Nitrogen Oxide Emissions by Vehicle Type at Different Speeds
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 - Line Graph
IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
The given graph shows the nitrogen oxide emissions produced by four vehicles. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant
Common Questions for the Line Graph
1. Graph Type: Line Graph
2. Title: Nitrogen Oxide Emissions by Vehicle Type at Different Speeds
3. What are the units of measurement?: Grams per kilometer (g/km)
4. Who: Four vehicle types (buses, lorries, diesel cars, petrol cars)
5. When: Not specified
6. Where: Not specified
7. Topic: Comparison of nitrogen oxide emissions based on vehicle type and speed
Comparison Showing and Trends Any change over time (such as an increase or a decrease) is a trend.
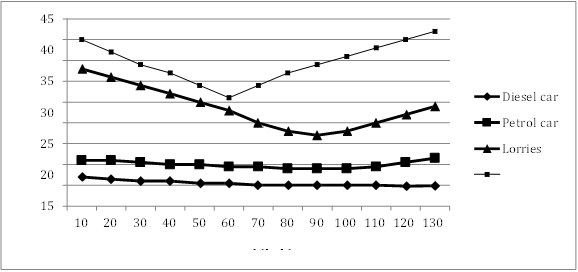
Comparison 1: Buses (Highest Emissions)
- Details:
1.Emit 40 g/km at 10 kph, the highest among all vehicles.
2. Emissions decrease as speed increases to 60 kph, reaching around 25 g/km.
3. Beyond 60 kph, emissions rise again, exceeding 40 g/km at 130 kph.
Comparison 2: Lorries (Similar Pattern to Buses)
-
Details:
1. Emissions are slightly lower than buses but follow a similar trend.
2. Emissions decrease until 90 kph, then increase beyond this speed
Comparison 3: Diesel and Petrol Cars (Lowest Emissions)
- Details:
1.Emissions remain relatively constant across speeds.
2. Diesel cars emit the least (around 5 g/km), while petrol cars emit around 10 g/km.
Sample Answer
The line graph compares the nitrogen oxide emissions of four vehicle types—buses, lorries, diesel cars, and petrol cars—at various speeds.
Overall, buses and lorries produce higher emissions with a clear pattern of decrease and increase at different speeds, while diesel and petrol cars show consistently low and stable emissions.
At a low speed of 10 kph, buses emit 40 g/km, the highest among all vehicles. As speed increases to 60 kph, their emissions decrease steadily to around 25 g/km. However, emissions begin to rise again beyond this speed, exceeding 40 g/km at 130 kph. Lorries show a similar pattern but produce slightly lower emissions. Their emissions decrease until 90 kph and then start to rise, mirroring the trend seen in buses.
