A typical American and a Japanese office
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Diagram
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
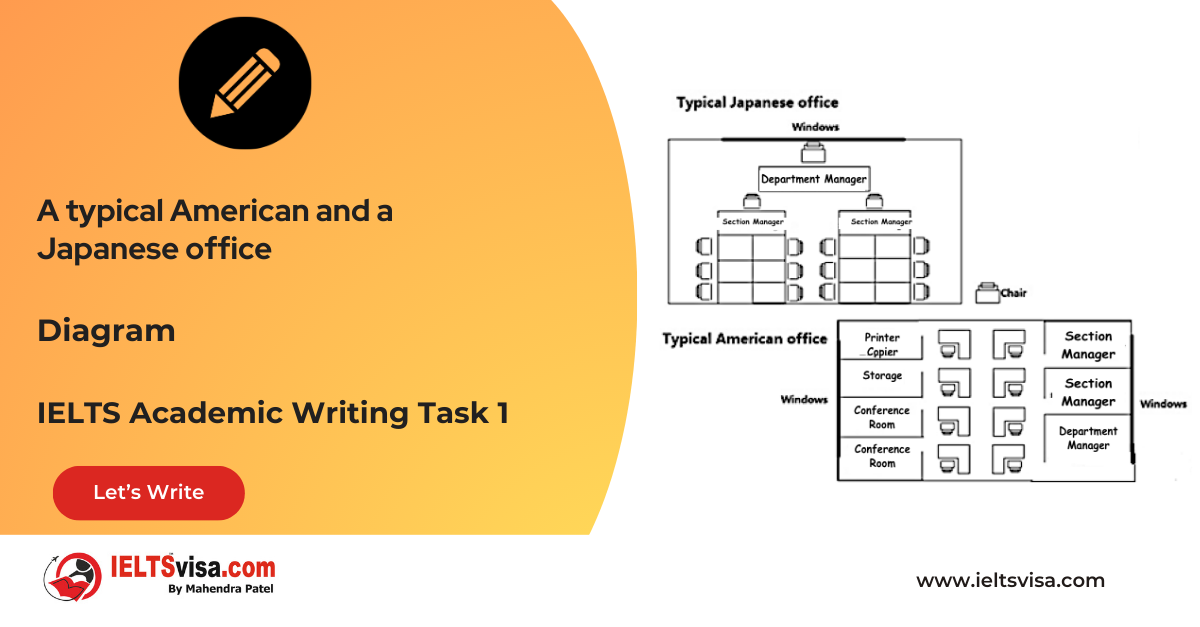
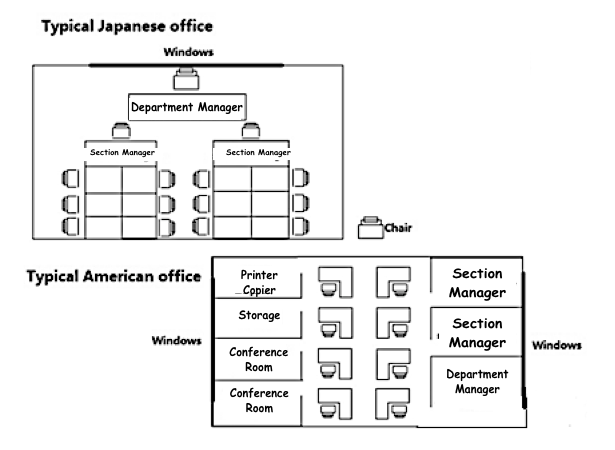
The graph below shows a typical American and a Japanese office. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Common Questions for the Office Layout Comparison
1. Graph Type: Diagram
2. Title: Comparison of Typical American and Japanese Office Layouts
3. What are the units of measurement?: Not applicable
4. Who: American and Japanese offices
5. When: Not specified
6. Where: Typical offices in the USA and Japan
7. Topic: Layout features and organizational structure of American and Japanese offices
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Comparison 1 : Office Structure
- Details:
1. Managerial Layout: Both offices include one department manager and two section managers.
2. American Office: Features separate cabins for managers and cubicles for junior employees.
3. Japanese Office: Utilizes a large open hall for all employees seated around tables.
Comparison 2 : Facilities and Environment
- Details
1. Meeting Spaces: The American office includes two conference rooms, a storage room, and a separate area for printers and copiers.
