Global Water Distribution and Its Usage in Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Canada
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Combination Pie Charts and Column Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The charts below give information about the amount and types of water in the world, and also tell the use of water in three areas in three countries. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Common Questions for the Chart
1. Graph Type: Pie Charts and Column Graph
2. Title: Global Water Distribution and Its Usage in Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Canada
3. What are the units of measurement?: Percentage
4. Who: The global population and specific countries (Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Canada)
5. What does the chart depict?: The quantity and types of water in the world, along with the usage of fresh water in three countries
6. When: Data not specified but generally represents recent statistics
7. Where: Worldwide and in three specific countries (Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Canada)
8. Topic: Water distribution and consumption
Main Features and Trends General Observations:
Comparison 1: Global Water Distribution
- Details:
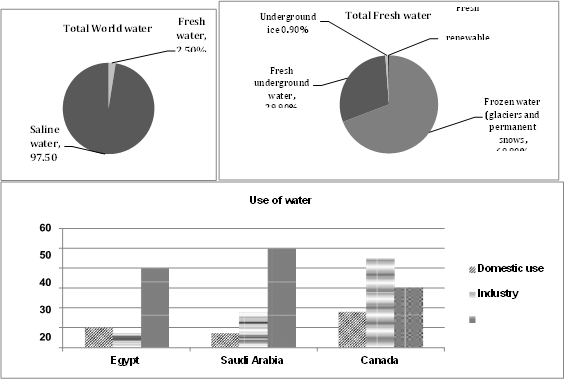
1. The first pie chart highlights that a staggering 97.5% of the world’s water is saline, leaving only 2.5% as fresh water. This emphasizes the scarcity of fresh water globally.
Comparison 2: Types of Fresh Water
- Details:
1. The second pie chart reveals that more than two-thirds (69.8%) of fresh water is locked in glaciers and permanent snow, while just under one-third (29.9%) exists as fresh underground water. A negligible fraction (0.3%) represents renewable fresh water, illustrating the limited availability for direct human use.
Comparison 3: Water Usage in Different Countries
- Details:
1.The column graph shows that both Egypt and Saudi Arabia primarily use fresh water for agriculture, with 40% and 50% of their water used respectively. In contrast, Canada has a different pattern, with the largest share (47%) allocated to industrial use, followed by 30% for agriculture and 18% for domestic purposes.
Sample Answer
The provided pie charts illustrate the distribution of water types globally, while the accompanying column graph presents the allocation of freshwater usage in Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Canada.
The first pie chart shows that a predominant 97.5% of the world’s water is saline, leaving only a mere 2.5% as fresh water. The second pie chart breaks down the fresh water, revealing that over two-thirds (69.8%) is found in glaciers and permanent snow, with fresh underground water making up nearly one-third (29.9%). A tiny fraction (0.3%) is renewable freshwater, underscoring its scarcity.
Examining the column graph, both Egypt and Saudi Arabia utilize a significant proportion of their fresh water for agriculture, with 40% and 50%, respectively. In contrast, Canada allocates the largest share (47%) of its fresh water for industrial use, with 30% for agriculture and 18% for domestic purposes.
Overall, these charts highlight the critical scarcity of fresh water, with only a small fraction being available for various uses across different countries.
