The percentage of young people who were employed in different sectors in one country in 2005 and 2010
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Tables
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
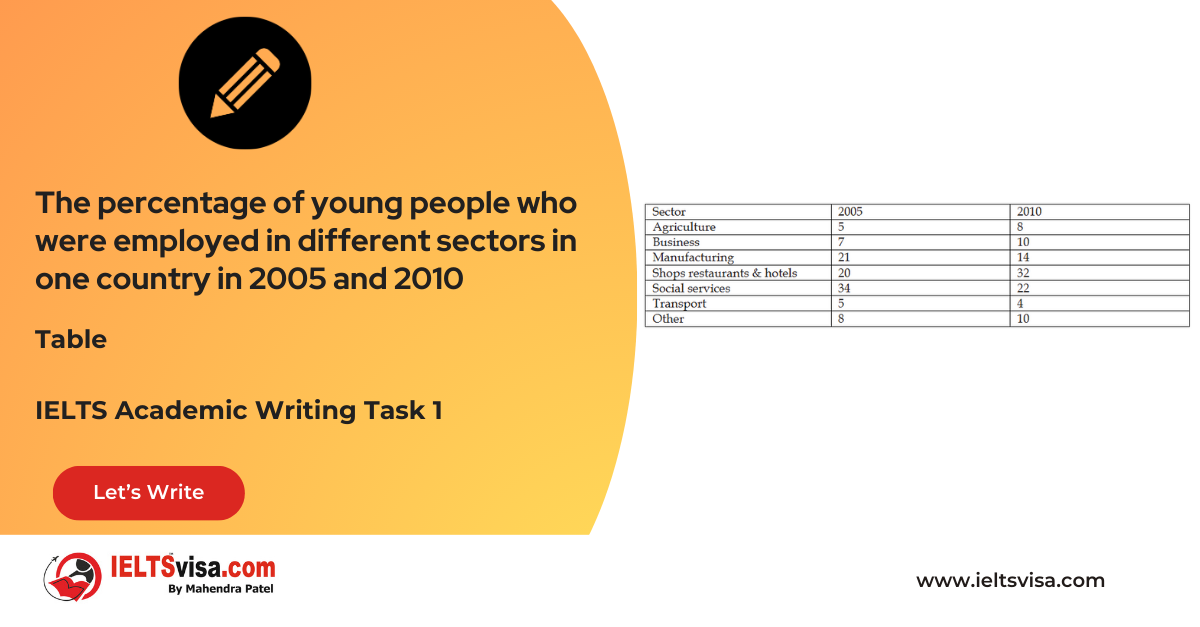
The table shows the percentage of young people who were employed in different sectors in one country in 2005 and 2010. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.

Common Questions for the Table
1. Graph Type: Table
2. Title: Employment of Young People by Sector (2005 and 2010)
3. What are the units of measurement?: Percentage (%)
4. Who: Young employees in a country
5. When: Years 2005 and 2010
6. Where: A specific country
7. Topic: Trends in employment sectors for young people
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
Comparison 1: Employment in Agriculture and Transport
- Details:
- Both sectors employed 5% of young people in 2005. In 2010, employment in agriculture increased to 8%, while transport decreased to 4%, indicating a shift in preferences.
Comparison 2 : Employment in Manufacturing vs. Shops, Restaurants, and Hotels
- Details:
- In 2005, manufacturing employed 21% and shops, restaurants, and hotels employed 20%. By 2010, employment in manufacturing dropped to 14%, while shops, restaurants, and hotels saw a rise to 32%, making it the most popular sector for young employees.
Comparison 2 : Social Services and Business Sector Employment
- Details:
- Social services was the most popular sector in 2005 with 34% but fell to 22% in 2010. In contrast, business and other sectors saw a stable employment rate of 7-8% in 2005, increasing to 10% in 2010.
Sample Answer
The table presents data on the percentage of young people employed in various sectors in a specific country for the years 2005 and 2010. Notably, there were changes in the popularity of different sectors during this period.
