Outlines literacy rates for a number of nations in 2004
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Bar Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The bar graph below outlines literacy rates for a number of nations in 2004. Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information shown here.
Common Questions for the Bar Graph
1. Graph Type: Bar Graph
2. Title: Literacy Rates for Selected Countries in 2004
3. What are the units of measurement?: Percentage of literacy rates
4. Who: People in various countries worldwide
5. When: 2004
6. Where: Countries including Georgia, Slovakia, Israel, and others
7. Topic: Literacy levels of selected countries in 2004
Comparison Showing and Trends
Comparison 1: High Literacy Rates
- Details:
- Georgia and Slovakia had the highest literacy rates, both at 100%.
2. Israel followed closely at 97%.
Comparison 2 : Moderate Literacy Rates
- Details:
- Colombia, Mexico, Indonesia, Qatar, Brazil, Peru, and Turkey had similar rates, averaging around 88%.
2. Syria recorded slightly lower literacy at 80%.
Sample Answer
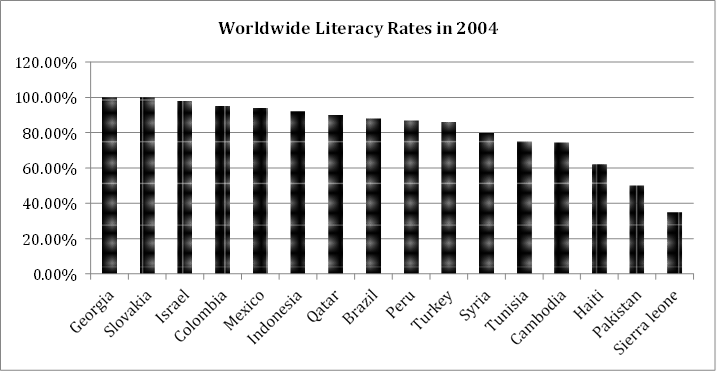
The bar graph illustrates literacy rates for a selection of countries worldwide in 2004. The countries are displayed along the x-axis, and their respective literacy rates are plotted on the y-axis.
Overall, while many nations demonstrated high literacy rates of 80% or more, a notable gap remained for countries such as Haiti, Pakistan, and Sierra Leone. These figures reflect varying levels of access to education across the globe.
Georgia and Slovakia led the list with perfect literacy rates of 100%, while Israel followed closely at approximately 97%. A group of nations, including Colombia, Mexico, Indonesia, Qatar, Brazil, Peru, and Turkey, shared similar literacy levels, all hovering around 88%. Syria was slightly lower, recording a literacy rate of 80%.
In contrast, countries like Tunisia and Cambodia fell below the 70% mark. Haiti’s literacy rate was 62%, while Pakistan’s literacy rate was less than 50%. The least literate country on the list was Sierra Leone, with only 35% of its population being literate in 2004.
Top 29 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary (type) | Type | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
| Literacy | Noun | The ability to read and write | Education, Proficiency | Literacy rates vary significantly across countries. |
| Disparity | Noun | A noticeable difference | Gap, Inequality | The disparity between high and low literacy rates is stark. |
| Moderate | Adverb | Average or middle level | Reasonable, Middling | Moderate literacy rates were seen in countries like Syria. |
| Hovering | Verb | Remaining close to a particular level | Staying, Lingering | Literacy rates hovered around 88% in several nations. |
| Access | Noun | The ability or right to use or benefit from | Availability, Entry | Access to education greatly impacts literacy rates. |
|
Illustrates |
Verb |
Explains or makes something clear using examples or visuals |
Depicts, Shows, Demonstrates |
“The bar graph illustrates literacy rates for various countries.” |
|
Rates |
Noun |
A measure, quantity, or frequency |
Levels, Percentages, Proportions |
“The literacy rates were highest in Georgia and Slovakia.” |
|
Worldwide |
Adverb |
Extending or reaching throughout the world |
Globally, Universally, Internationally |
“The graph compares literacy rates worldwide in 2004.” |
|
Selection |
Noun |