Top 29 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples | Type |
| Saline | Containing or having the characteristics of salt | Briny, salty | “97.5% of the world’s water is saline.” | Adjective |
| Scarcity | The state of being in short supply, rarity | Shortage, lack | “Freshwater scarcity is a global concern.” | Noun |
| Allocation | The action of distributing something for a specific purpose | Distribution, apportionment | “Water allocation varies between countries.” | Noun |
| Glacier | A large mass of ice that moves slowly over land | Ice cap, icefield | “Most of the world’s freshwater is found in glaciers.” | Noun |
| Domestic | Relating to the running of a home or to family life | Household, family | “18% of Canada’s water is used for domestic purposes.” | Adjective |
| Illustrate | To explain or make clear using examples or visuals | Depict, Represent | “The pie charts illustrate the distribution of water types globally.” | Verb |
| Predominant | Being the most noticeable or largest in amount | Main, Dominant | “Saline water is the predominant type globally.” | Adjective |
| Fraction | A small part or portion of something | Segment, Part | “Only a tiny fraction of water is renewable freshwater.” | Noun |
| Renewable | Capable of being replenished or restored | Sustainable, Replenishable | “Renewable freshwater accounts for just 0.3% of global water.” | Adjective |
| Underscore | To emphasize the importance of something | Highlight, Stress | “The data underscores the scarcity of freshwater.” | Verb |
| Distribution | The way in which something is shared or spread | Allocation, Spread | “The distribution of freshwater varies greatly by source.” | Noun |