Diesel and petrol cars emit far less nitrogen oxide than buses and lorries. Diesel cars consistently produce the least emissions, hovering around 5 g/km regardless of speed. Petrol cars emit slightly more at approximately 10 g/km and show minimal variation across speeds.
Top 26 Vocabularies
| Vocabulary | Type | Meaning | Synonyms | Examples |
|
Emission |
Noun |
The release of gas or substance into the air |
Discharge, Release |
The emissions from buses were the highest at 10 kph. |
|
Pattern |
Noun |
A repeated or consistent trend |
Trend, Arrangement |
Buses and lorries follow a similar emission pattern. |
|
Decrease |
Verb/Noun |
To reduce the amount |
Decline, Drop |
Emissions decrease as bus speed increases to 60 kph. |
|
Hover |
Verb |
To remain around a specific value |
Float, Stay |
Emissions from diesel cars hover around 5 g/km. |
|
Variation |
Noun |
A change or difference |
Fluctuation, Change |
Diesel and petrol cars show minimal variation in emissions. |
|
Compare |
Verb |
To examine differences and similarities |
Contrast, Relate |
“The line graph compares emissions from different vehicle types.” |
|
Consistently |
Adverb |
In a reliable or unchanging manner |
Uniformly, Steadily |
“Diesel cars consistently produce the least emissions.” |
|
Stable |
Adjective |
Remaining unchanged or steady |
Constant, Steady |
“Petrol cars showed stable emissions across various speeds.” |
|
Fluctuation |
Noun |
Irregular changes in level or value |
Variance, Oscillation |
“Lorries exhibit some fluctuation in their emissions.” |
|
Peak |
Verb/Noun |
To reach the highest point |
Summit, Climax |
“Bus emissions peaked at 40 g/km at high speeds.” |
|
Significant |
Adjective |
Large or important enough to be noticed |
Notable, Substantial |
“There is a significant difference between diesel and bus emissions.” |
|
Trend |
Noun |
A general direction in which something is developing |
Pattern, Movement |
“The graph highlights a trend in emissions reduction at lower speeds.” |
|
Decline |
Verb/Noun |
A gradual decrease in value |
Reduction, Drop |
“Bus emissions show a decline at moderate speeds.” |
|
Steady |
Adjective |
Happening in a regular, continuous manner |
Stable, Gradual |
“There is a steady decrease in emissions from buses as speed increases.” |
|
Exceed |
Verb |
To go beyond a certain limit |
Surpass, Overtake |
“Bus emissions exceed 40 g/km at high speeds.” |
|
Proportion |
Noun |
A part or share in relation to a whole |
Percentage, Ratio |
