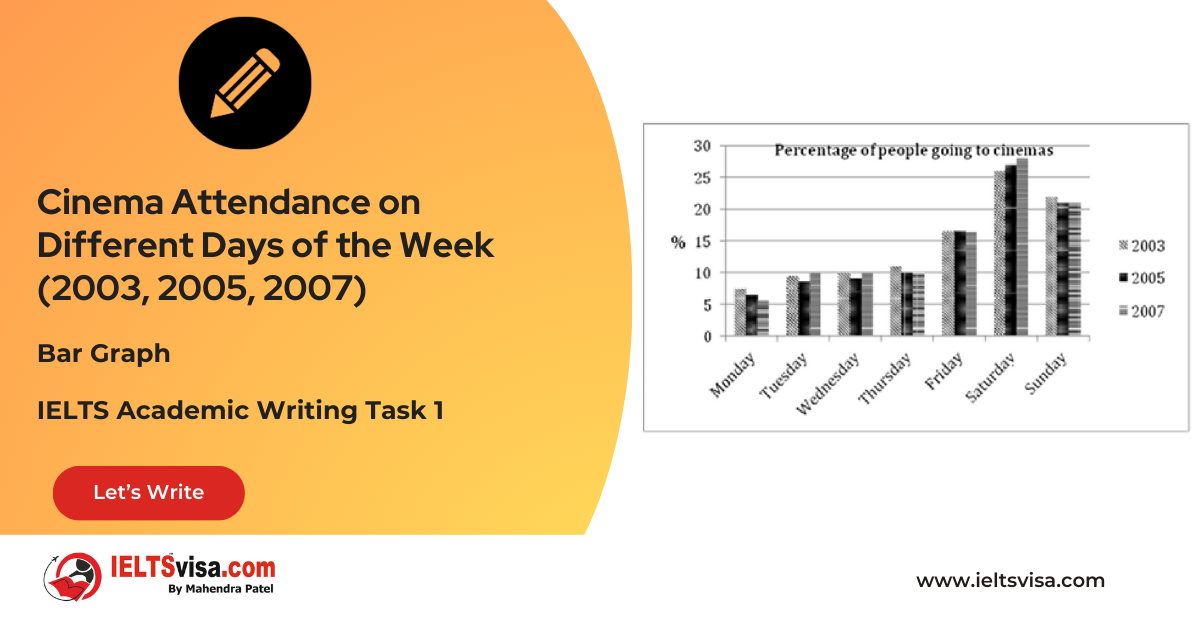
The six developed countries to developing countries from 2008-2010
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Bar Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
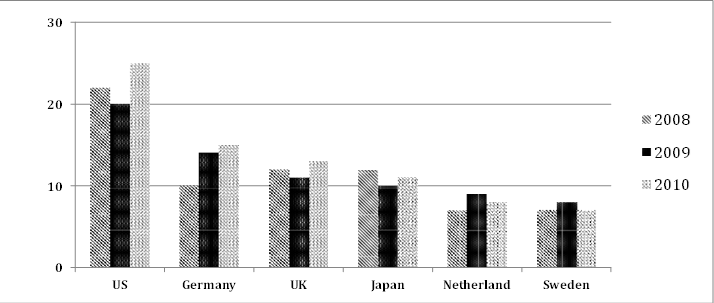
The chart below shows the aid from six developed countries to developing countries from 2008-2010. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Common Questions for the Bar Graph
1. Graph Type: Bar Graph
2.Title: Aid from Six Developed Countries to Developing Countries (2008-2010)
3.Units of Measurement : Billions of dollars
4.Who: Six developed countries (US, Germany, UK, Japan, Netherlands, Sweden)
5. When: 2008, 2009, 2010
6. Where: Global comparison to developing countries
7. Topic: Amount of aid provided by developed countries
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Comparison 1 : Aid from the United States
- Details:
1. The US was the largest donor throughout the period, contributing $22 billion in 2008.
2. Aid decreased to $20 billion in 2009 but increased to $25 billion in 2010.
Comparison 2: Aid from Germany, UK, and Japan
-
Details:
1. Germany’s aid rose steadily from about $10 billion in 2008 to $15 billion in 2010.
2. The UK and Japan showed fluctuations, with both countries providing between $10 and $15 billion in aid.
Comparison 3 : Aid from the Netherlands and Sweden
-
Details:
1. Both countries provided aid consistently below $10 billion.
2. The aid amounts exhibited similar patterns over the three years, reflecting minor changes.
Sample Answer
The column graph presents the amount of aid provided by six developed countries to developing nations from 2008 to 2010, measured in billions of dollars. The United States emerged as the largest donor in all three years.
Overall, the data indicates that the US provided the most substantial support to developing countries, while Germany showed consistent increases in aid contributions throughout the observed period.
2008 the US contributed $22 billion, although this figure dropped to $20 billion in 2009. However, aid levels rebounded significantly to $25 billion by 2010. Germany followed as a major donor, with its aid steadily increasing from around $10 billion in 2008 to $15 billion in 2010, highlighting a consistent growth trend.