| Proportion | A part, share, or number in relation to a whole | Percentage, Ratio | “A large proportion of freshwater is locked in glaciers.” | Noun |
| Accompanying | Occurring along with or in addition to | Related, Supplementary | “The accompanying graph shows water usage by country.” | Adjective |
| Utilize | To make practical use of something | Use, Employ | “Egypt and Saudi Arabia utilize water predominantly for agriculture.” | Verb |
| Scarce | Limited or hard to obtain | Rare, Insufficient | “Freshwater is a scarce resource globally.” | Adjective |
| Allocation | The action of dividing and assigning resources | Assignment, Distribution | “Freshwater allocation differs among regions.” | Noun |
| Examine | To look at or study something carefully | Analyze, Inspect | “The column graph examines freshwater usage by sector.” | Verb |
| Significant | Sufficiently important or large enough to notice | Substantial, Major | “Significant amounts of freshwater are used for agriculture.” | Adjective |
| Critical | Extremely important or vital | Essential, Crucial | “Freshwater scarcity is a critical issue worldwide.” | Adjective |
| Sector | A specific area of activity, especially economic | Division, Category | “Water use varies significantly by sector across countries.” | Noun |
| Allocate | To assign resources for a specific purpose | Apportion, Distribute | “Countries allocate water differently based on their needs.” | Verb |
| Contrast | To compare in a way that highlights differences | Differ, Compare | “The graph contrasts water usage in three countries.” | Verb/Noun |
| Predicted | Expected to happen based on current knowledge | Forecasted, Projected | “Water scarcity is predicted to worsen in the coming decades.” | Adjective/Verb |
