly | Depicts, demonstrates | “The table illustrates the housing distribution in Denmark in 2012.” | Verb |
| Preference | A greater liking for one option over others | Favor, inclination | “Green Park showed a strong preference for terrace houses.” | Noun |
| Accommodation | A place to live or stay | Housing, residence | “The types of accommodation compared included bungalows and terrace houses.” | Noun |
| Proportion | A part or amount in relation to the whole | Percentage, ratio | “A significant proportion of residents in Central Park lived in bungalows.” | Noun |
| Bungalows | A one-story house | Single-story home | “Bungalows were the most popular housing type in Central Park.” | Noun |
| Detached | Not joined to another house | Independent, free-standing | “Detached houses were less popular in all three areas.” | Adjective |
| Terrace | A row of houses joined together | Row houses, linked homes | “Terrace houses were the dominant housing type in Green Park.” | Noun |
| Semi-detached | Sharing a wall with one other house | Partially connected | “Semi-detached houses accounted for a smaller portion of the housing types in all areas.” | Adjective |
| Mixed | Containing a variety of different elements | Varied, diverse | “The Central area had a more mixed distribution of housing types.” | Adjective |
| Accounted for | To make up or comprise a certain amount | Represented, constituted | “Detached houses accounted for only 5% of the housing in the Central area.” | Phrase |
| Varied | Including a wide range of different elements | Diverse, assorted | “The distribution of housing types was varied across the areas.” | Adjective |
| Dominant | Most prominent or influential | Main, prevalent | “Terrace houses were the dominant housing type in Green Park.” | Adjective |
| Equally | To the same degree or extent | Evenly, uniformly | “The remaining residents were equally divided between semi-detached houses and bungalows.” | Adverb |
| Constitute | To make up or form something | Comprise, compose | “Terrace houses constitute the majority of housing in Green Park.” | Verb |
| Notable | Worthy of attention | Remarkable, significant | “The notable difference in housing preferences was seen in Central Park.” | Adjective |
| Allocation | The distribution or assignment of something | Assignment, apportionment | “The allocation of housing types varied significantly across the areas.” | Noun |
| Dominance | The state of being most influential or prevalent | Supremacy, preeminence | “The dominance of terrace houses was evident in Green Park.” | Noun |
| Residential | Relating to housing or areas where people live | Suburban, domestic | “The residential patterns in Central Park favored bungalows.” | Adjective |
| Urban | Relating to a city or densely populated area | City-based, metropolitan | “Urban areas often have mixed housing distributions.” | Adjective |
| Significant | Sufficiently important or large | Noteworthy, considerable | “A significant number of residents in Green Park lived in terrace houses.” | Adjective |
| Population | All the people living in a particular area | Residents, community | “Two-thirds of the population in Green Park lived in terrace houses.” | Noun |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
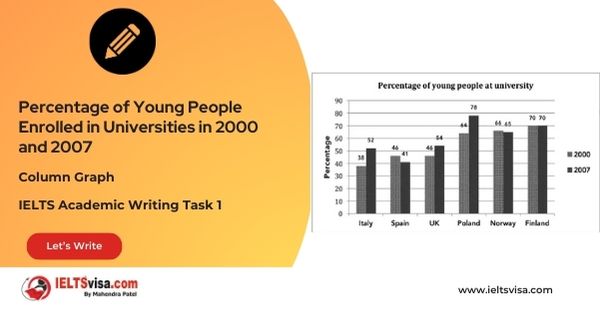
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
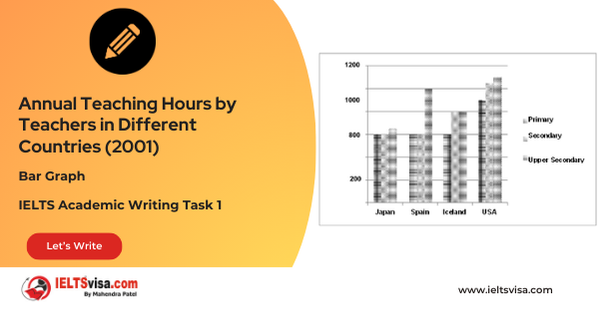
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
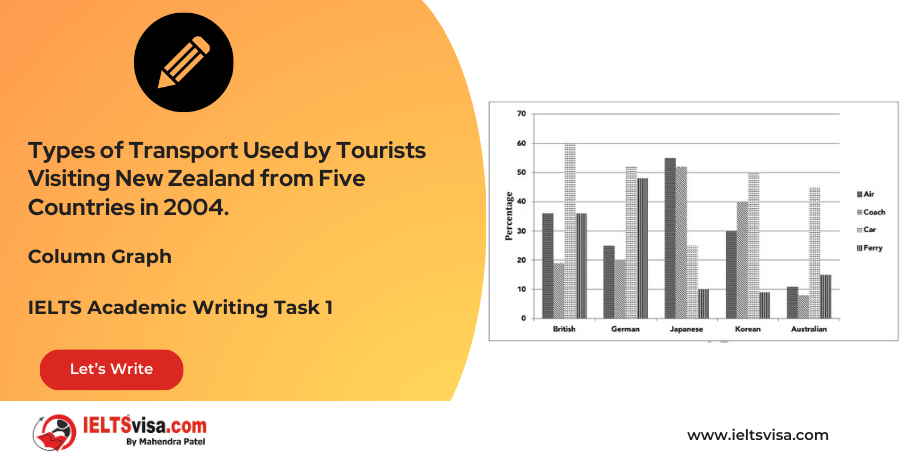
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
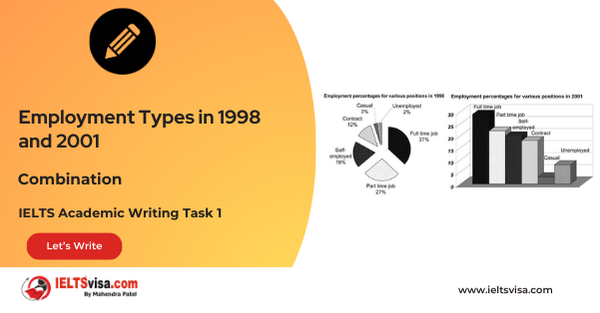
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...