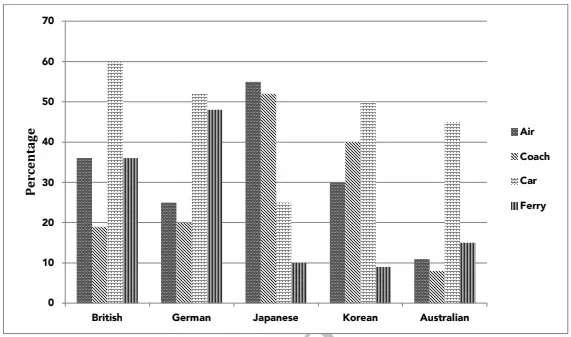
Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Column Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The graph below shows the types of transport used by tourists who visited New Zealand from five countries in 2004. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Common Questions for Column Graph Data
1. Graph Type: Column graph.
2. Title: Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
3. What are the units of measurement?: Percentage (%).
4. Who: Tourists from Britain, Germany, Japan, Korea, and Australia.
5. When: 2004.
6. Where: New Zealand.
7. Topic: The types of transport used by tourists from five countries when visiting New Zealand.
Comparison Showing and Trends
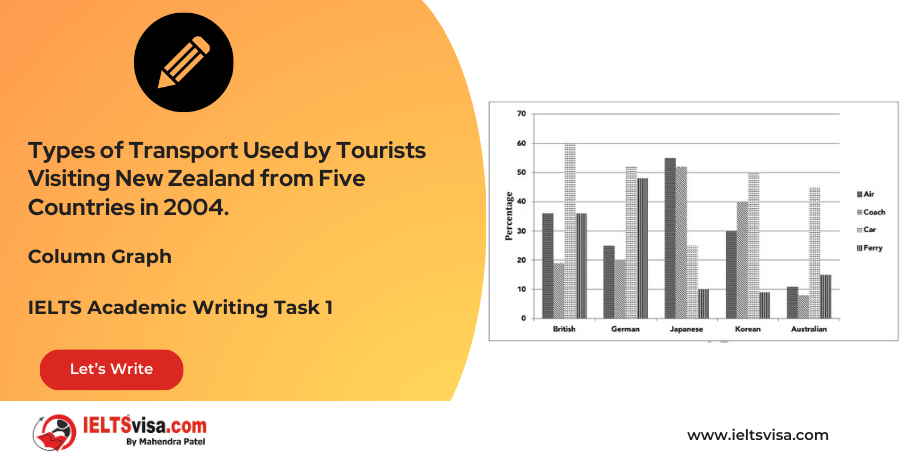
- The Japanese tourists overwhelmingly preferred air transport (55%), while other countries favored cars, with over 50% usage from Britain (60%), Germany (52%), Korea (50%), and Australia (45%).
- Coaches were most popular with Japanese tourists (52%), and least popular with Australians (8%). While the British and Germans had similar coach usage (20%), Koreans were the second-highest (40%).
- The ferry was most commonly used by Germans (48%) and British (35%), with very few tourists from Japan, Korea, and Australia choosing the ferry (less than 15%).
Sample Answer
The given column graph illustrates the types of transport used by tourists from five countries—Britain, Germany, Japan, Korea, and Australia—when visiting New Zealand in 2004.
Overall, the choice of transport varied significantly, with car travel dominating for most countries and Japanese tourists showing a marked preference for air travel.
Car travel was the most common mode of transport, with 60% of British tourists, 52% of German tourists, 50% of Korean tourists, and 45% of Australian tourists using it. In contrast, only 25% of Japanese tourists used cars, with 55% of them opting for air travel, the highest percentage among the countries. The next most common mode of transport was the coach, used by 52% of Japanese tourists. While coach use was moderate for Germans (20%) and British (20%), it was much higher for Koreans (40%) and much lower for Australians (8%).
The ferry was preferred by 48% of Germans and 35% of British tourists. In contrast, fewer Japanese, Korean, and Australian tourists used the ferry, with only 15% or fewer opting for it.