In contrast, the aid from the UK and Japan exhibited fluctuations, generally ranging between $10 and $15 billion during the period. While providing less aid overall, the Netherlands and Sweden consistently remained under the $10 billion mark. Despite some variation, both countries displayed similar trends in their aid amounts across the three years.
Top 27 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary (type) | Type | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
|
Illustrate (v.) |
Verb |
To explain or make evident by using examples or visuals |
Demonstrate, show, depict |
“The graph illustrates the aid contributions over three years.” |
|
Contribute (v.) |
Verb |
To give or supply in order to help achieve something |
Donate, provide, supply |
“The US contributed the most aid during the period.” |
|
Fluctuation (n.) |
Noun |
A change or variation, especially in amount or level |
Variation, oscillation, instability |
“Aid from the UK and Japan showed fluctuations over the years.” |
|
Consistent (adj.) |
Adjective |
Acting or done in the same way over time |
Steady, reliable, unchanging |
“Germany’s aid showed consistent increases.” |
|
Overall (adv.) |
Adjective |
In general; as a whole |
Generally, in total, on the whole |
“Overall, the US provided the most support to developing countries.” |
|
Aid |
Noun |
Assistance or support, typically financial or material |
Help, support, assistance |
“Developed nations provide aid to developing countries to improve their infrastructure.” |
|
Donor |
Noun |
A person, group, or entity that provides something, especially money |
Contributor, benefactor |
“The United States was the largest donor among the six countries.” |
|
Rebound |
Verb |
To recover or increase again after a decline |
Recover, bounce back |
“The aid levels rebounded significantly in 2010 after a drop in 2009.” |
|
Consistent |
Adjective |
Unchanging in nature, standard, or effect over time |
Steady, reliable |
“Germany’s aid showed a consistent upward trend throughout the period.” |
|
Fluctuate |
Verb |
To vary irregularly, especially in amount or level |
Vary, oscillate, waver |
“The aid from the UK fluctuated between $10 billion and $15 billion during this period.” |
|
Steadily |
Adverb |
At a consistent rate or pace |
Gradually, progressively |
“Germany steadily increased its aid contributions from 2008 to 2010.” |
|
Highlight |
Verb |
To emphasize or draw attention to something |
Emphasize, underscore |
“The report highlights Germany’s steady growth in aid contributions.” |
|
Substantial |
Adjective |
Of considerable importance, size, or worth |
Significant, notable |
“The US provided the most substantial aid among all the countries.” |
|
Trend |
Noun |
A general direction in which something is developing or changing |
Pattern, movement |
“A consistent growth trend was observed in Germany’s aid contributions.” |
|
Period |
Noun |
A length of time during which something happens |
Interval, duration |
