The water supply system in Australia at present and in future
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Diagrams
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The diagrams below show the water supply system in Australia at present and in future. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features.

Common Questions for the Water Supply System Diagrams
1. Graph Type: Diagrams
2. Title: Current and Future Water Supply System in Australia
3. What are the units of measurement?: Not applicable
4. Who: Residents and industries in Australia
5. When: Present and future
6. Where: Australia
7. Topic: Water supply and recycling system Comparison Showing and Trends
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Comparison 1 : Current Water Supply System
- Details:
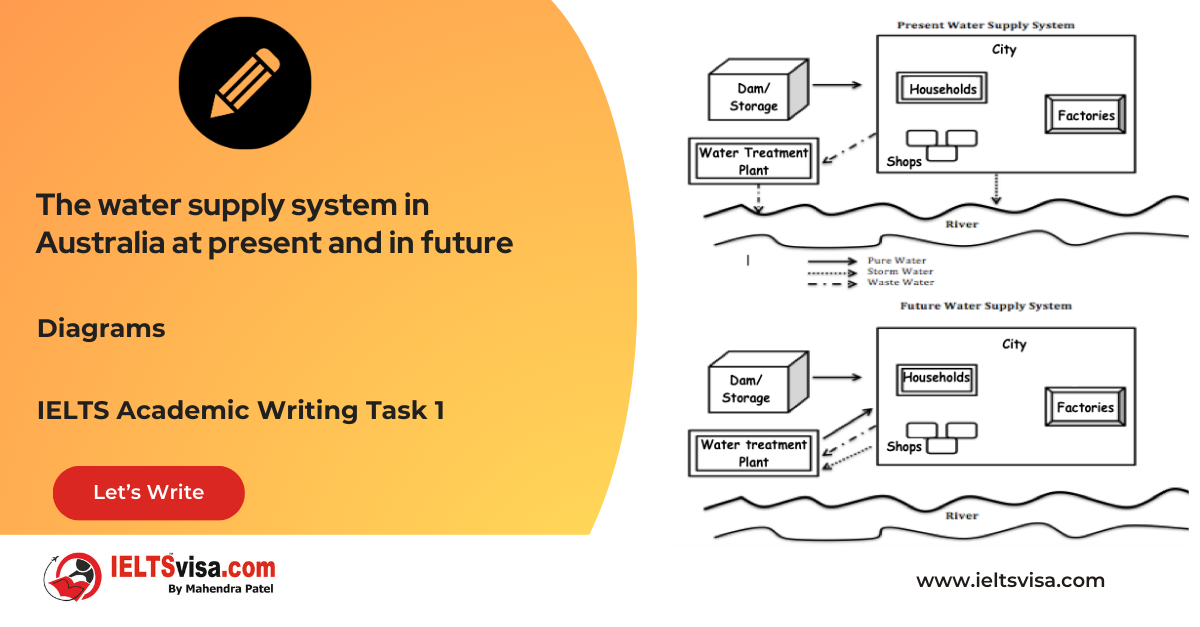
1. Source: Pure water is supplied from a dam to households, factories, and shops.
2. Storm Water Management: Currently, stormwater is released into the river.
3. Wastewater Treatment: Wastewater is sent to a treatment plant and then released into the river.
Comparison 2 : Future Water Supply System
- Details:
1. Continued Supply: Pure water will still be sourced from the dam.
2. Storm Water and Wastewater Management: Both stormwater and wastewater will be directed to the treatment plant instead of being released into the river.
3. Recycling Process: Treated water will be sent back to the city for use, ensuring no water is discharged into the river.
Sample Answer
The diagrams illustrate Australia’s current and future water supply systems, highlighting proposed changes aimed at improving water recycling and eliminating river discharge.
The water supply system in Australia draws pure water from a dam, which is then distributed to households, factories, and shops. Currently, stormwater is released into the river, while the wastewater generated by the city is directed to a water treatment plant. After treatment, the wastewater is also released into the river.
In contrast, the future water supply system maintains the same source of pure water from the dam but introduces significant changes in stormwater and wastewater management. Instead of being released into the river, stormwater and wastewater from various sources will be transported to the treatment plant. After undergoing treatment, this water will be returned to the city for reuse, preventing any river discharge.
Overall, the proposed changes to Australia’s water supply system emphasize enhanced recycling practices, ensuring sustainability while protecting the river ecosystem from wastewater release.