“Buses emit the largest proportion of nitrogen oxides at low speeds.” |
|
Contrast |
Noun/Verb |
A noticeable difference between two or more things |
Difference, Distinction |
“The graph contrasts emissions from buses and diesel cars.” |
|
Level |
Noun/Verb |
A specific value or point |
Rate, Position |
“The emissions level from lorries starts to rise at higher speeds.” |
|
Rise |
Verb/Noun |
An increase in quantity or level |
Increase, Surge |
“Bus emissions rise beyond 60 kph.” |
|
Moderate |
Adjective |
Average in amount, intensity, or degree |
Medium, Reasonable |
“Lorries show moderate emissions compared to buses.” |
|
Maintain |
Verb |
To keep in the same state or condition |
Sustain, Preserve |
“Diesel cars maintain low emissions regardless of speed.” |
|
Noticeable |
Adjective |
Easy to see or observe |
Visible, Distinct |
“The difference in emissions becomes noticeable at higher speeds.” |
|
Mirror |
Verb |
To reflect or show similarities |
Resemble, Echo |
“Lorry emissions mirror the trend of buses at higher speeds.” |
|
Recover |
Verb |
To return to a normal or improved state |
Rebound, Improve |
“Lorry emissions recover slightly after a sharp decrease.” |
|
Consistent |
Adjective |
Remaining the same over time |
Steady, Regular |
“Diesel cars show consistent emission levels throughout.” |
|
Highlight |
Verb |
To emphasize or draw attention to |
Emphasize, Underline |
“The graph highlights the significant differences between vehicle types.” |

Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Task 1 – Map -Changes in Pentland Coastal Area from 1950 to 2007
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Map -Changes in a Park from 1980 to Present
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
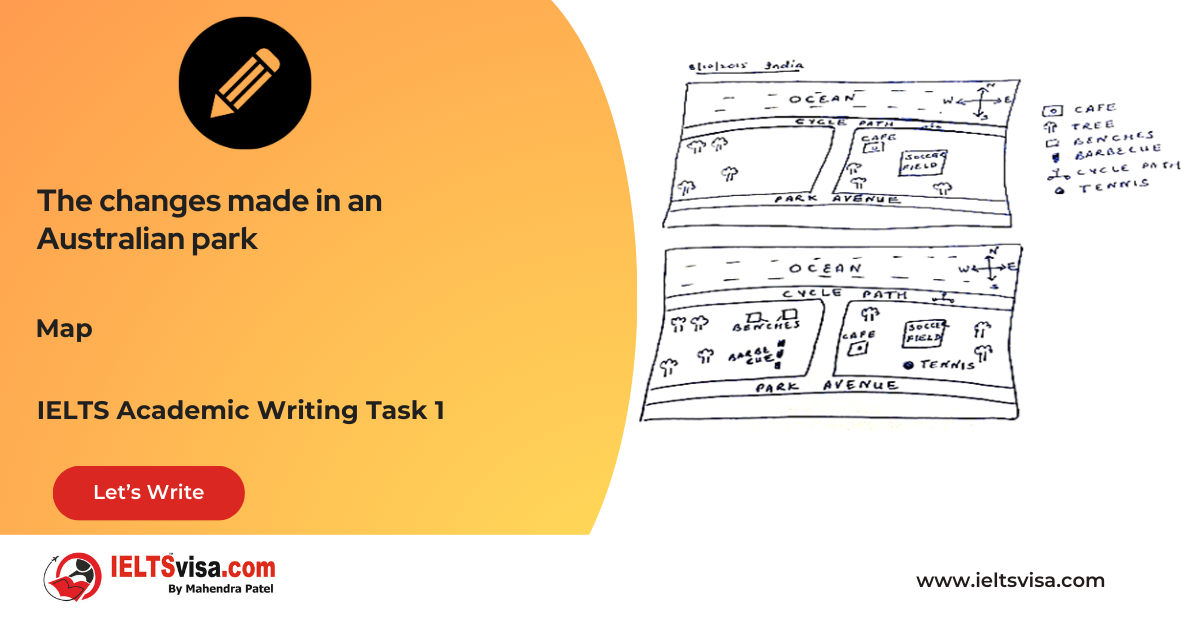
Task 1 – Maps – The changes made in an Australian park
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
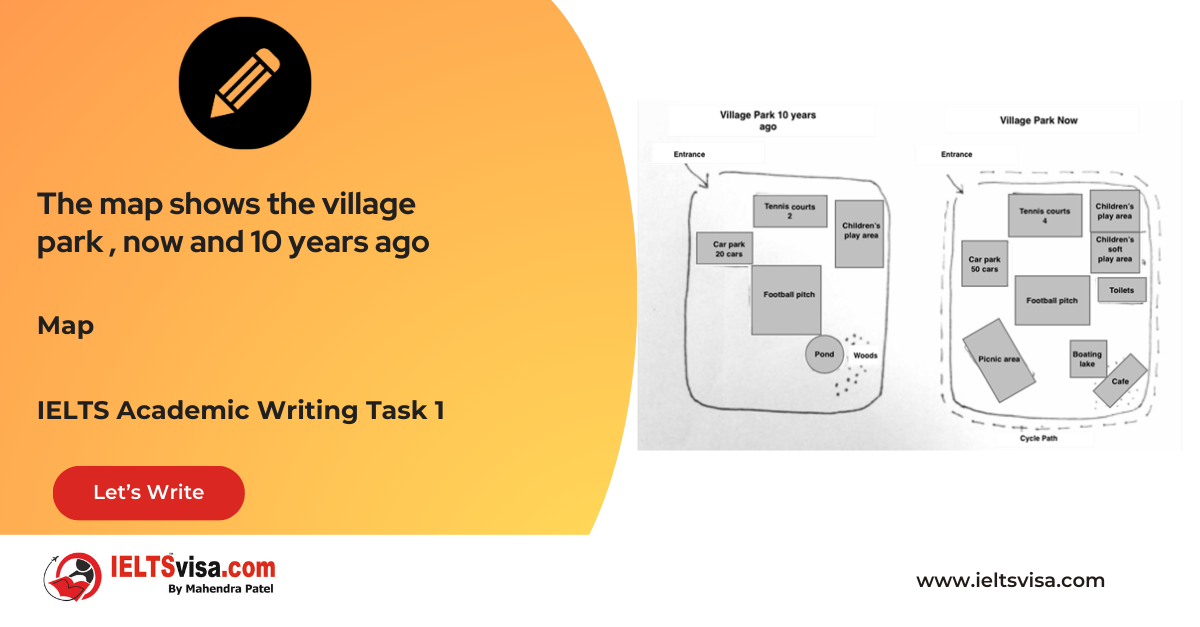
Task 1 – Maps- The map shows the village park, now and 10 years ago
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
Task 1 – Map -Changes in Sydney International Airport from 1930 to Present
[df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...
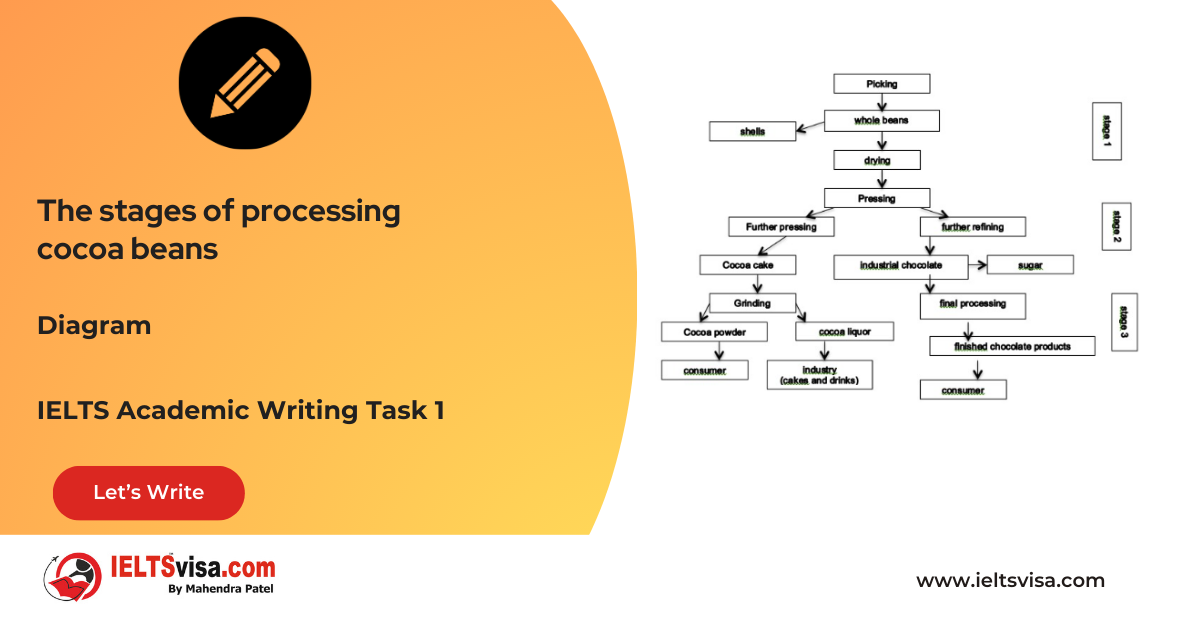
Task 1 – Diagram – The stages of processing cocoa beans
20:00 Start Pause Stop [df_adh_heading title_infix="IELTS Writing Task 1 Question" use_divider="on"...