2. Lighting: Windows in the American office are located on both the east and west walls; Japanese office windows are positioned on the north side.
3. Supervision Structure: In the Japanese office, section managers supervise employees directly seated around them, while in the American office, managers have separate spaces.
Sample Answer
The diagrams compare the layout of a typical American office with that of a Japanese office, highlighting both similarities and differences in their design and organizational structures.
Both office layouts accommodate one department manager, two section managers, and several junior employees. However, the American office features separate cabins for the department and section managers, along with individual cubicles for junior employees. In contrast, the Japanese office operates from a large open hall where employees are seated around tables, with section managers overseeing them directly.
Another notable distinction is the facilities available in each office. The American office includes two conference rooms, a storage area, and a dedicated room for printers and copiers. In comparison, the Japanese office lacks these additional facilities, focusing instead on a more communal working environment. Regarding natural light, the American office benefits from windows on both the east and west walls, while the Japanese office has its windows positioned on the north wall.
Overall, the layout differences reflect contrasting work cultures, with the American office emphasizing individual space and the Japanese office promoting collaboration and teamwork.
Top 28 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary (type) | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
| Layout (noun) | The arrangement or design of something | Design, configuration | “The office layout was designed for efficiency.” |
| Supervise (verb) | To oversee or manage the work of others | Manage, oversee | “Section managers supervise their teams.” |
| Facility (noun) | A place, amenity, or piece of equipment provided for a particular purpose | Amenity, service | “The office includes several facilities.” |
| Communal (adj) | Shared by all members of a community | Shared, collective | “The Japanese office promotes a communal atmosphere.” |
| Distinction (noun) | A difference or contrast between similar things | Difference, contrast | “There is a clear distinction between the two layouts.” |
|
Compare (verb) |
To examine the similarities and differences between things |
Contrast, evaluate |
“The diagrams compare the layouts of two office designs.” |
|
Organizational (adj) |
Related to the structure or arrangement of something |
Structural, managerial |
“The organizational structure differs in both offices.” |
|
Cubicle (noun) |
A small, enclosed workspace within a larger office |
Booth, workspace |
“Junior employees work in individual cubicles in the American office.” |
|
Oversee (verb) |
To watch over or supervise |
Monitor, supervise |
“Section managers oversee the employees in the Japanese office.” |
|
Collaborative (adj) |
Involving teamwork or joint effort |
Cooperative, joint |