Agriculture and transport were the least popular sectors, with both employing only 5% of young people in 2005. By 2010, employment in agriculture rose to 8%, while transport decreased to 4%. Young employment was nearly equal in the manufacturing and the hospitality sector in 2005, with 21% and 20%, respectively. However, by 2010, manufacturing saw a decline to 14%, while the hospitality sector surged to 32%, becoming the most sought-after employment option.
Social services was the most favored sector in 2005, employing 34% of young people, but this figure dropped to 22% in 2010. Conversely, the business sector maintained a stable employment rate, increasing from 7-8% in 2005 to 10% in 2010.
Overall, while transport, manufacturing, and social services saw decreased employment rates, sectors like agriculture and hospitality experienced growth in youth employment.
Top 26 Vocabulary
| Vocabulary (type) | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
| Employed (v.) | Having a job or being engaged in work | Hired, occupied | “Only 5% of young people were employed in agriculture.” |
| Sector (n.) | A distinct part of an area of economic or social activity | Industry, field | “The hospitality sector became the most popular choice.” |
| Decline (v.) | To decrease in quality, quantity, or strength | Diminish, reduce | “Employment in social services declined from 34% to 22%.” |
| Surge (v.) | To rise suddenly and powerfully | Increase, spike | “The hospitality sector surged to 32% in 2010.” |
| Percentage (n.) | A rate, number, or amount in each hundred | Proportion, fraction | “The percentage of young employees in manufacturing fell.” |
|
Data (n.) |
Facts and statistics collected for reference |
Information, statistics |
“The table presents data on employment trends.” |
|
Popularity (n.) |
The state of being liked or favored |
Appeal, favor |
“The popularity of hospitality increased in 2010.” |
|
Least (adj.) |
The smallest amount, degree, or extent |
Minimum, lowest |
“Transport was the least popular sector in 2005.” |
|
Rose (v.) |
To increase or move upward |
Increased, climbed |
“Employment in agriculture rose to 8% in 2010.” |
|
Decreased (v.) |
To become smaller in quantity or intensity |
Reduced, declined |
“Transport employment decreased to 4%.” |
|
Equal (adj.) |
Being the same in amount or degree |
Equivalent, identical |
“Young employment was nearly equal in two sectors.” |
|
Favored (adj.) |
Preferred or chosen above others |
Preferred, popular |
“Social services was the most favored sector.” |
|
Specific (adj.) |
Clearly defined or identified |
Particular, precise |
“The data covers a specific country.” |
|
Stable (adj.) |
Not likely to change or fluctuate |
