GLASS - Capturing The Dance Of Light Reading Answer
IELTS Academic Reading Passage
A
Glass, in one form or another, has long been in noble service to humans. As one of the most widely used of manufactured materials, and certainly the most versatile, it can be as imposing as a telescope mirror the width of a tennis court or as small and simple as a marble rolling across dirt. The uses of this adaptable material have been broadened dramatically by new technologies glass fibre optics — more than eight million miles — carrying telephone and television signals across nations, glass ceramics serving as the nose cones of missiles and as crowns for teeth; tiny glass beads taking radiation doses inside the body to specific organs, even a new type of glass fashioned of nuclear waste in order to dispose of that unwanted material.
B
On the horizon are optical computers. These could store programs and process information by means of light – pulses from tiny lasers – rather than electrons. And the pulses would travel over glass fibres, not copper wire. These machines could function hundreds of times faster than today’s electronic computers and hold vastly more information. Today fibre optics are used to obtain a clearer image of smaller and smaller objects than ever before – even bacterial viruses. A new generation of optical instruments is emerging that can provide detailed imaging of the inner workings of cells. It is the surge in fibre optic use and in liquid crystal displays that has set the U.S. glass industry (a 16 billion dollar business employing some 150,000 workers) to building new plants to meet demand.
C
But it is not only in technology and commerce that glass has widened its horizons. The use of glass as art, a tradition spins back at least to Roman times, is also booming. Nearly everywhere, it seems, men and women are blowing glass and creating works of art. «I didn’t sell a piece of glass until 1975,» Dale Chihuly said, smiling, for in the 18 years since the end of the dry spell, he has become one of the most financially successful artists of the 20th century. He now has a new commission – a glass sculpture for the headquarters building of a pizza company – for which his fee is half a million dollars.
D
But not all the glass technology that touches our lives is ultra-modern. Consider the simple light bulb; at the turn of the century most light bulbs were hand blown, and the cost of one was equivalent to half a day’s pay for the average worker. In effect, the invention of the ribbon machine by Corning in the 1920s lighted a nation. The price of a bulb plunged. Small wonder that the machine has been called one of the great mechanical achievements of all time. Yet it is very simple: a narrow ribbon of molten glass travels over a moving belt of steel in which there are holes. The glass sags through the holes and into waiting moulds. Puffs of compressed air then shape the glass. In this way, the envelope of a light bulb is made by a single machine at the rate of 66,000 an hour, as compared with 1,200 a day produced by a team of four glassblowers.
E
The secret of the versatility of glass lies in its interior structure. Although it is rigid, and thus like a solid, the atoms are arranged in a random disordered fashion, characteristic of a liquid. In the melting process, the atoms in the raw materials are disturbed from their normal position in the molecular structure; before they can find their way back to crystalline arrangements the glass cools. This looseness in molecular structure gives the material what engineers call tremendous “formability” which allows technicians to tailor glass to whatever they need.
F
Today, scientists continue to experiment with new glass mixtures and building designers test their imaginations with applications of special types of glass. A London architect, Mike Davies, sees even more dramatic buildings using molecular chemistry. “Glass is the great building material of the future, the «dynamic skin»,’ he said. “Think of glass that has been treated to react to electric currents going through it, glass that will change from clear to opaque at the push of a button, that gives you instant curtains. Think of how the tall buildings in New York could perform a symphony of colours as the glass in them is made to change colours instantly.” Glass as instant curtains is available now, but the cost is exorbitant. As for the glass changing colours instantly, that may come true. Mike Davies’s vision may indeed be on the way to fulfilment.
Questions 1-5
Reading Passage has six paragraphs (A-F).
Choose the most suitable heading/or each paragraph from the list of headings below. Write the appropriate numbers (i-x) in boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet.
Paragraph A has been done for you as an example.
NB There are more headings than paragraphs so you will not use all of them.
You may use any heading more at once.
|
Example |
Answer |
|
Paragraph A |
x |
List of Headings
i Growth in the market for glass crafts
ii Computers and their dependence on glass
iii What makes glass so adaptable
iv Historical development of glass
v Scientists’ dreams cost millions
vi Architectural experiments with glass
vii Glass art galleries flourish
viii Exciting innovations in fibre optics
ix A former glass technology
x Everyday uses of glass
1 Paragraph B
2 Paragraph C
3 Paragraph D
4 Paragraph E
5 Paragraph F
Questions 6-8
The diagram below shows the principle of Coming’s ribbon machine.
Label the diagram by selecting NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the Reading Passage to fill each numbered space.
Write your answers in boxes 6-8 on your answer sheet.
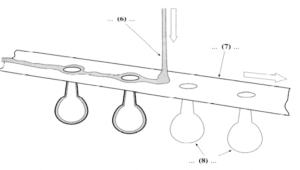
6___________________
7 ___________________
8 ___________________
Questions 9-13
Look at the list below of the uses of glass.
According to the passage, state whether these uses exist today, will exist in the future or are not mentioned by the writer.
In boxes 9-13 write
A if the uses exist today
B if the uses will exist in the future
C if the uses are not mentioned by the writer
9 dental fittings
10 optical computers
11 sculptures
12 fashions
13 curtains

Solution for: GLASS – Capturing The Dance Of Light Reading Answer
| 1. viii | 8. (lightbulb) moulds |
| 2. i | 9. A |
| 3. ix | 10. B |
| 4. iii | 11. A |
| 5. vi | 12. C |
| 6. molten glass//ribbon of glass//molten glass ribbon | 13. A |
| 7. belt of steel//steel belt//moving belt |
Review and Practice
- Regularly practice with IELTS reading samples and time yourself to get used to the pressure of the exam.
- Review your mistakes to understand where you went wrong and how to avoid similar errors in the future.
Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
GLASS - Capturing The Dance Of Light Reading Answer Explanation
Comin Soon
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Becoming An Expert Reading Answer
A Expertise is commitment coupled with creativity. Specifically, it is the commitment of...
STUDY CENTRE COURSES Reading Answer
SELF-STUDY TIPS AHowever difficult you find it to arrange your time, it will pay off in the...
The Extrinct Grass In Britain Reading Answer
A The British grass interrupted brome was said to be extinct, just like the Dodo. Called...
Morse Code Reading Answer
A. A new satellite-based system is being implemented to replace Morse code for sending...
Magnetic Therapy Reading Answer
AMagnetic therapy, which is a $5-billion market worldwide, is a form of alternative medicine...
Lack Of Sleep Reading Answer
Section A It is estimated that the average man or woman needs between seven-and-a-half and...