Top 25 Vocabulary
Vocabulary |
Meaning |
Synonyms |
Examples |
Vocabulary Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Predominantly |
Mainly; for the most part |
Mostly, primarily |
“Tourists from most countries predominantly used cars to travel in New Zealand.” |
Adverb |
|
Opting |
Choosing or selecting |
Choosing, selecting |
“Japanese tourists were opting for air travel more than any other transport.” |
Verb |
|
Overwhelmingly |
In an overpowering manner |
Predominantly, largely |
“Japanese tourists overwhelmingly preferred air travel.” |
Adverb |
|
Mode |
A particular way or method |
Method, manner |
“Cars were the most preferred mode of transport for tourists from several countries.” |
Noun |
|
Trend |
A general direction or tendency |
Pattern, movement |
“The trend shows a preference for air travel among Japanese tourists.” |
Noun |
|
Preference |
A greater liking or choice for one thing over another |
Liking, choice |
“The preference for car travel was evident among most tourists.” |
Noun |
|
Alternative |
A different option or choice |
Option, substitute |
“Air travel was the alternative choice for Japanese tourists.” |
Noun |
|
Dominating |
Having the most influence or control over something |
Leading, prevailing |
“Car travel was dominating among tourists from most countries.” |
Verb |
|
Opt |
To choose or decide on something |
Choose, decide |
“Tourists from Japan opted for air travel more than any other transport.” |
Verb |
|
Significantly |
To a large extent or in an important way |
Considerably, greatly |
“The percentage of Japanese tourists using air travel was significantly higher.” |
Adverb |
|
Prefer |
To choose something over other options |
Choose, favor |
“British tourists preferred cars over other modes of transport.” |
Verb |
|
Mode of transport |
The method or way of moving from one place to another |
Means of travel, method |
“The most common mode of transport for tourists was the car.” |
Noun |
|
Marked |
Clearly noticeable or distinct |
Significant, noticeable |
“Japanese tourists showed a marked preference for air travel.” |
Adjective |
|
Rate |
The percentage or proportion of something |
Percentage, proportion |
“The rate of coach use was highest among Korean tourists.” |
Noun |
|
Pervasive |
Spread throughout, affecting many places or people |
Widespread, prevalent |
“Car travel was the pervasive mode of transport for tourists in New Zealand.” |
Adjective |
|
Considerably |
To a great extent or in a significant way |
Significantly, appreciably |
“The percentage of German tourists using the ferry was considerably higher than other countries.” |
Adverb |
|
Commonplace |
Frequently occurring; usual |
Usual, frequent |
“Coach travel was a commonplace choice for German tourists.” |
Adjective |
|
Ferry |
A type of boat used to carry people and vehicles over water |
Boat, ship |
“A ferry was used by 48% of German tourists when visiting New Zealand.” |
Noun |
|
Substantially |
To a large degree or extent |
Significantly, greatly |
“Japanese tourists substantially favored air travel over other modes.” |
Adverb |
|
Less frequent |
Occurring with less regularity or in fewer numbers |
Infrequent, rare |
“The ferry was less frequent among Japanese tourists.” |
Adjective |
|
Preference pattern |
A general trend or habit regarding choices |
Tendency, trend |
“The preference pattern among British tourists leaned towards the car.” |
Noun |
|
Attributable |
To be considered as the result of something |
Due to, caused by |
“The increased air travel was attributable to Japan’s higher rate of international flights.” |
Adjective |
|
Revealed |
Made known or shown |
Exposed, disclosed |
“The graph revealed that most tourists chose cars as their mode of transport.” |
Verb |
|
Predominantly |
Mainly or for the most part |
Mainly, largely |
“Korean tourists predominantly used coaches while traveling in New Zealand.” |
Adverb |
|
Comparable |
Able to be likened or compared |
Similar, equivalent |
“The use of coaches by Japanese tourists was comparable to that of Koreans.” |
Adjective |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...