Top 28 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary (type) | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
| Illustrate (verb) | To explain or demonstrate something clearly | Show, depict | “The diagrams illustrate the water supply system.” |
| Supply (noun) | The provision of something needed | Provision, delivery | “The city receives its water supply from a dam.” |
| Discharge (verb) | To release or emit something | Release, expel | “Currently, storm water is discharged into the river.” |
| Treatment (noun) | The act of treating a substance or condition | Processing, handling | “Wastewater undergoes treatment before disposal.” |
| Recycling (noun) | The process of converting waste into reusable material | Reprocessing, recovery | “The future system focuses on better recycling of water.” |
| Ecosystem (noun) | A biological community of interacting organisms and their environment | Environment, biosphere | “The changes aim to protect the river ecosystem from pollution.” |
| Proposed (adj) | Suggested or planned but not yet implemented | Suggested, recommended | “The proposed changes focus on water recycling.” |
| Management (noun) | The process of dealing with or controlling things or people | Administration, handling | “Effective water management is crucial for sustainability.” |
| Generate (verb) | To produce or create something | Create, produce | “Wastewater is generated by households and industries.” |
| Reuse (verb) | To use something again | Repurpose, recycle | “Treated water will be reused in the future system.” |
| Eliminate (verb) | To remove or get rid of something | Remove, eradicate | “The new system aims to eliminate river discharge.” |
| Distribute (verb) | To share or spread something across a wide area | Allocate, supply | “Water is distributed to various parts of the city.” |