A group of things chosen from a larger number |
Choice, Range, Variety |
“The data includes a selection of countries worldwide.” |
|
Axis |
Noun |
A fixed line used to display data |
Reference line, Coordinate line |
“Countries are displayed along the x-axis.” |
|
Respective |
Adjective |
Belonging or relating separately to each item |
Corresponding, Individual |
“Their respective literacy rates are plotted on the y-axis.” |
|
Demonstrated |
Verb |
Showed clearly through evidence |
Displayed, Indicated, Revealed |
“Many nations demonstrated high literacy rates.” |
|
Reflect |
Verb |
To show or express |
Indicate, Represent, Depict |
“The figures reflect the level of education in each country.” |
|
Varying |
Verb |
Showing differences or changes |
Differing, Fluctuating, Changing |
“Varying levels of education access were evident globally.” |
|
Globe |
Noun |
The earth or world |
World, Planet |
“Education varies significantly across the globe.” |
|
Perfect |
Adjective |
Having all required qualities or elements |
Flawless, Complete, Ideal |
“Georgia and Slovakia achieved perfect literacy rates.” |
|
Recording |
Verb |
Documenting or registering data |
Logging, Noting, Registering |
“Syria recorded a literacy rate of 80%.” |
|
Slightly |
Adverb |
To a small degree or extent |
Marginally, Moderately, Barely |
“Syria’s literacy rate was slightly lower than 80%.” |
|
Below |
Preposition |
Lower in amount, level, or rank |
Under, Beneath, Less than |
“Tunisia’s literacy rate was below 70%.” |
|
Population |
Noun |
The total number of people in a specific area |
Inhabitants, Residents, Demographics |
“Sierra Leone had only 35% literacy in its population.” |
|
Notable |
Adjective |
Worthy of attention or remarkable |
Significant, Remarkable, Prominent |
“A notable gap existed in literacy rates between regions.” |
|
Impacts |
Verb |
Affects or influences |
Influences, Affects, Alters |
“Access to education impacts literacy levels.” |
|
Least |
Adverb |
The smallest amount or degree |
Smallest, Minimum, Fewest |
“Sierra Leone was the least literate country on the list.” |
|
Remaining |
Verb |
Continuing to exist after other parts are removed |
Persisting, Staying, Lasting |
“Sierra Leone’s literacy rate remained the lowest.” |
|
Achievement |
Noun |
Something successfully completed or accomplished |
Accomplishment, Success, Attainment |
“Achieving 100% literacy is an extraordinary achievement.” |
|
Variation |
Noun |
A change or difference in condition or amount |
Fluctuation, Discrepancy, Diversity |
“The variation in literacy rates was significant.” |
|
Highlight |
Verb |
To emphasize or make something stand out |
Stress, Emphasize, Underline |
“The data highlights global disparities in education.” |
|
Rank |
Noun |
The position of someone or something in a hierarchy |
Position, Standing, Level |
“The countries are ranked by their literacy rates.” |
|
Achievement |
Noun |
A successful result through effort |
Accomplishment, Attainment |
“A literacy rate of 100% is a rare achievement globally.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
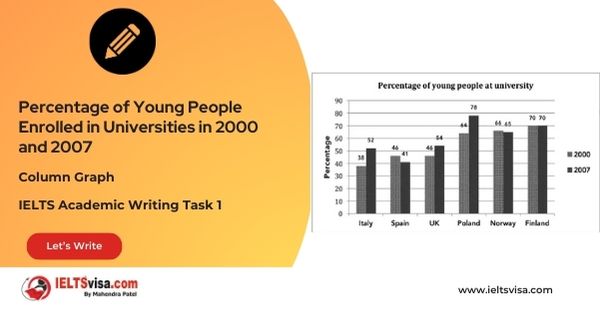
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
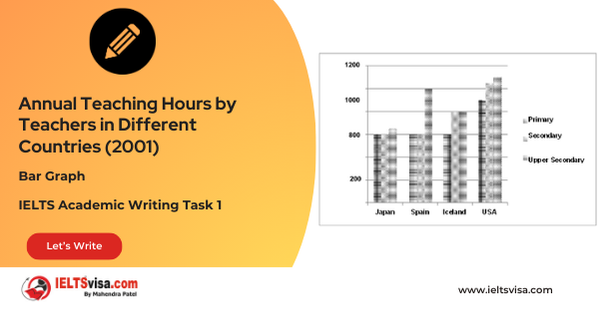
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
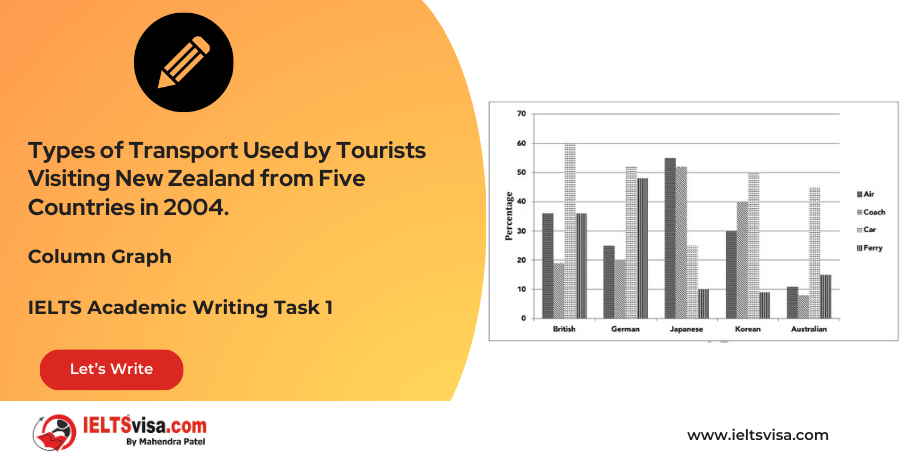
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
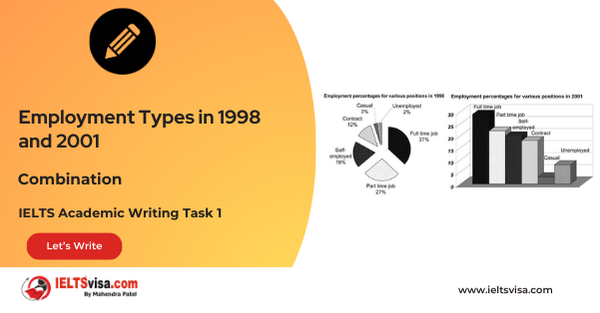
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...