Average Ticket Prices and Percentage of Tickets Sold at a Theatre (2010-2011)
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Combination: Line graph and bar chart
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
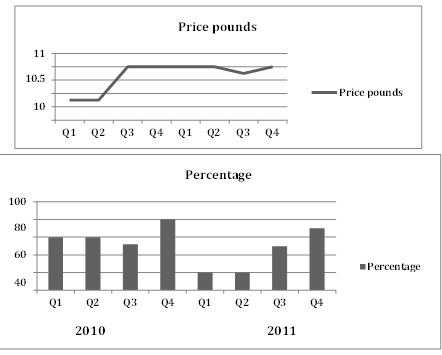
The line graph shows the average prices of tickets sold at a theatre, and the bar chart shows the average percentage of tickets sold in 2010 and 2011.
Common Questions for the Ticket Price and Sales Graphs
1. Graph Types: Line graph and bar chart
2. Title: Average Ticket Prices and Percentage of Tickets Sold at a Theatre (2010-2011)
3. What are the units of measurement ? : Price (GBP), percentage (%)
4. Who: Theatre attendees
5. When: Quarterly data for 2010 and 2011
6. Where: A theatre (unspecified location)
7. Topic: Ticket pricing and sales performance
Process Showing and Trends
Comparison 1: Average Ticket Prices
Details:
- Price Stability:
-
- Q1 and Q2 2010: £9.25
- Q3 2010: £10.50 (sharp increase)
- Q4 2010 to Q2 2011: £10.50 (stable)
- Q3 2011: £10.25 (slight decrease)
- Q4 2011: £10.50 (increase again)
Comparison 2 : Percentage of Tickets Sold
- Details:
1. Sales Performance:
- Q1 and Q2 2010: 60%
- Q3 2010: 50% (slight decline despite price increase)
- Q4 2010: 80% (highest percentage)
- Q1 and Q2 2011: Lowest sales (unspecified percentage)
- Q4 2011: 70% (recovery in sales)
Overall Comparison
-
Details:
1. Ticket prices showed an initial stability, followed by a significant increase in Q3 2010. Despite this increase, ticket sales experienced only a slight drop, indicating potential resilience among customers.
2. The highest ticket sales occurred in Q4 2010, even as prices were at their peak, suggesting a strong demand.
3. Sales dipped in early 2011 but rebounded by Q4, reflecting consumer adjustment to pricing changes.
Sample Answer
The line graph and bar chart present a comparative analysis of average ticket prices and the percentage of tickets sold at a theatre during 2010 and 2011.
The line graph indicates that average ticket prices were stable at £9.25 for the first two quarters of 2010. However, there was a significant price hike in the third quarter, where the average ticket price rose sharply to £10.50. This price level remained unchanged until the second quarter of 2011 when it slightly dipped to £10.25 before rising again to £10.50 by the end of 2011.
In contrast, the bar chart illustrates ticket sales performance, showing that 60% of tickets were sold in both the first and second quarters of 2010. Interestingly, despite the sharp increase in prices during Q3 2010, ticket sales experienced only a minor decline to 50%. The fourth quarter of 2010 saw the highest sales percentage at 80%, indicating strong demand even at elevated prices. In 2011, the percentage of tickets sold fell in the first half but showed improvement by the end of the year, reaching 70% in Q4.
Overall, the data suggests that while ticket prices experienced fluctuations, ticket demand remained relatively robust, with significant sales peaks despite rising costs.
Top 28 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary (type) | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
|
Fluctuations (noun) |
Variations or changes over time |
Oscillations, changes |
“Ticket prices saw fluctuations throughout the year.” |
|
Resilience (noun) |
The ability to recover quickly from difficulties |
Flexibility, adaptability |
“The audience showed resilience in ticket purchases.” |
|
Demand (noun) |
The desire of consumers to purchase goods |
Need, requirement |
“There was a strong demand for tickets in Q4 2010.” |
|
Stability (noun) |
The condition of being steady or unchanging |
Consistency, steadiness |
“Prices showed stability in the early quarters.” |
|
Recovery (noun) |
The process of regaining strength or success |
Comeback, improvement |
“Ticket sales experienced a recovery by the end of 2011.” |
|
Comparative (adj.) |
Relating to the comparison of things |
Relative, measured |
“The report provides a comparative analysis of ticket prices.” |
|
Indicate (verb) |
To show or point out |
Demonstrate, reveal |
“The graph indicates a sharp rise in ticket prices.” |
|
Stable (adj.) |
Not changing or fluctuating |
Steady, constant |
“Ticket prices remained stable for the first two quarters.” |
|
Significant (adj.) |
Important or noticeable |
Substantial, considerable |
“There was a significant increase in prices in Q3 2010.” |
|
Hike (noun/verb) |
A sudden increase in value or price |
Surge, rise |
“A sharp price hike was observed in the third quarter.” |
|
Sharp (adj.) |
Sudden and intense |
Steep, abrupt |
“The graph shows a sharp increase in ticket prices.” |
|
Dip (noun/verb) |
A slight decrease |
Drop, decline |
“Ticket prices experienced a minor dip in Q2 2011.” |
|
Illustrate (verb) |
To visually demonstrate or explain something |
Depict, show |
“The bar chart illustrates the percentage of ticket sales.” |
|
Performance (noun) |
The effectiveness or success of something |
Outcome, result |
“Ticket sales performance varied across quarters.” |
|
Minor (adj.) |
Small or insignificant |
Slight, negligible |
“Despite the price hike, there was only a minor decline in sales.” |
|
Elevated (adj.) |
Increased or raised |
Higher, boosted |
“Sales remained strong even at elevated prices.” |
|
Quarter (noun) |
A three-month period in a financial year |
Term, period |
“The first two quarters showed stable ticket prices.” |
|
Percentage (noun) |
A proportion or fraction expressed as part of 100 |
Ratio, fraction |
“The percentage of tickets sold varied between 50% and 80%.” |
|
Decline (noun/verb) |
A reduction or downward trend |
Decrease, drop |
“Ticket sales saw a slight decline in Q3 2010.” |
|
Peak (noun/verb) |
The highest level or point |
High point, climax |
“Ticket sales peaked at 80% in Q4 2010.” |
|
Contrast (noun/verb) |
A noticeable difference |
Distinction, variation |
“In contrast to price trends, ticket sales showed fluctuations.” |
|
Robust (adj.) |
Strong and resilient |
Sturdy, solid |
“Despite price increases, demand remained robust.” |
|
Consumption (noun) |
The act of using or purchasing something |
Usage, expenditure |
“Ticket consumption patterns varied across the year.” |
|
Revenue (noun) |
Income generated from sales |
Earnings, turnover |
“Higher ticket prices led to increased revenue.” |
|
Consistent (adj.) |
Showing little variation |
Steady, uniform |
“Ticket demand remained fairly consistent despite price changes.” |
|
Unchanged (adj.) |
Remaining the same |
Stable, constant |
“The price remained unchanged for two quarters.” |
|
Reflect (verb) |
To show or demonstrate a particular situation |
Indicate, reveal |
“The graph reflects changes in ticket pricing trends.” |
|
Surge (noun/verb) |
A sudden and large increase |
Jump, spike |
“There was a surge in ticket sales during Q4 2010.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Percentage of UK Households with Selected Consumer Durables (1998–2005).
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – The process of canning of fish.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – The life cycle of the salmon
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Methods of Waste Disposal in Four Countries
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Combination : Bar Graph – Employment Rates of Men and Women Aged 60-64 in Four Countries (1970 and 2000)
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Table – The information about medical care in three European countries between 1980 and 2000
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...