Life Cycle of a Frog
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Flow chart

IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
Life Cycle of a Frog
Common Questions for the Flow chart
1. Graph Type: Flow Chart
2. Title: Life Cycle of a Frog
3. What are the units of measurement? (e.g., percentage, kilogrammes, number of people or periods, amount, %, age, etc.): No specific units; sequential stages of development
4. Who: (e.g., groups, such as three different countries or men or women): Developmental stages of a frog
5. When: (Periods like Jan-Mar or 1999 to 2015): Not specified
6. Where: (Place, e.g., Australia): General (applies to frogs in natural habitats)
7. Topic: The process of frog development from egg to adult
Detailed Process and Observations
Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
- Comparison 1: Initial Stage – Eggs
- Details:
- Frog life cycle starts as eggs, floating as frogspawn on water.
- Comparison 2: Transition from Tadpole to Frog
- Details:
- Tadpoles emerge from eggs with small bodies and long tails.
- Body enlarges and legs start to form over time.
- Transformation into a young frog occurs before maturity is reached.
Sample Answer
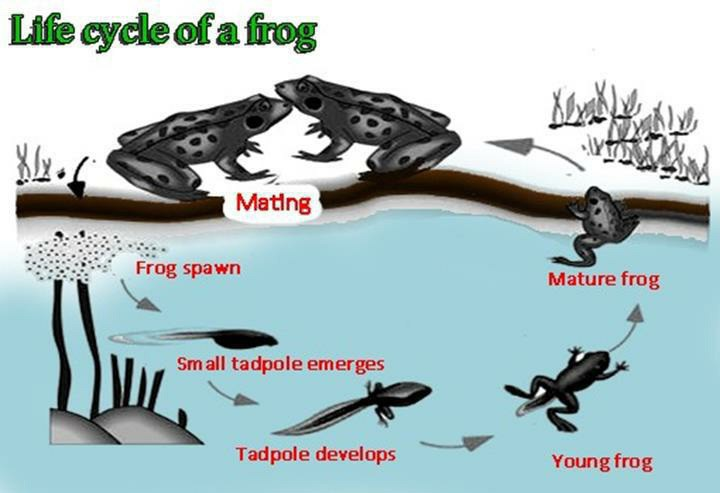
The flowchart illustrates the stages in a frog’s life cycle, beginning with egg production and concluding with a fully mature adult.
Overall, the process comprises six distinct stages, each marking a transition from one life phase to the next. The sequence begins in water with frogspawn, which eventually grows into a mature frog that transitions onto land.
In the first stage, frog eggs, or frogspawn, float on the lake’s surface. Following this, tadpoles emerge as they hatch from the frogspawn. At this stage, tadpoles possess a small body and a long tail, allowing them to move effectively in water. As tadpoles grow, their bodies enlarge, tails lengthen, and legs gradually develop to enable a future terrestrial life.
Subsequently, the tadpole transitions into a young frog. It develops a broader mouth, larger legs, and a shortened tail but continues to live in water. In the final stage, the mature frog moves onto land, begins breathing air, and loses its tail. The adult frog then seeks a mate to lay eggs, thus restarting the cycle.
Top 26 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lifecycle | A sequence of stages in an organism’s life | Life stages, process | “The frog’s lifecycle includes six distinct stages.” | Noun |
| Mature | Fully developed or grown | Fully grown, adult | “The frog reaches a mature stage on land.” | Adjective |
| Tadpole | The larval stage of a frog | Larva, young frog | “The tadpole has a small body with a long tail.” | Noun |
| Emerge | Come into view or become apparent | Appear, develop | “Tadpoles emerge from the eggs in the lake.” | Verb |
| Transition | Movement from one state to another | Change, shift | “The transition to adulthood includes losing the tail.” | Noun |
|
Process |
A series of steps or stages leading to a particular outcome |
Procedure, sequence |
“The process starts with the frogspawn and ends with an adult frog.” |
Noun |
|
Stage |
A phase or step in a sequence of events |
Phase, period |
“There are six stages in the frog’s life cycle.” |
Noun |
|
Float |
To rest or move on the surface of a liquid |
Drift, glide |
“Frog eggs float on the surface of the water.” |
Verb |
|
Egg |
A reproductive body from which an organism develops |
Spawn, ovum |
“Frog eggs hatch into tadpoles after a few days.” |
Noun |
|
Body |
The physical structure of an organism |
Form, shape |
“The tadpole’s body is small and streamlined.” |
Noun |
|
Tail |
A long, flexible part of an organism’s body, often for movement |
Appendage, extension |
“Tadpoles have a long tail to help them swim.” |
Noun |
|
Grow |
To increase in size or develop |
Expand, develop |
“The tadpole grows larger as it develops legs.” |
Verb |
|
Legs |
Limbs used for movement in animals |
Limbs, appendages |
“The tadpole’s legs gradually form, allowing it to move on land.” |
Noun |
|
Enlarge |
To become larger or bigger |
Expand, grow |
“The tadpole’s body enlarges as it matures.” |
Verb |
|
Mouth |
The opening through which food is taken in |
Oral cavity, jaw |
“The young frog develops a wider mouth.” |
Noun |
|
Broaden |
To make something wider or more expansive |
Widen, expand |
“The young frog’s mouth broadens as it matures.” |
Verb |
|
Shorten |
To make something shorter or reduce its length |
Reduce, trim |
“The frog’s tail shortens during its transition into adulthood.” |
Verb |
|
Breathe |
To take in air or oxygen and expel carbon dioxide |
Inhale, respire |
“The mature frog begins to breathe air on land.” |
Verb |
|
Seek |
To attempt to find or look for |
Look for, search for |
“The adult frog seeks a mate to reproduce.” |
Verb |
|
Mate |
To pair with another for reproduction |
Partner, breed |
“The frog mates to continue the lifecycle.” |
Noun/Verb |
|
Lay |
To produce or deposit eggs |
Deposit, produce |
“The female frog lays eggs in water.” |
Verb |
|
Larval |
The early developmental stage of an organism |
Immature, juvenile |
“Tadpoles are in the larval stage of their life cycle.” |
Adjective |
|
Mature |
Fully developed or grown |
Adult, grown-up |
“The frog matures and moves onto land.” |
Verb/Adjective |
|
Cycle |
A series of events that repeat regularly |
Sequence, loop |
“The frog’s life cycle starts with eggs and ends with mating.” |
Noun |
|
Lifeform |
A living organism or being |
Organism, creature |
“The frog undergoes changes throughout its lifeform.” |
Noun |
|
Fully Developed |
Having reached a complete or final form |
Complete, matured |
“The fully developed frog can now live both on land and in water.” |
Adjective |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...