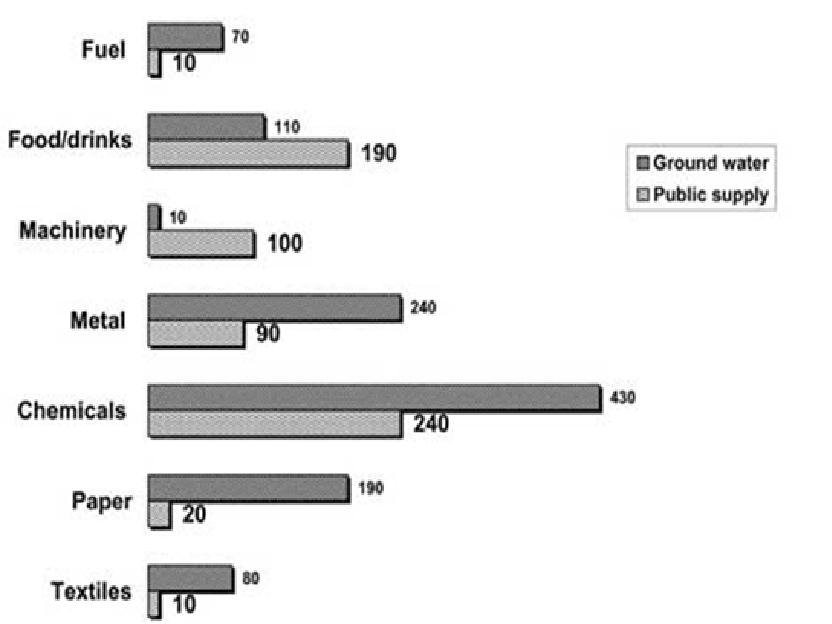
The annual water usage (in millions of cubic metres) by industries in Somecountry.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Bar-Charts

IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The annual water usage (in millions of cubic metres) by industries in Somecountry.
Common Questions for the Bar graph
1.Diagram Type: Bar graph
2. Title: Annual Water Usage by Industries in Somecountry
3. What are the units of measurement? Millions of cubic meters
4. Who: University tutors, environmental scientists, industrial analysts
5. When: Annual data, unspecified year
6. Where: Somecountry
7. Topic: Water usage by industrial sectors
Detailed Process and Observations
Summary of Data : The bar graph compares the annual water usage by different industrial sectors in some countries, measured in millions of cubic meters. Overall, it is clear that the chemical industry consumed the most water from both ground and public supply sources.
- Chemical Industry:
- The chemical sector had the highest water usage, with 430 million cubic meters of groundwater and 240 million cubic meters from public supply.
- Metal Industry:
- The metal industry ranked second in water usage, with 240 million cubic meters of groundwater and 90 million cubic meters from public supply.
- Food and Drinks Industry:
- This sector used considerable water, with 190 million cubic meters from public supply and 110 million from groundwater.
- Paper Industry:
- The paper industry used 190 million cubic meters of groundwater and only 20 million cubic meters from public supply.
- Machinery Sector:
- The machinery sector’s water usage was predominantly from public supply, with 100 million cubic meters and a much smaller amount (10 million) from groundwater.
- Fuel and Textile Industries:
- Both the fuel and textile industries used a small amount of public supply water (10 million cubic meters each), but their groundwater consumption was higher, at 70 million cubic meters for fuel and 80 million cubic meters for textiles.
Sample Answer
The bar graph shows the annual water usage by various industrial sectors in some countries, measured in millions of cubic meters.
Overall, the chemical industry was the largest consumer of both groundwater and public supply, while other industries showed more varied patterns in their water usage.
The chemical sector is led by 430 million cubic meters of groundwater and 240 million cubic meters of water from public supply. The metal industry followed with 240 million cubic meters of groundwater and 90 million from public supply. The food and drinks sector also used significant amounts of public supply water (190 million cubic meters) and slightly less groundwater (110 million cubic meters).
On the other hand, the paper industry’s water usage was more balanced, with 190 million cubic meters of groundwater and just 20 million cubic meters from public supply. The machinery industry used a higher proportion of public supply (100 million cubic meters) compared to groundwater (10 million cubic meters).
The fuel and textile sectors showed the lowest public supply usage (10 million cubic meters), but they relied heavily on ground water, with 70 million cubic meters for fuel and 80 million for textiles.