| Enhance (verb) | To improve the quality or value of something | Improve, boost | “The proposed system enhances recycling practices.” |
| Stormwater (noun) | Rainwater that runs off streets, rooftops, and other surfaces | Rainwater runoff | “Stormwater will no longer be discharged into the river.” |
| Prevent (verb) | To stop something from happening | Avoid, prohibit | “The changes prevent wastewater from polluting the river.” |
| Sustainability (noun) | The ability to maintain or preserve resources | Conservation, endurance | “The system ensures sustainability by recycling water.” |
| Infrastructure (noun) | The basic facilities and systems needed for a community | Framework, facilities | “Australia’s water infrastructure is undergoing significant changes.” |
| Draw (verb) | To pull or take something from a source | Extract, take | “Water is drawn from a dam as the primary source.” |
| Transport (verb) | To carry or move something from one place to another | Convey, deliver | “Stormwater is transported to the treatment plant.” |
| Ensure (verb) | To make certain that something happens | Guarantee, secure | “The changes ensure better water recycling.” |
| Emission (noun) | The act of releasing something into the environment | Release, discharge | “Reducing water emissions into the river is a priority.” |
| Focus (verb) | To concentrate attention on something | Emphasize, highlight | “The future system focuses on sustainability.” |
| Reuse (noun) | The act of using something again | Repurposing, recycling | “Water reuse is central to the new system.” |
| Treatment plant (noun) | A facility where substances are cleaned or processed | Processing facility | “The treatment plant handles both stormwater and wastewater.” |