| Consumption | The act of using up a resource | Use, Utilization | “Water consumption for industrial purposes is highest in Canada.” | Noun |
| Percentage | A portion of 100 | Fraction, Proportion | “A small percentage of freshwater is used for domestic purposes.” | Noun |
| Global | Relating to the entire world | Worldwide, Universal | “Global water resources are unevenly distributed.” | Adjective |
| Availability | The state of being able to be used or accessed | Accessibility, Supply | “Freshwater availability is limited in some regions.” | Noun |
| Sectoral | Relating to a specific economic or activity sector | Divisional, Regional | “Sectoral water use varies in Egypt and Canada.” | Adjective |
| Prominent | Easily noticeable or important | Noticeable, Leading | “Agriculture remains a prominent use of freshwater in Egypt.” | Adjective |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Task 1 – Map -Changes in Pentland Coastal Area from 1950 to 2007
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
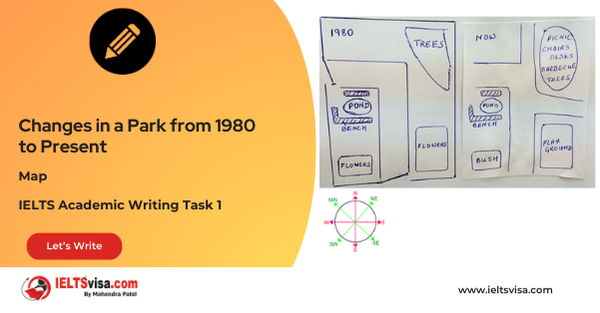
Task 1 – Map -Changes in a Park from 1980 to Present
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
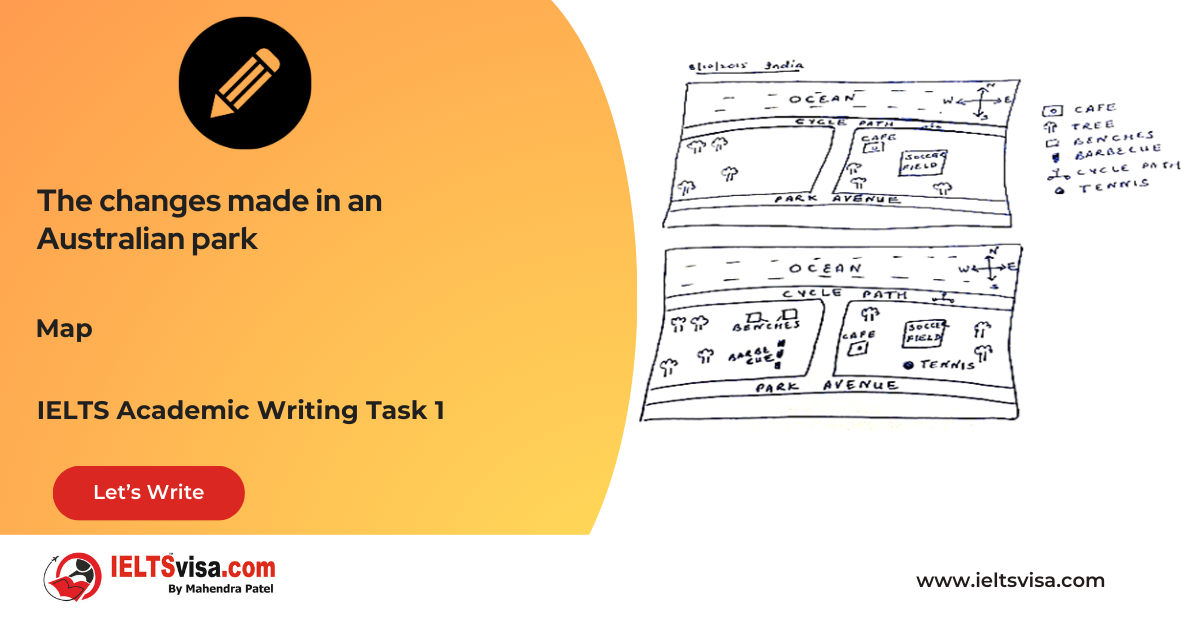
Task 1 – Maps – The changes made in an Australian park
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
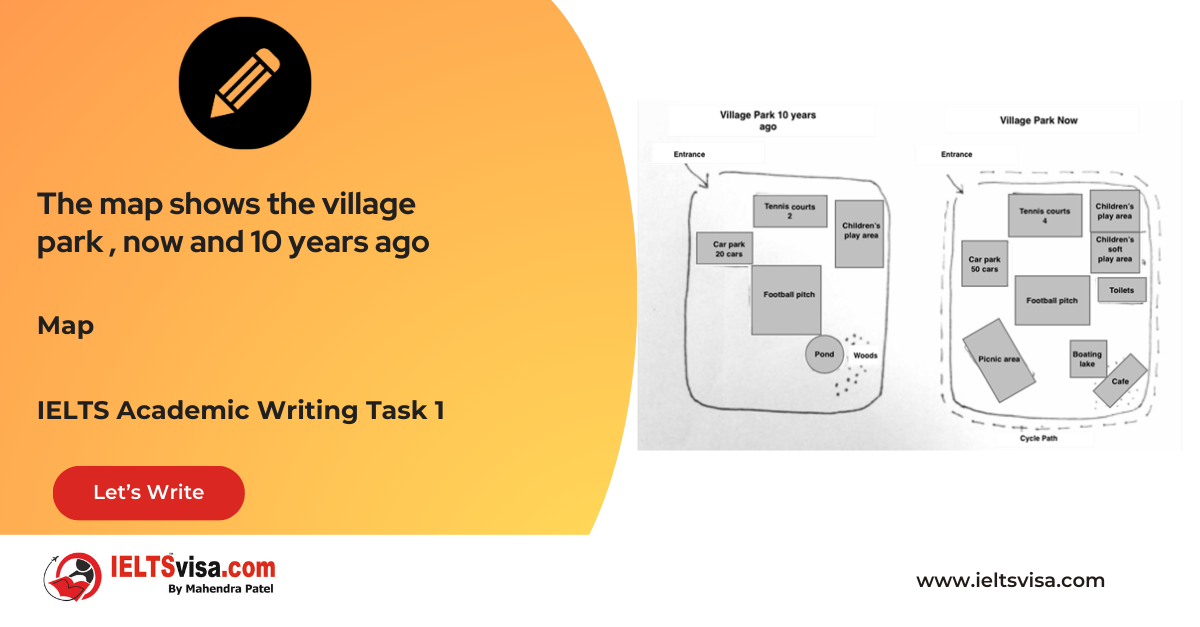
Task 1 – Maps- The map shows the village park, now and 10 years ago
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Map -Changes in Sydney International Airport from 1930 to Present
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
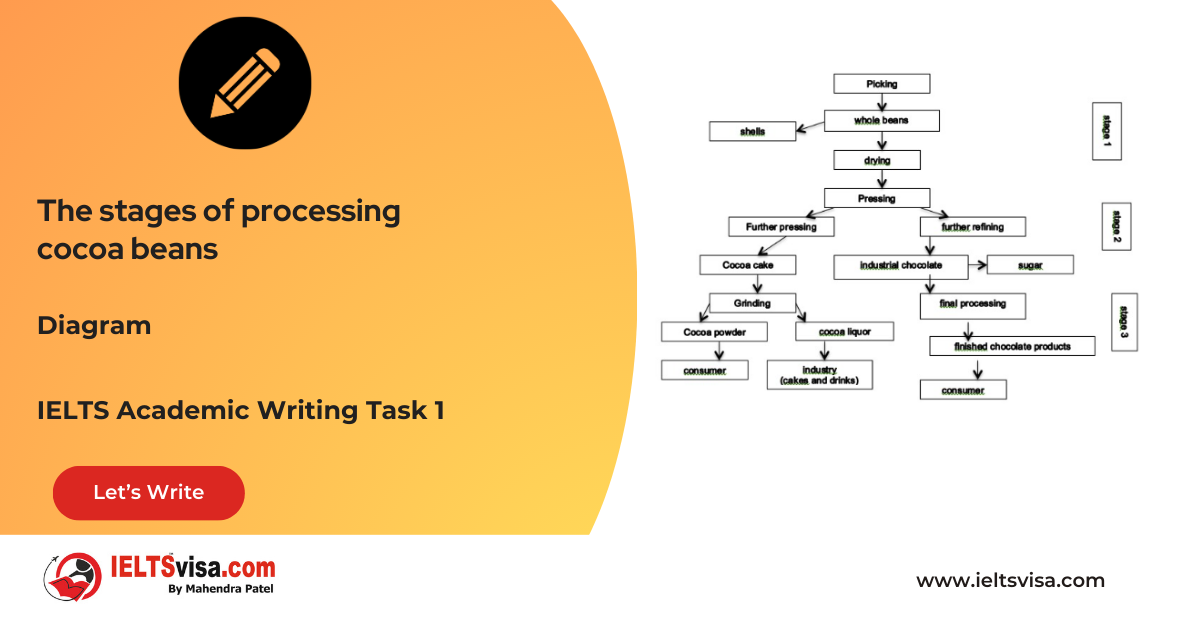
Task 1 – Diagram – The stages of processing cocoa beans
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...