Top 27 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Verb Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predominantly | Mainly or mostly | Primarily, chiefly | The machinery sector’s water usage was predominantly from public supply. | Adverb |
| Sector | A distinct part of an area of activity or industry | Industry, division | The chemical sector consumed the most water. | Noun |
| Rank | To position in order of importance or size | Stand, place, rate | The metal industry ranked second in water consumption. | Verb |
| Insignificant | Not important or noticeable | Minor, negligible, small | The fuel industry’s use of public supply water was insignificant. | Adjective |
| Consumption | The act of using or consuming something | Use, expenditure, intake | The paper industry had a higher groundwater consumption. | Noun |
| Utilization | The act of using something effectively | Usage, application | The chemical industry had the highest water utilization of all sectors. | Noun |
| Allocation | The process of distributing resources | Distribution, apportionment | The allocation of water to the food and drinks sector was significant. | Noun |
| Proportion | A part or share of the whole | Percentage, fraction | The machinery industry relied on a higher proportion of public supply water. | Noun |
| Balanced | Having equal or fair proportions | Equitable, stable | The paper industry had a more balanced usage of groundwater and public supply water. | Adjective |
| Dominant | Being the most influential or prevalent | Leading, primary | Groundwater was the dominant source for the chemical sector. | Adjective |
| Heavy reliance | Strong dependence on something | Dependence, dependency | The textile sector showed heavy reliance on groundwater. | Noun |
| Significant | Sufficiently large or important | Noteworthy, substantial | The food and drinks industry made significant use of public supply water. | Adjective |
| Varied | Diverse or different in character | Diverse, assorted | Water usage patterns across industries were varied. | Adjective |
| Intake | The amount of something consumed | Consumption, usage | The public supply intake for the machinery sector was higher than its groundwater usage. | Noun |
| Minimal | Very small in amount or degree | Negligible, slight | The fuel industry’s usage of public supply water was minimal. | Adjective |
| Reliance | Dependence on something | Dependence, trust | Fuel and textile sectors had a greater reliance on groundwater. | Noun |
| Sector-specific | Pertaining to a specific sector | Industry-specific, targeted | Water usage varied in sector-specific patterns. | Adjective |
| Predominance | The state of being greater in importance or quantity | Supremacy, dominance | There was a predominance of groundwater usage in most sectors. | Noun |
| Moderate | Average in amount or degree | Reasonable, medium | The food and drinks sector had a moderate use of groundwater. | Adjective |
| Scarcity | The state of being in short supply | Shortage, deficiency | Scarcity of public supply water did not impact the chemical sector’s heavy reliance. | Noun |
| Reservoir | A supply or source of water | Storage, pool | The paper industry drew more from its groundwater reservoir than public supply. | Noun |
| Extraction | The process of obtaining something, especially from a source | Withdrawal, removal | Groundwater extraction was highest in the chemical industry. | Noun |
| Intensity | The degree of strength or force | Strength, magnitude | The intensity of water usage in the chemical sector surpassed other industries. | Noun |
| Comparative | Involving comparison between two or more items | Relative, similar | The comparative water usage in the machinery industry was skewed towards public supply. | Adjective |
| Steady | Regular and unchanging over time | Stable, constant | The steady increase in groundwater usage was evident in all sectors. | Adjective |
| Aggregate | The total amount of something | Total, sum | The aggregate water usage by all industries exceeded expectations. | Noun |
| Dependency | A state of relying on something | Reliance, need | The dependency on groundwater was evident in the textile and fuel sectors. | Noun |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
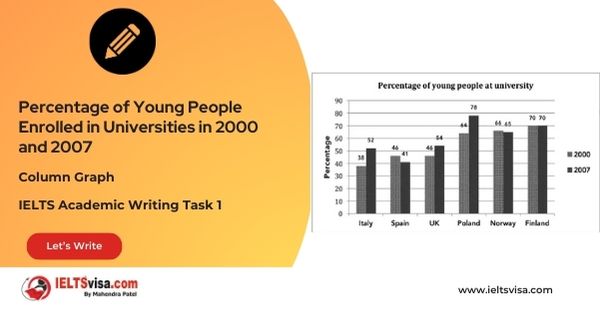
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
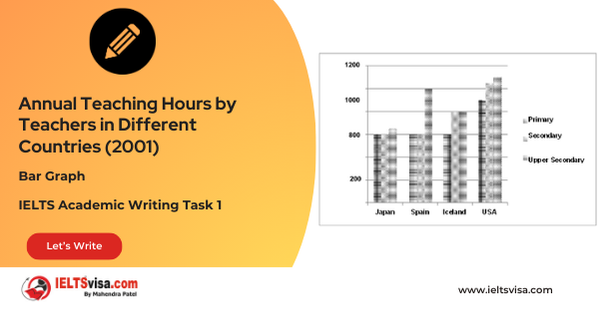
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
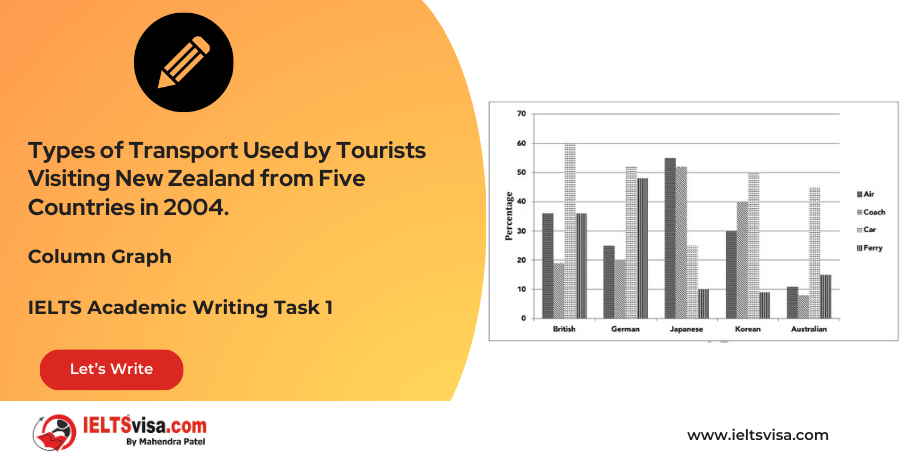
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
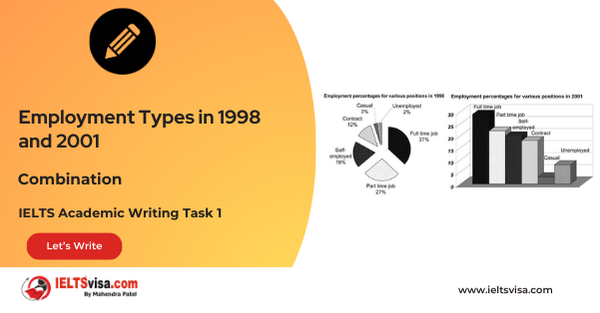
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...