Steady, consistent |
“The business sector maintained a stable rate.” |
|
Increase (n.) |
A rise in quantity, number, or value |
Growth, rise |
“The business sector showed an increase in employment.” |
|
Trends (n.) |
General directions in which something is changing |
Patterns, movements |
“Employment trends varied across sectors.” |
|
Sought-after (adj.) |
Highly desired or in demand |
Popular, desirable |
“Hospitality became the most sought-after option.” |
|
Maintain (v.) |
To continue or preserve a certain state |
Preserve, uphold |
“The business sector maintained stable growth.” |
|
Dropped (v.) |
To fall to a lower level |
Fell, declined |
“Employment in social services dropped significantly.” |
|
Favored (adj.) |
Preferred or popular among a group |
Preferred, liked |
“Hospitality became a favored sector in 2010.” |
|
Fluctuated (v.) |
To change irregularly |
Varied, wavered |
“Employment rates fluctuated across sectors.” |
|
Employment (n.) |
The state of having paid work |
Work, job |
“The table shows youth employment statistics.” |
|
Hospitality (n.) |
The business of providing services like lodging and food |
Tourism, catering |
“The hospitality sector experienced a surge.” |
|
Option (n.) |
A choice or alternative |
Choice, selection |
“Hospitality became the most preferred option.” |
|
Proportion (n.) |
A part or share of a whole |
Fraction, percentage |
“The proportion of youth in manufacturing declined.” |
|
Fluctuation (n.) |
An irregular rising and falling in number or amount |
Variation, instability |
“Fluctuations were observed in social services employment.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Writing Task 1 Question Types
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
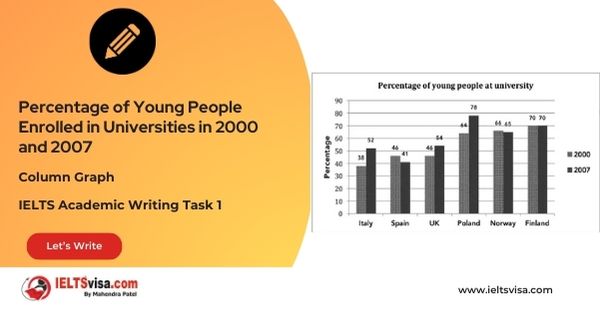
Task 1 – Column graph – Percentage of Young People Enrolled in Universities in 2000 and 2007.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
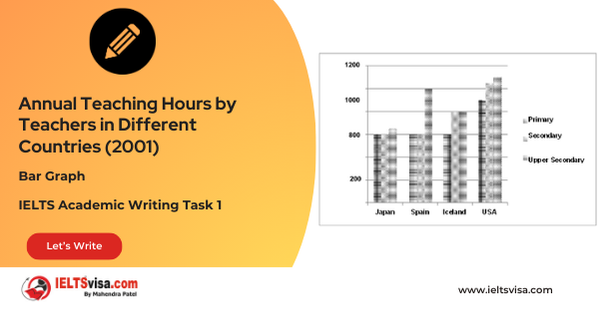
Task 1 – Bar Graph – Annual Teaching Hours by Teachers in Different Countries (2001)
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Pie Charts – Coffee Production, Consumption, and Profit Distribution Worldwide
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
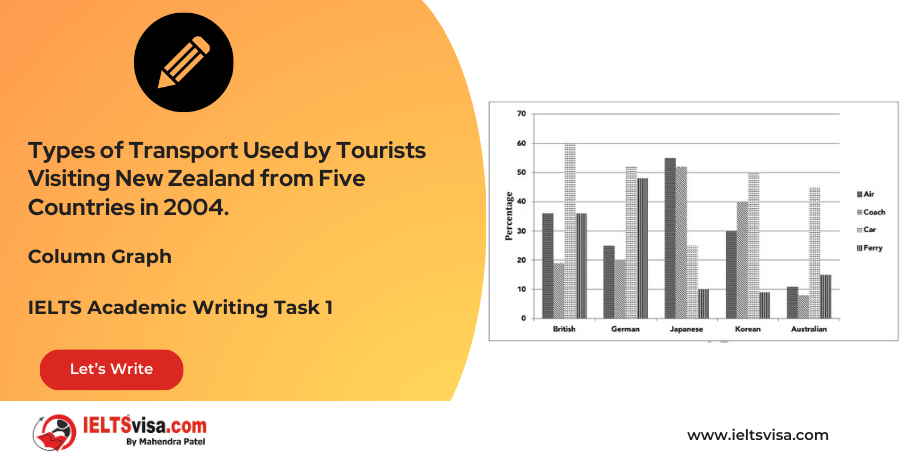
Task 1 – Column graph – Types of Transport Used by Tourists Visiting New Zealand from Five Countries in 2004.
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
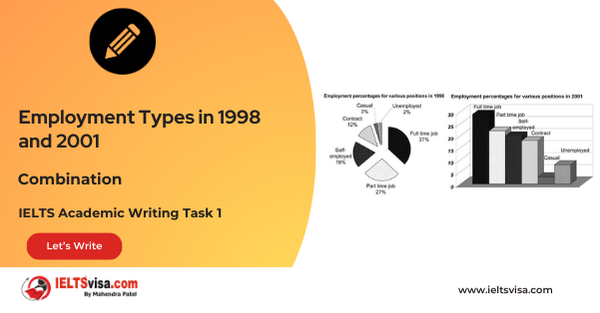
Task 1 – Bar and Pie Chart Combination – Employment Types in 1998 and 2001
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Diagram – Comparison of Stone Tool Development Over Time
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...