“The Japanese office promotes a collaborative work environment.” |
|
Hall (noun) |
A large open space within a building |
Room, corridor |
“The Japanese office operates from a large open hall.” |
|
Contrast (verb) |
To show the differences between two or more things |
Differentiate, distinguish |
“The passage contrasts the work cultures of the two offices.” |
|
Junior (adj) |
Relating to lower rank or position |
Subordinate, lower-level |
“Junior employees are provided cubicles in the American office.” |
|
Dedicated (adj) |
Reserved or set aside for a specific purpose |
Exclusive, specialized |
“There is a dedicated room for printers in the American office.” |
|
Seating (noun) |
The arrangement of seats in a space |
Placement, arrangement |
“The seating in the Japanese office encourages teamwork.” |
|
Amenity (noun) |
A useful feature or facility of a building |
Facility, convenience |
“The American office includes amenities like conference rooms and storage areas.” |
|
Efficiency (noun) |
The ability to achieve a goal with minimal waste |
Productivity, effectiveness |
“The layout of the American office prioritizes efficiency.” |
|
Overhead (adj) |
Situated above or in the higher area |
Above, top |
“The open hall design lacks overhead partitions.” |
|
Reflect (verb) |
To show, express, or represent something |
Represent, indicate |
“The layouts reflect cultural differences in work practices.” |
|
Natural (adj) |
Existing in or derived from nature |
Organic, unprocessed |
“Natural light is an important feature in both offices.” |
|
Emphasize (verb) |
To give special importance to something |
Highlight, stress |
“The American office emphasizes individual workspaces.” |
|
Arrangement (noun) |
The organization or layout of elements in a space |
Order, placement |
“The arrangement of the Japanese office is communal and open.” |
|
Promote (verb) |
To encourage or support an idea or activity |
Advocate, encourage |
“The Japanese office promotes teamwork and collaboration.” |
|
Adapt (verb) |
To change or adjust to fit a new situation |
Modify, adjust |
“The design adapts to the specific cultural work habits.” |
|
Structure (noun) |
The arrangement of and relations between parts of something |
Framework, composition |
“The structure of the Japanese office reflects its work culture.” |
|
Partition (noun) |
A division or separation within a space |
Divider, screen |
“Partitions are used in the American office to create individual workspaces.” |
|
Adjacent (adj) |
Next to or adjoining something |
Neighboring, beside |
“The storage area is adjacent to the conference rooms.” |
|
Commercial (adj) |
Related to business activities |
Business-oriented, trade |
“The office layouts reflect commercial needs and cultural preferences.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
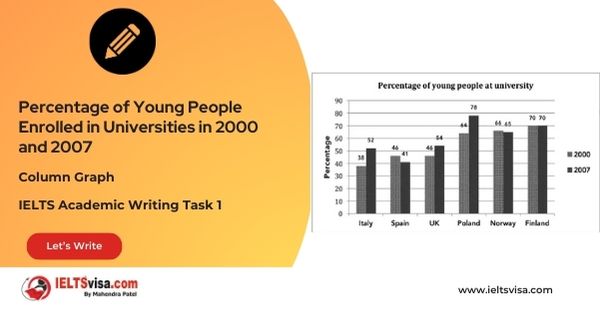
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
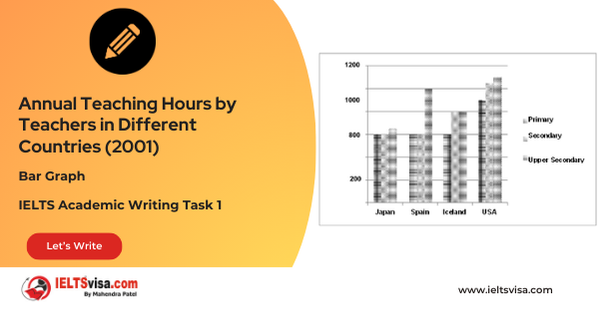
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
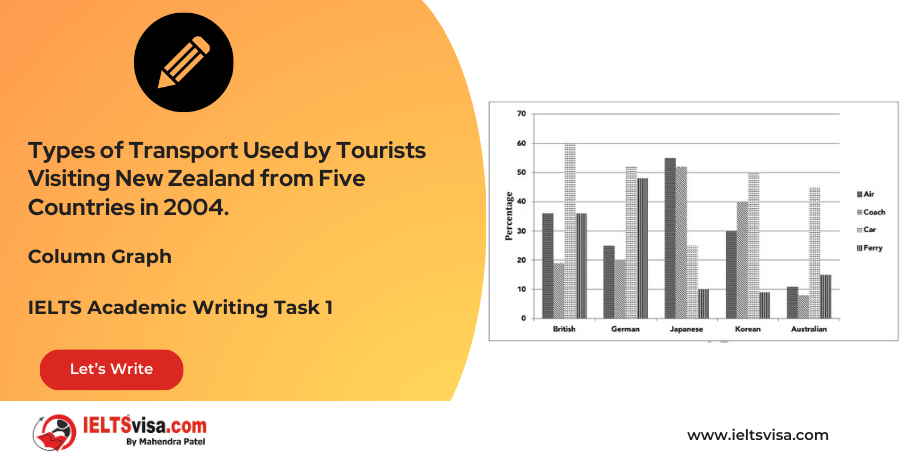
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
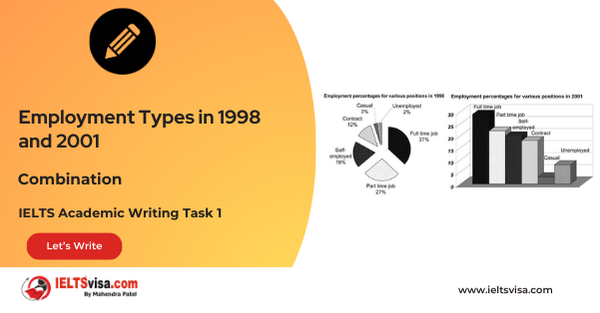
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...