How drinking water is made using solar power
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Process Diagram
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The process below shows how drinking water is made using solar power. Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information given below
Common Questions for the Process Diagram
1. Graph Type: Process Diagram
2. Title: Process of Making Drinking Water Using Solar Power
3. What are the units of measurement?: Not applicable
4. Who: The process of making drinking water
5. When: Not specified
6. Where: Not specified
7. Topic: Steps involved in purifying underground water using solar energy Comparison Showing and Trends
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Comparison 1 : Steps in the Process
- Details:
1. Solar Panel Function: Heat from the sun is collected and converted to electricity.
2. Pumping Water: Electricity powers a pump that extracts underground water.
3. Filtration: Water is filtered before storage.
4. Storage: Clean water is stored in a tank with a tap for access.
Comparison 2 : Overall Efficiency
- Details
1. Renewable Energy Source: Utilization of solar energy for water purification.
2. Accessibility: Safe drinking water is made available through an outlet tap.
3. Sustainability: The process promotes the use of renewable resources.
Sample Answer
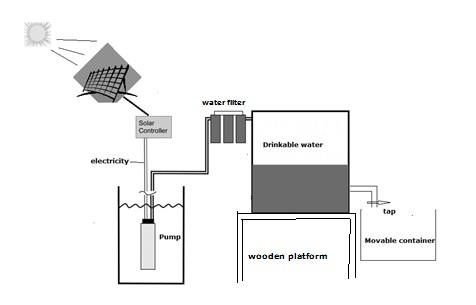
The process diagram illustrates how drinking water is produced using solar power, detailing the steps involved in extracting and purifying underground water. The entire procedure consists of four main stages.
Initially, solar panels collect heat from the sun, which is then converted into electricity. This generated electricity powers a pump that extracts water from underground sources. Following this extraction, the water is passed through a filtration system to remove impurities, ensuring its safety for consumption.
Once filtered, the clean water is stored in a large tank situated on a wooden platform. At the bottom of this tank, an outlet pipe with a tap allows users to dispense potable water into movable containers as needed. This design facilitates easy access to safe drinking water.
Overall, the process effectively demonstrates how renewable solar energy can be harnessed to extract, filter, and store underground water, transforming it into safe drinking water while promoting sustainability and accessibility.
Top 27 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary (type) | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
| Illustrate (verb) | To explain or make something clear by using examples | Show, demonstrate | “The diagram illustrates the process.” |
| Extract (verb) | To remove or take out from a source | Remove, withdraw | “Water is extracted from underground sources.” |
| Purification (noun) | The process of making something clean or safe | Filtration, cleansing | “Purification ensures the water is safe to drink.” |
| Storage (noun) | The action or method of keeping something for future use | Holding, reserving | “The tank is used for storage.” |
| Potable (adj) | Safe to drink; drinkable | Drinkable, safe | “The water is treated to make it potable.” |
|
Harness (verb) |
To utilize or make use of a resource effectively |