| Sustain (verb) | To maintain or continue over time | Maintain, uphold | “The system is designed to sustain water resources for future generations.” |
| Preventive (adj) | Intended to stop something from happening | Protective, preemptive | “Preventive measures ensure no wastewater is discharged into the river.” |
| Redirect (verb) | To change the course or direction of something | Divert, reroute | “Stormwater will be redirected to the treatment plant.” |
| Efficient (adj) | Achieving maximum productivity with minimal wasted effort | Effective, streamlined | “The system ensures efficient recycling of water.” |
| Cycle (noun) | A series of events that repeat in a specific order | Loop, sequence | “The water recycling process follows a continuous cycle.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
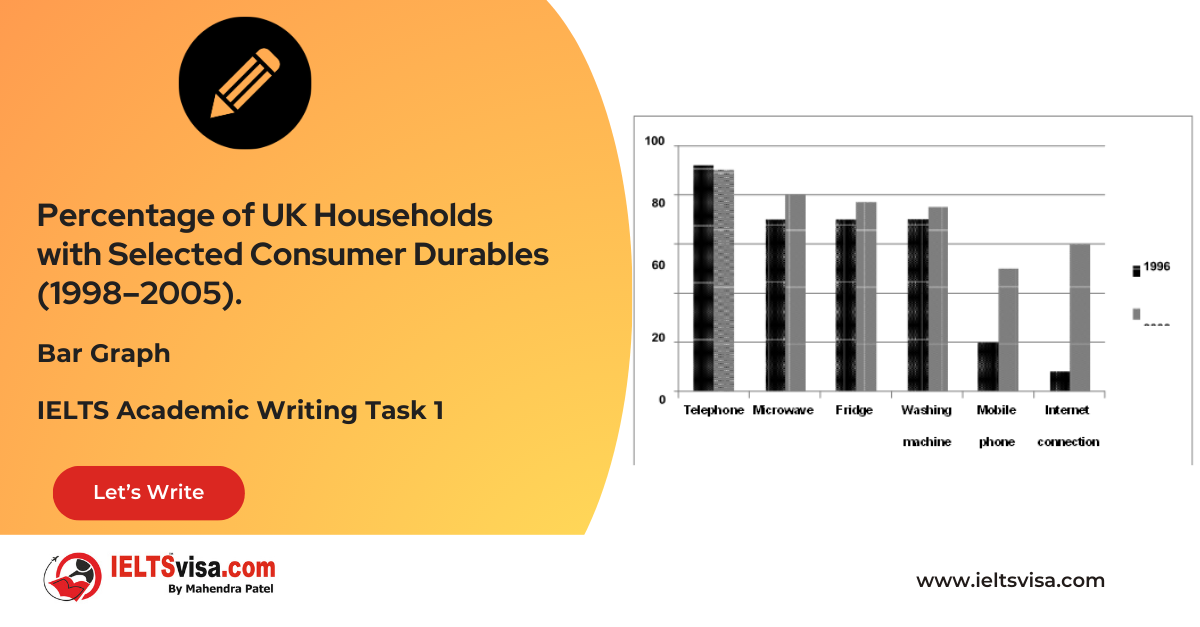
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Percentage of UK Households with Selected Consumer Durables (1998–2005).
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
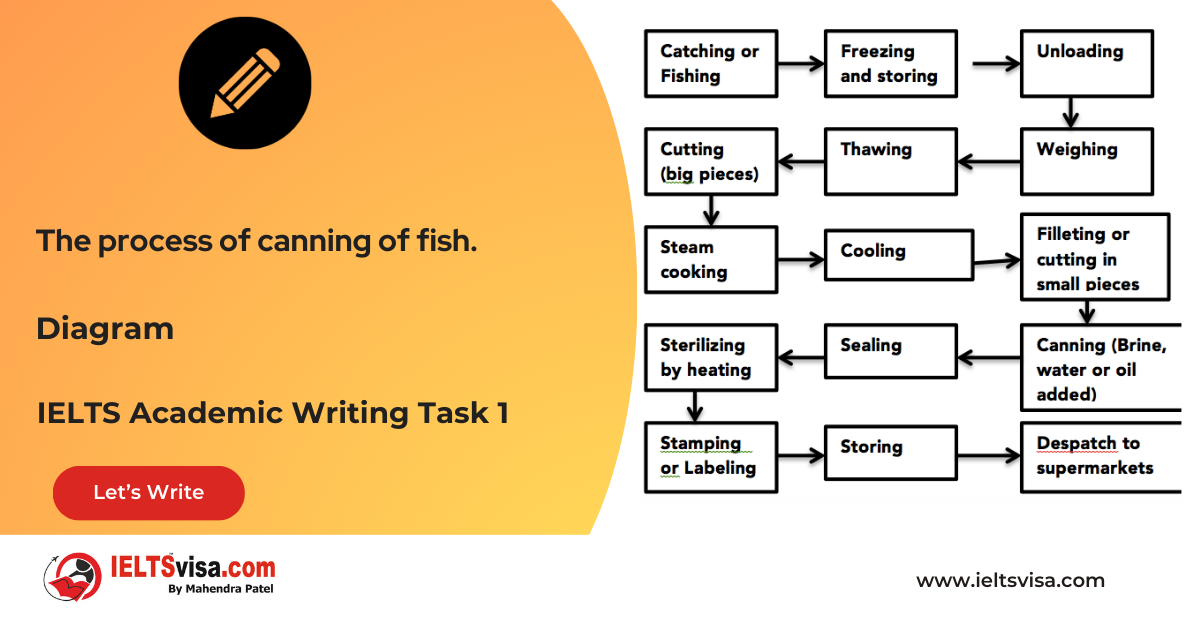
Task 1 – Diagram – The process of canning of fish.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
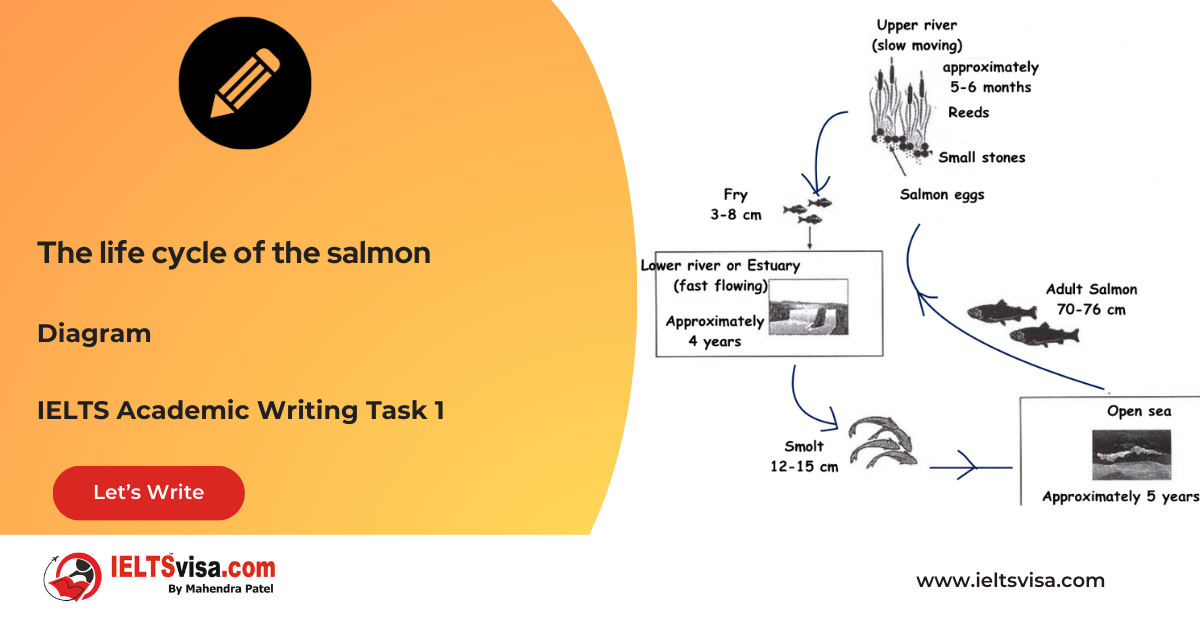
Task 1 – Diagram – The life cycle of the salmon
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
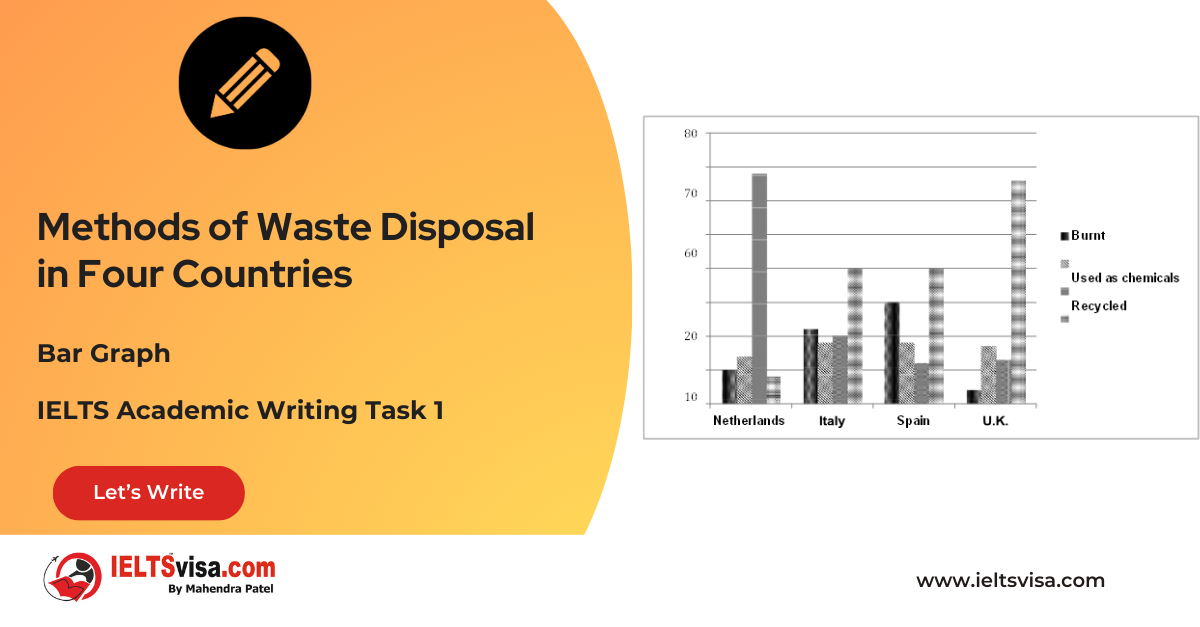
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Methods of Waste Disposal in Four Countries
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Combination : Bar Graph – Employment Rates of Men and Women Aged 60-64 in Four Countries (1970 and 2000)
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Table – The information about medical care in three European countries between 1980 and 2000
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...