“The data represents the aid provided over a three-year period.” |
|
Variation |
Noun |
A change or difference in condition, amount, or level |
Difference, deviation |
“The Netherlands and Sweden displayed minor variations in their aid amounts.” |
|
Observe |
Verb |
To notice or perceive something |
Notice, perceive |
“The observed data highlights significant differences in aid contributions.” |
|
Measure |
Verb |
To ascertain the size, amount, or degree of something |
Quantify, evaluate |
“The aid contributions are measured in billions of dollars.” |
|
Emerge |
Verb |
To become known or prominent |
Appear, arise, surface |
“The US emerged as the largest donor in all three years.” |
|
Allocate |
Verb |
To distribute resources or duties for a specific purpose |
Assign, distribute |
“Countries allocate aid to developing nations based on specific priorities.” |
|
Consistently |
Adverb |
In a way that does not change; steadily |
Reliably, uniformly |
“Sweden consistently contributed under $10 billion.” |
|
Support |
Noun/Verb |
Assistance or help given to someone or something |
Aid, backing, help |
“Financial support to developing countries is crucial for global stability.” |
|
Significant |
Adjective |
Sufficiently large or important to warrant attention |
Noteworthy, considerable |
“The US showed a significant rebound in aid levels in 2010.” |
|
Level |
Noun |
A position or amount within a scale or hierarchy |
Degree, magnitude |
“Aid levels from Japan fluctuated over the three-year period.” |
|
Drop |
Verb/Noun |
To decrease suddenly or fall to a lower level |
Decrease, decline |
“There was a slight drop in US aid contributions in 2009.” |
|
Developing |
Adjective |
Referring to countries with a less advanced economy |
Emerging, growing |
“Developing nations rely heavily on international aid to foster growth.” |
|
Billions |
Noun |
A numerical term representing one thousand million |
N/A |
“Aid contributions are measured in billions of dollars for accuracy.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Comparison of Males Preferring Watching vs. Participating in Sports
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Line-Bar – The total volume of telephone calls (in million minutes) in Denmark, divided into three categories, from 1995- 2004
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
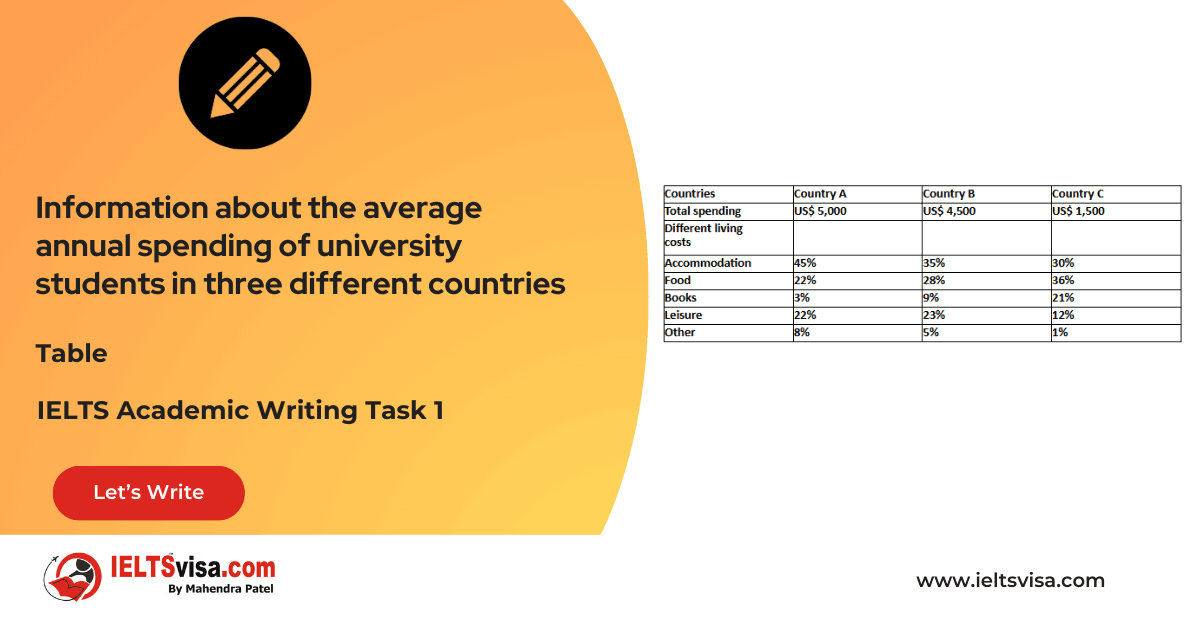
Task 1 – Table – Information about the average annual spending of university students in three different countries
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Table -The production of carbon dioxide in five different countries in 2006
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
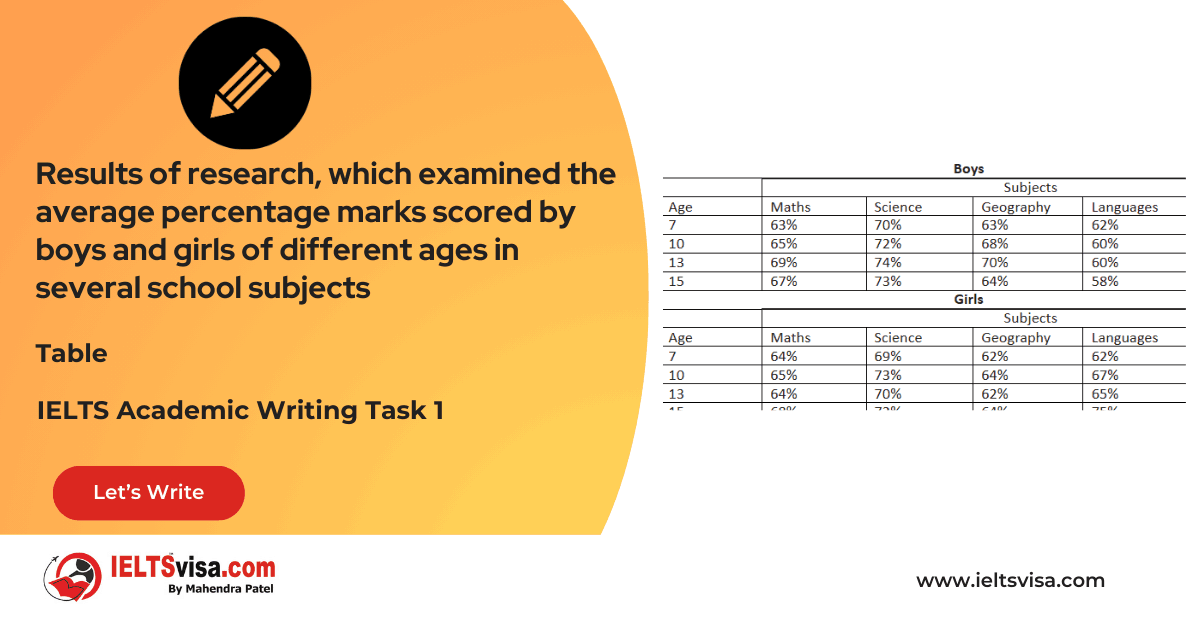
Task 1 – Table – Results of research, which examined the average percentage marks scored by boys and girls of different ages in several school subjects
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – The structure of a home smokery and how it works
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...