Utilize, exploit |
“Solar energy is harnessed to power the process.” |
|
Renewable (adj) |
Capable of being replenished naturally |
Sustainable, inexhaustible |
“The process relies on renewable energy sources.” |
|
Procedure (noun) |
A set of actions conducted in a specific order |
Process, method |
“The procedure involves four main stages.” |
|
Generate (verb) |
To produce or create something |
Produce, create |
“Electricity is generated by the solar panels.” |
|
Filtration (noun) |
The act of removing impurities from a substance |
Straining, purification |
“Filtration removes impurities from the extracted water.” |
|
Impurities (noun) |
Unwanted substances or contaminants |
Contaminants, pollutants |
“Impurities are removed during the filtration process.” |
|
Platform (noun) |
A raised flat surface used to support something |
Stage, base |
“The water tank is placed on a wooden platform.” |
|
Outlet (noun) |
A pipe or opening for releasing or dispensing a substance |
Exit, opening |
“An outlet pipe with a tap is used to dispense water.” |
|
Dispense (verb) |
To distribute or provide to users |
Distribute, allocate |
“The tap dispenses potable water.” |
|
Consumption (noun) |
The act of using something, particularly for eating or drinking |
Usage, intake |
“The filtered water is safe for human consumption.” |
|
Accessible (adj) |
Easy to reach or use |
Reachable, available |
“The design makes water accessible to users.” |
|
Transform (verb) |
To change the form or function of something |
Convert, alter |
“Underground water is transformed into safe drinking water.” |
|
Stage (noun) |
A step in a process or development |
Phase, level |
“The procedure is divided into four main stages.” |
|
Sustainability (noun) |
The ability to maintain a process or resource over time |
Durability, viability |
“This system promotes sustainability by using renewable energy.” |
|
Extraction (noun) |
The act of taking something out, especially with effort |
Removal, withdrawal |
“Water extraction is powered by electricity generated from solar panels.” |
|
Safe (adj) |
Free from harm or risk |
Secure, harmless |
“The water is filtered to ensure it is safe for drinking.” |
|
Convert (verb) |
To change into a different form |
Transform, alter |
“Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity.” |
|
Underground (adj) |
Located below the surface of the earth |
Subterranean, buried |
“Water is extracted from underground sources.” |
|
Purify (verb) |
To make something clean and free from contaminants |
Cleanse, sanitize |
“The water is purified through filtration.” |
|
Sustain (verb) |
To maintain or continue a process |
Support, uphold |
“The system is designed to sustain access to clean water.” |
|
Efficiency (noun) |
The ability to accomplish a task with minimal waste or effort |
Productivity, efficacy |
“The procedure showcases the efficiency of solar-powered systems.” |
|
Design (noun) |
A plan or arrangement for how something will be created or used |
Layout, blueprint |
“The design of the water tank facilitates easy access.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
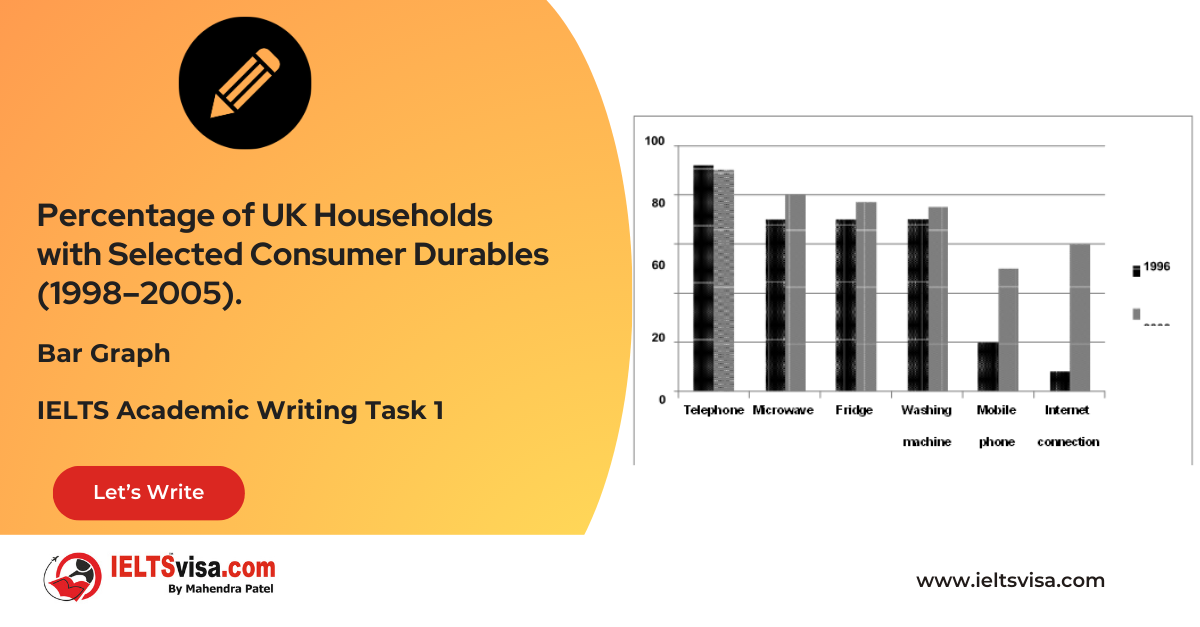
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Percentage of UK Households with Selected Consumer Durables (1998–2005).
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
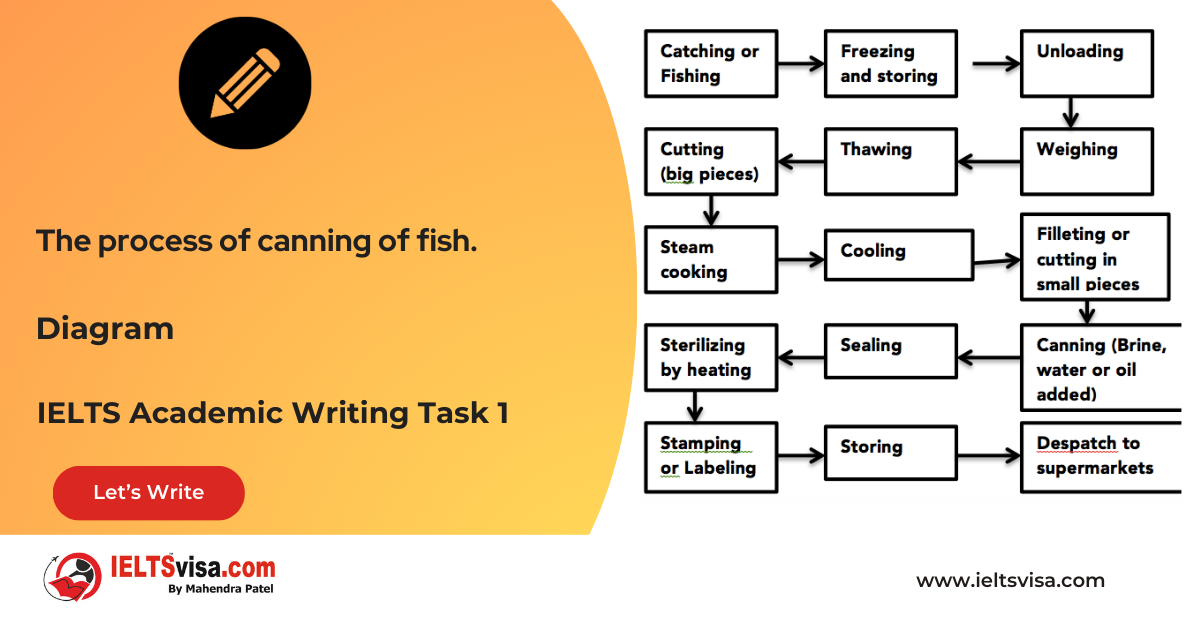
Task 1 – Diagram – The process of canning of fish.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
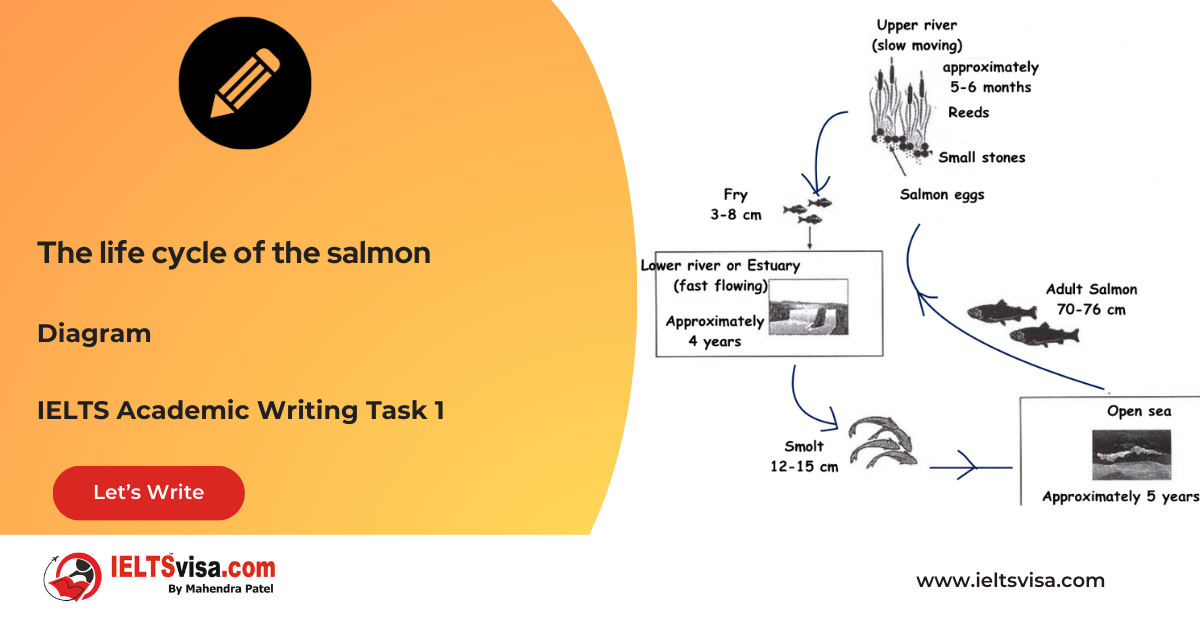
Task 1 – Diagram – The life cycle of the salmon
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
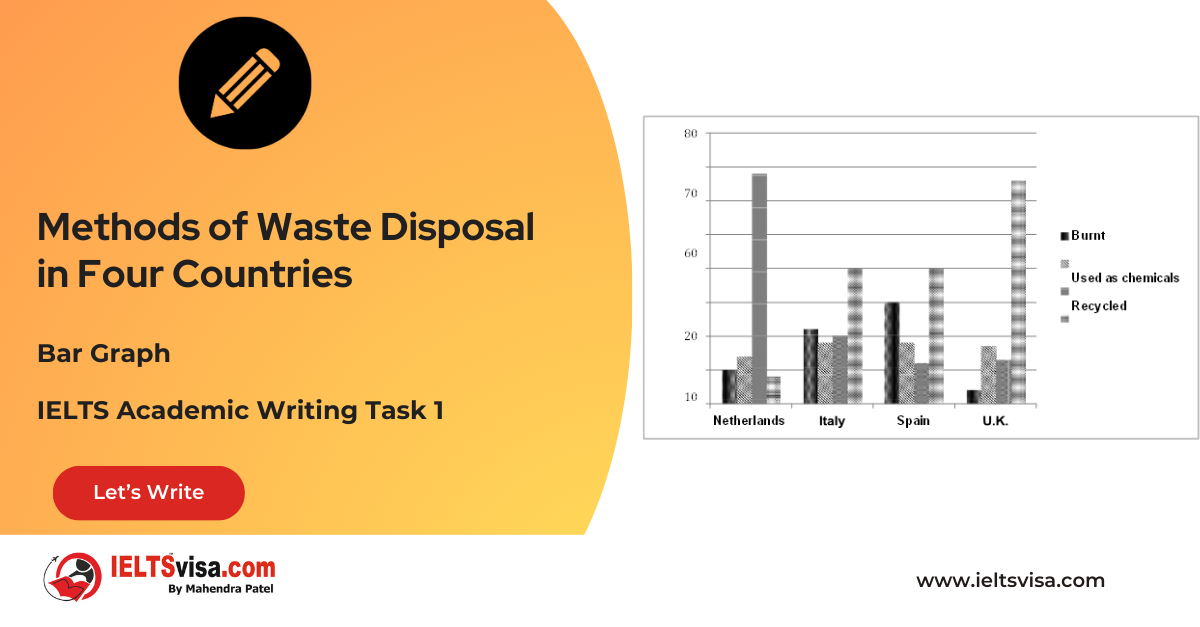
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Methods of Waste Disposal in Four Countries
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Combination : Bar Graph – Employment Rates of Men and Women Aged 60-64 in Four Countries (1970 and 2000)
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Table – The information about medical care in three European countries between 1980 and 2000
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...